Ahmad, Table S1, EJPP Primers name sequence 5`
advertisement
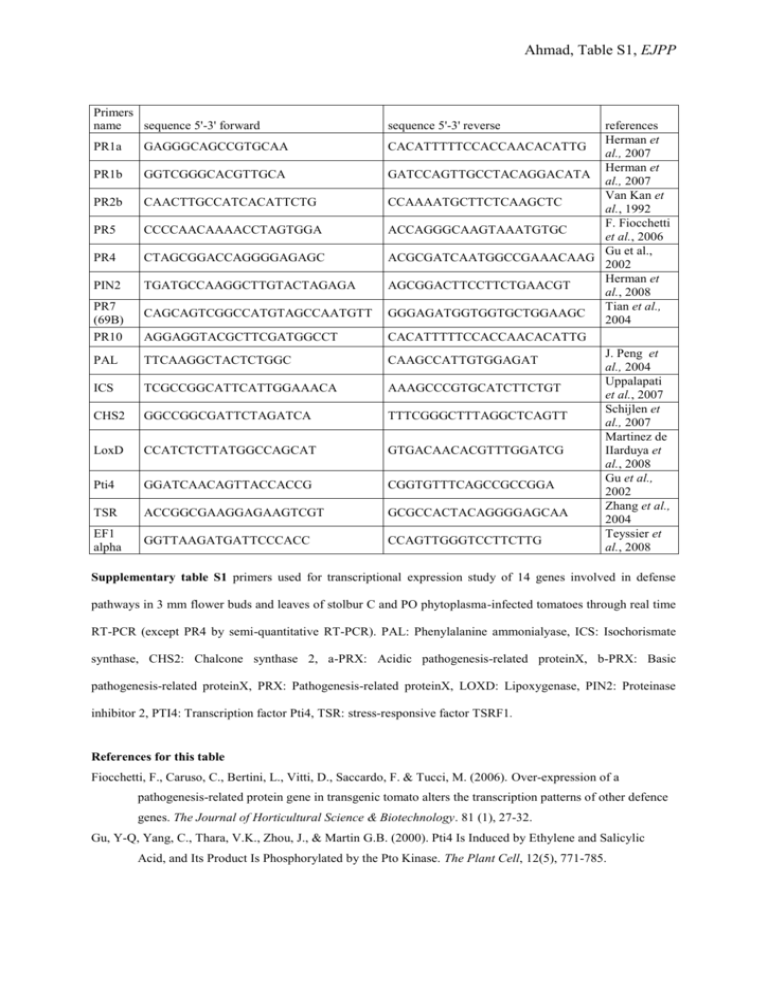
Ahmad, Table S1, EJPP Primers name sequence 5'-3' forward PR1a GAGGGCAGCCGTGCAA PR1b GGTCGGGCACGTTGCA PR2b CAACTTGCCATCACATTCTG PR5 CCCCAACAAAACCTAGTGGA PR4 CTAGCGGACCAGGGGAGAGC PIN2 TGATGCCAAGGCTTGTACTAGAGA PR7 (69B) PR10 CAGCAGTCGGCCATGTAGCCAATGTT AGGAGGTACGCTTCGATGGCCT PAL TTCAAGGCTACTCTGGC ICS TCGCCGGCATTCATTGGAAACA CHS2 GGCCGGCGATTCTAGATCA LoxD CCATCTCTTATGGCCAGCAT Pti4 GGATCAACAGTTACCACCG TSR ACCGGCGAAGGAGAAGTCGT EF1 alpha GGTTAAGATGATTCCCACC sequence 5'-3' reverse references Herman et CACATTTTTCCACCAACACATTG al., 2007 Herman et GATCCAGTTGCCTACAGGACATA al., 2007 Van Kan et CCAAAATGCTTCTCAAGCTC al., 1992 F. Fiocchetti ACCAGGGCAAGTAAATGTGC et al., 2006 Gu et al., ACGCGATCAATGGCCGAAACAAG 2002 Herman et AGCGGACTTCCTTCTGAACGT al., 2008 Tian et al., GGGAGATGGTGGTGCTGGAAGC 2004 CACATTTTTCCACCAACACATTG J. Peng et CAAGCCATTGTGGAGAT al., 2004 Uppalapati AAAGCCCGTGCATCTTCTGT et al., 2007 Schijlen et TTTCGGGCTTTAGGCTCAGTT al., 2007 Martinez de GTGACAACACGTTTGGATCG IIarduya et al., 2008 Gu et al., CGGTGTTTCAGCCGCCGGA 2002 Zhang et al., GCGCCACTACAGGGGAGCAA 2004 Teyssier et CCAGTTGGGTCCTTCTTG al., 2008 Supplementary table S1 primers used for transcriptional expression study of 14 genes involved in defense pathways in 3 mm flower buds and leaves of stolbur C and PO phytoplasma-infected tomatoes through real time RT-PCR (except PR4 by semi-quantitative RT-PCR). PAL: Phenylalanine ammonialyase, ICS: Isochorismate synthase, CHS2: Chalcone synthase 2, a-PRX: Acidic pathogenesis-related proteinX, b-PRX: Basic pathogenesis-related proteinX, PRX: Pathogenesis-related proteinX, LOXD: Lipoxygenase, PIN2: Proteinase inhibitor 2, PTI4: Transcription factor Pti4, TSR: stress-responsive factor TSRF1. References for this table Fiocchetti, F., Caruso, C., Bertini, L., Vitti, D., Saccardo, F. & Tucci, M. (2006). Over-expression of a pathogenesis-related protein gene in transgenic tomato alters the transcription patterns of other defence genes. The Journal of Horticultural Science & Biotechnology. 