1_2 NOTES
advertisement

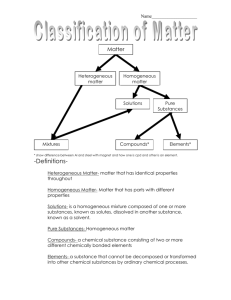
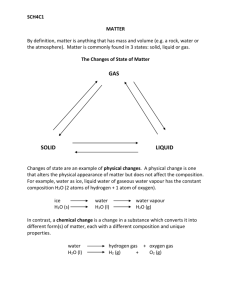
Chemistry Notes – Chapter 1, Section 1.2 Ms. Cox’s Classes Mass – a measure of the amount of matter in an object. Matter – anything that has mass and takes up space. Atom – the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element. Put another way, the smallest chunk you can divide an element into and still have it be the same element. Element – a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. Compound – a substance made up of atoms from two or more elements that are chemically bonded. A compound CAN be broken down into simpler substances. Extensive Properties – depend on the amount of matter present. Examples of Extensive Properties: mass, volume, height, weight, etc. Intensive Properties – do not depend on the amount of matter present. Examples of Intensive Properties: density, melting point, boiling point, etc. Physical Properties – can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance. Physical properties describe the substance itself, rather than describing how it can change into other substances. Physical Changes – a change in a substance that DOES NOT involve a change in the identity of the substance. Example: ICE > WATER > STEAM These are changes of form, but all three forms are water (H20). Change of State – the change of matter from one state to another like the previous example with ice, water and steam. Solid – has a definite volume and a definite shape. Liquid – has a definite volume but a shape that can change. Gas – has neither definite volume nor definite shape. Plasma – found in fluorescent bulbs and stars, plasma has a high temperature and its matter is made up of charged particles. Chemical Property – a substance’s ABILITY to undergo changes that transform it into difference substances. Chemical Change – a change in which one or more substances are converted into different substances. A chemical change is IRREVERSIBLE. Chemical Reaction – a change in which at least one new substance is formed. Reactants – the substances that react in a chemical change (chemical reaction). These are what you start out with in a chemical reaction. Products – the substances formed in a chemical change (chemical reaction). Mixture – a blend of two or more kinds of matter, each of which keeps its own identity and properties. Homogeneous – a mixture is called homogeneous if it is uniform in composition. It looks the same throughout. Heterogeneous - a mixture is called heterogeneous if it is NOT uniform in composition. A sample from one area of the substance will not be exactly like a sample from another area of the substance. Solution – a homogeneous mixture like salt dissolved in water or dish soap. Pure Substances – any sample of a pure substance is homogeneous. A pure substance has a fixed composition. Every sample has the same physical and chemical properties. These properties are so specific, that they can be used to identify the substance. Every sample of a pure substance has exactly the same composition as every other sample. Example: pure water is always 11.2% hydrogen and 88.8% oxygen by mass. Pure substances are either compounds or elements. A compound can only be broken down into two or more simpler compounds or elements by chemical means. An element can’t be broken down into simpler parts at all! Not without a nuclear reactor, anyway ;0)