Ch. 2 – Understanding Weather
advertisement

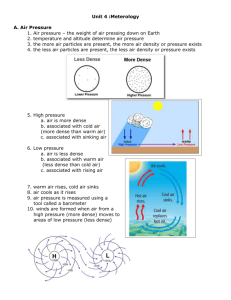
Ch. 2 – Understanding Weather 1. What is the water cycle? The water cycle is the continuous movement of water from water sources, into the air, onto land, into ground and back to water sources Where does the energy come from that makes the water cycle work? The sun provides energy for the water cycle 2. Explain what is happening during the process of evaporation? Evaporation occurs when water changes into a water vapor, a gas Explain what is happening during the process of condensation? Condensation occurs when water vapor cools and changes into liquid drops Explain what is happening during the process of precipitation? Precipitation occurs when ran snow, sleet or hail fall from the clouds. 3. What instrument measures the amount of rainfall? A rain gauge measures rainfall amounts. 4. What is humidity? Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. What does the graph on page 37 tell you about humidity? Warmer air can hold more water vapor than cooler air. 5. What is dew point? Dew point is the temperature to which air must cool to be completely saturated. 6. What are clouds and how do they form? A cloud is a collection of millions of tiny water droplets or ice crystals. Clouds form as warm as rises and cools. As the air cools, it becomes saturated. The water vapor will change physical states as it collects on a surface as liquid droplets or ice crystals. 7. What are the three main cloud types? The three types of clouds are cumulus, cirrus, and stratus. 8. What is an air mass? An air mass is a large body of air that has similar temperature and humidity throughout. 9. What is a front? A front is a boundary between two air masses 10. What is weather like when a front moves in? When a front moves in the weather is usually cloudy and stormy. 11. Describe a cold front. (look at p. 46) A cold air mass meets and cuts under a warm air mass. This pushes the less dense warm air up. 12. Describe a warm front. (look at p. 46) A warm air mass meets and over rides a cold air mass. This warm air moves over the cold, denser air. 13. What is happening with the air masses in a stationary front? At a stationary front, the air masses meet and there will be very little movement. 14. Look at the map on p. 57. What is the symbol for a warm front? A warm front symbol looks like a bubble. 15. What is the symbol for a cold front? Cold front symbol is a triangle. 16. How do you know what direction the front is moving? The bubbles or triangles are pointing the way of travel 17. What do the H and L mean on the map? H is the symbol for a high pressure cell L is symbol for a low pressure cell 18. Fill in the blanks. Areas of __low_____________ pressure are associated with frontal boundaries, while areas of______high________________pressure usually mean clear weather.