81 (1), 27-32. Gu, Y-Q, Yang, C., Thara, V.K., Zhou, J., & Martin G.B. (2000). Pti4 Is Induced by Ethylene and Salicylic Acid, and Its Product Is Phosphorylated by the Pto Kinase. The Plant Cell, 12(5), 771-785. Ahmad, Table S1, EJPP Herman, M. A., Davidson, J. K. & Smart C. D. (2008). Induction of plant defence gene expression by plant activators and Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato in greenhouse-grown tomatoes. Phytopathology, 98, 1226-1232. Martinez de Ilarduya, O., Xie, Q. & Kaloshian, I. (2003). Aphid-induced defense responses in Mi-1-mediated compatible and incompatible tomato interactions. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 16(8), 699‑ 708. Peng, J., Deng, X.., Huang, J., Jia, S., Miao, X. & Huang, Y. (2004). Role of Salicylic Acid in Tomato Defense against Cotton Bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera Hubner. Z. Naturforsch. 59c, 856-862. Teyssier, E., Bernacchia, G., Maury, S., How Kit, A., Stammitti-Bert, L., Rolin, D., et Gallusci, P. 2008. Tissue dependent variations of DNA methylation and endoreduplication levels during tomato fruit development and ripening. Planta, 228, 391-399. Tian, M., Huitema, E., da Cunha, L., Torto-Alalibo, T. & Kamoun, S. (2004). A Kazal-like Extracellular Serine Protease Inhibitor from Phytophthora infestans Targets the Tomato Pathogenesis-related Protease P69B. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 26370-26377. Uppalapati, S. R., Ishiga, Y., Wangdi, T., Kunkel, B. N., Anand, A., Mysore, K. S., & Bender, C. L. (2007). The Phytotoxin Coronatine Contributes to Pathogen Fitness and Is Required for Suppression of Salicylic Acid Accumulation in Tomato Inoculated with Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 20(8), 955‑965. Van Kan, J. A. L., Joosten, M. H. A. J., Wagemakers, C. A. M., Berg-Velthuis, G. C. M. & Wit, P. J. G. M. 1992 Differential accumulation of mRNAs encoding extracellular and intracellular PR proteins in tomato induced by virulent and avirulent races of Cladosporium fulvum. Plant Molecular Biology 20, 513-527. Zhang, H., Zhang, D., Chen, J., Yang, Y., Huang, Z., Huang, D., Wang, X.C. & Huang, R. (2004) Tomato stressresponsive factor TSRF1 interacts with ethylene responsive element GCC box and regulates pathogen resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum. Plant Molecular Biology, 55, 825-834.