Louisiana`s Physical & Cultural Geography / Name
advertisement

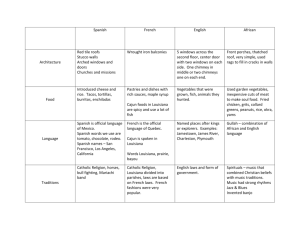
Louisiana’s Physical & Cultural Geography / Name: _________________ Louisiana Basics Louisiana Basics • __________largest state, 3600 square miles of water, ___________ of U.S. wetlands are in LA. • ___________________ of coastline. • One of the biggest problems is always __________________ Louisiana Land • Lowest Points – ______________________ Located along the gulf coast & City of New Orleans • Some sections above sea level, some sections as much as _________________________ • Highest Points, Northern portions. _____________________ (535 ft. above sea level) Boundaries ____________ – Arkansas. 33°North and 31° North _______________ – Texas & Sabine River _________________– Mississippi, Mississippi River & Pearl River __________________ – Gulf of Mexico Louisiana Symbols • Flag / Motto: ____________________________________ • Bird: ____________________________________ • Flower: ____________________________________ • Tree: _____________________________________ Louisiana is a coastal plain • Louisiana is the only state made up ENTIRELY by the ____________________________ Low & flat region created by ____________________________ Deltas • Land created from _____________________Where the Mississippi River meets the Gulf of Mexico. Coastal Marshes • _______________________ formed by river sediment deposited along the coast. Brackish • Fresh & __________________ mixed together Coastal Erosion • Land is disappearing. – LA loses ___________________ per year, 2 football fields per hour _____________________destroyed 64,000 acres in one day. Salt Domes • ___________________________ once covered Louisiana. • When it dried massive salt domes were left standing, Most are about 10 miles below the Earth. Some jut above the marsh in high columns = Why they are called islands. _______________________ (where Tabasco is made) Earthquakes in Louisiana • Louisiana experiences frequent ________________________. • Most are so small and go unnoticed • _________________ – earthquake in Missouri shook buildings in New Orleans • 1964 – Alaskan earthquake caused ______________________ from the Gulf of Mexico. Louisiana Waterways and Cities Physical vs. Cultural Geography _________________________-Study of landforms, oceans, weather and climate. __________________________l - Study of how people have interacted with, changed and adapted to different places on earth. Cities • Most Populated - ______________________________ • Built in 1718 by Bienville, under French Rule • Oldest - ___________________________ • Build by St. Denis under French Rule in 1714 • Capitol - _______________________________ • Meaning “Red Stick.” Named by Iberville. Other Important Cities • Northern area • ___________________________ & Monroe • Southwest • Lafayette and ______________________________ • Central • Alexandria Mississippi River • Largest river in the ______________. and ______________largest in the world. • Starts in ____________________and empties into the _____________________________. • 375 billion gallons flow through LA each day. Atchafalaya River • The longest ____________________ of the Mississippi River. – Flows into the ________________________ at Morgan City. • Atchafalaya Basin is the largest swamp in the US – 23 million pounds of ________________________ per year – Habitat of the _________________________________ Gulf of Mexico • Our southern border • Greatly affects our climate. Ex. ________________________ • Resources – Food,________________, Natural gas Controlling the Water • __________________and levees are always a concern for the people of Louisiana. • ___________________are to protect us from flooding. – They also create problems. • By controlling water with levees, we create high levels of water inside levees. – LEVEES CAN BREAK. Ex. Hurricane Katrina. – Does not allow __________________deposit and increases erosion Spillways • Manmade and created to_________________ water to prevent flooding. – 2 in Louisiana • ____________________ Takes water from the Mississippi and deposits it in Lake Pontchartrain • ______________________ Diverts water to the Atchafalaya Basin – Not opened very often Hurricanes Hurricanes the Basics • Hurricane comes from the Indian word “__________________ the name of an Indian god. • Large violent storms that start in the moist air of the __________________________________________ • Louisiana’s Gulf Coast location makes it vulnerable to hurricanes. Storm Formation Storm name changes as it ___________________. – ____________________ – if it lasts 24 hours – ____________________ – lasts more than 24 hours and winds are less than 39 mph – ___________________ – Winds reach 39 mph or higher – ___________________ – Winds reach 74 mph or higher. Hurricane Ratings • Called the _____________________________ Hurricane Layout • Storm gathers strength from the ________________________. • Circulates in a spiraling ___________________________motion around an ______________. – The eye is the center of the storm and has_________________winds a blue sky. – _______________________ is the center of circulation and extremely dangerous. • Storms can be 40,000 feet high and 400 miles wide. Hurricane Damage • Violent ________________, Torrential rains, ______________________________ • _____________________ – High winds push walls of water on shore – The most violent part of hurricanes. – Can travel many miles______________________ – 90% of people killed by hurricanes are killed by the storm surge. Naming Hurricanes • Starting naming hurricanes (female names) in the _________________ • By 1979 male names were also used • Extremely powerful storms’ names are _________________. Ex: Katrina, Camille, & Georges… Powerful Hurricanes to Hit Louisiana • Audrey 1957, _______________, Andrew 1992, _______________, Rita 2005 Habitat and Migration Habitat • A ______________ that enables________________ to be maintained (food and shelter) and nesting (reproducing) to occur. Types of Habitats • ________________________________ etc. Migration • is a ________________ behavior that involves the regular,__________________ or annual journey of an ____________________ from one place to another and back again Migratory Routes • Common examples are __________________________ and hummingbirds. • Travel from Canada, to________________________, to South America.