Weather Instruments
advertisement

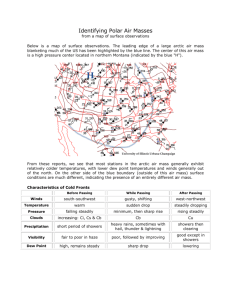
Weather Instruments P 611-620 We need data to _______________ the weather 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Instruments used to gather the data ___________________________ Atmospheric Conditions Temperature Instrument ____________________________ • Uses a ______________ either mercury or alcohol sealed in a glass tube Electrical thermometer • As temp ____________the electrical current increases • A thermistor responds very quickly and is used where temps change quickly Air pressure Instrument ____________________________ Aneroid Mercury _______________ are usually indicated by a drop in air pressure Wind Speed and Direction Instrument __________________________ Wind _____________________ Instrument Wind vane Wind _______________________ Measuring Upper Atmospheric Conditions Radar Stands for Ra______________, D________________& R__________________ Uses ____________________ radio waves Doppler radar Can indicate precise location, intensity of precip and extent of a storm Shows wind patterns _______________ or ______________ from the radar Radiosonde An instrument package that is carried by a heliumfilled _______________________ _______________ sends info to ground Determines direction and speed of high altitude winds Skew-T Shows a _______________slice of the atmosphere Temperature on right Dew point on left Air pressure Wind speed and direction Weather _______________________ Can measure visible Infrared Ocean conditions temperature and flow of ocean currents and height of ocean waves Computers Solve _________________________________ equations that describe the __________________________ of the atmosphere Can store weather _________________ Can store weather records This info is reported from _______________________ WMO World Meteorological Organization 10,000 land based stations and hundreds of ship-based stations Weather satellites ______________ Global Orbiting Earth Satellite Data from stations is compiled and analyzed to forecast In the past this was done by _______________________ Now much is done by computer But, different programs work better for different ____________ and types of weather Often two or three computer _________________ are consulted to make one forecast Weather Station Symbols p616 ____________________ is upper left corner Barometric (_______) pressure is upper _____________________ Air pressure represents the last three digits of the observed pressure reading in _________________________ (mb) Like on previous labs Dew point Dew Point is lower ______________corner When the air temperature and the dew point are the ___________ the air is _______________________________ Relative humidity can be ____________________ High if temp and dp are close Low if large difference between dp and temp Relative Humidity can be ______________________ When the air and dew point temperatures are very close, this indicates that the air has a _______________relative humidity. The opposite is true when there is a large difference between air and dew point temperatures, which points to air with a ___________ relative humidity. Wind Speed and Direction Wind barbs point in the direction _____________ which the wind is blowing Look at the picture and answer the following questions. What is the temperature?___________________ What is the dew point?_____________________ What is the air pressure? (careful)____________ Which direction is the wind from? ____________ What is the wind speed? ___________________ What is the percent of cloud cover? __________ Methods of Forecasting 1. Persistence 2. Trend 3. Analog Persistence—based on ___________________of a weather pattern—if it is raining now it will probably be raining tomorrow Trend—based on the ___________________ or trend of the weather system Ex. Cold front moving E at 20 Km/hr will affect weather 80 KM away in 4 hours Analog Others Climatology—data accumulated through many years th of July is usually hot and dry 4 Numerical Weather Prediction—uses programs built by meteorologists Not exact compares present weather (cloud cover, wind, temperature, humidity, etc) with weather conditions produced by same features in the past Meteorologists What high school courses are necessary to prepare for a career in meteorology? Because meteorology is a science, a good background in mathematics and the sciences is mandatory. Knowledge of physics and chemistry is helpful toward a career in the atmospheric sciences. OU is the best Recognizing fronts on a map sharp temperature changes over relatively short distances changes in the moisture content of the air (dew point) shifts in wind direction low pressure troughs and pressure changes clouds and precipitation patterns Types of fronts Named for the invader Each type of front has a typical weather scenario Cold Front heavy cold air displaces lighter warm air, pushing it upward Cumulus clouds form and usually grow into thunderstorms Temperatures drop anywhere from 5 to 15. Winds become gusty and erratic. Rain, snow, sleet, and hail can occur with a cold front. Warm Front Warm fronts occur when warm air replaces cold air by sliding over it. Altocumulus clouds form and may be associated with rain, snow, or sleet. Temperatures may warm slightly. Winds are usually gentle with this kind of front. Stationary Front neither warm nor cold air advances. The two air masses reach a stalemate. That is what stationary means - that neither front is moving. can last for days, producing nothing but Altocumulus clouds Temperatures remain stagnant and winds are gentle to nil Occluded Front cold air is replacing cool air or vice versa at the surface, with warm air above. Both types of fronts are usually associated with rain or snow and cumulus clouds. Temperature fluctuations are small and winds are gentle. Where are the fronts? Stationary front Change in wind direction Can dump heavy rains Warm Front Marked temperature difference Cold front Cold temperatures are moving in If it is not exactly on the value it will not Points shown are reporting stations Here, the stations reported pressure and temperature The lines are drawn in different colors to help differentiate them There may be areas that do not report or have no station The closer contour lines are to one another, the higher the wind speed. Where is the wind speed high? Where is it low? Inside a series of closed contours (the contours make a circle) is a High or Low pressure Describe the motion of the wind. Wind Flow around Isobars Winds flow roughly parallel to the isobars, as depicted in the schematic below Current Weather Conditions Current Weather Station Data Source:University of Illinois http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/home.rxml