ChemRxn5EtoCompletewConcepts - Workshops+SJCOE Workshop
advertisement

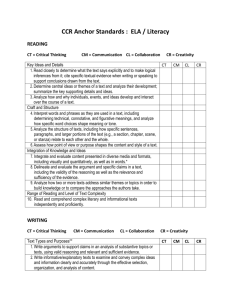
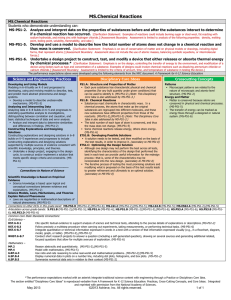
Kirk’s Lesson on Chemical Reactions Lesson Objective: Course/Grade Level: 8th grade Materials: Students working in 8 groups of 4 lab benches. Standard(s) addressed: Sample NGSS PE: MS- PS1-2 Science and Engineering Practice 3 RST.6-8.1 WHST.6-8.7 PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter PS1.B: Chemical Reactions Cross Cutting Concepts Analyze and interpret data on the properties of substances before and after the substances interact to determine if a chemical reaction has occurred. Planning and carrying out an investigation Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts Conduct a short research project to answer a question, drawing on several resources and generating additional related, focused questions that allow for multiple avenues of exploration. Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties (for any bulk quantity under given conditions) that can be used to identify it. (MS-PS1-2),(MS-PS1-3) Supplemental DCI ESS3.C, LS4.D Substances react chemically in characteristic ways. In a chemical process, the atoms that make up the original substances are regrouped into different molecules, and these new substances have different properties from those of the reactants. (MS-PS1-2),(MS-PS1-3) Supplemental DCI ESS3.C, LS4.D,(MS-PS1-5) Patterns: Microscopic Patterns are related to the nature of microscopic and atomic level structure. (Patterns of reactions) Cause and Effect Scale Proportion and Quantity Energy and Matter Structure and Function CCSS-ELA and CA ELD Standards Addressed: Sample Comprehension and Collaboration CCRSpeaking/Listening 1. Prepare for and participate effectively in a range of conversations and collaborations with diverse partners, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly and persuasively. 2. Integrate and evaluate information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. 3. Evaluate a speaker’s point of view, reasoning, and use of evidence and rhetoric. Presentation of Knowledge and Ideas 4. Present information, findings, and supporting evidence such that 1 CCR- Reading CCR- Writing CCR- Language listeners can follow the line of reasoning and the organization, development, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. 5. Make strategic use of digital media and visual displays of data to express information and enhance understanding of presentations. 6. Adapt speech to a variety of contexts and communicative tasks, demonstrating command of formal English when indicated or appropriate. Key Ideas and Details 1. Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text. 2. Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas. 3. Analyze how and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and interact over the course of a text. Craft and Structure 4. Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze how specific word choices shape meaning or tone. 5. Analyze the structure of texts, including how specific sentences, paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a section, chapter, scene, or stanza) relate to each other and the whole. Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity 10. Read and comprehend complex literary and informational texts independently and proficiently. Text Types and Purposes* 1. Write arguments to support claims in an analysis of substantive topics or texts, using valid reasoning and relevant and sufficient evidence. 2. Write informative/explanatory texts to examine and convey complex ideas and information clearly and accurately through the effective selection, organization, and analysis of content. Production and Distribution of Writing 4. Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. Research to Build and Present Knowledge 7. Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects based on focused questions, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation. Conventions of Standard English 1. Demonstrate command of the conventions of Standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. 2. Demonstrate command of the conventions of Standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. Knowledge of Language 3. Apply knowledge of language to understand how language functions in different contexts, to make effective choices for meaning or style and to comprehend more fully when reading or 2 CA ELD Interactions listening. Vocabulary Acquisition and Use 4. Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiplemeaning words and phrases by using context clues, analyzing meaningful word parts, and consulting general and specialized reference materials, as appropriate. A. Collaborative (engagement in dialogue with others) 1. Exchanging information/ideas via oral communication and conversations 2. Interacting via written English (print and multimedia) 3. Offering opinions and negotiating with/persuading others 4. Adapting language choices to various contexts B. Interpretive (comprehension and analysis of written and spoken texts) 5. Listening actively and asking/answering questions about what was heard 6. Reading closely and explaining interpretations/ideas from reading C. Productive (creation of oral presentations and written texts) 9. Expressing information and ideas in oral presentations 10. Composing/writing literary and informational texts 11. Supporting opinions or justifying arguments and evaluating others’ opinions or arguments 12. Selecting and applying varied and precise vocabulary and other language resources 5-E Lesson Plan components: Engage: Connect to Prior Knowledge and Experience Estimated Time 58 min Descriptions: Students will make observations of baking soda, calcium chloride, granulated sugar, and water. Students will combine the four substances, observe what happens and write a scientific explanation. Teacher’s Role Teacher Questions Students’ Role Concepts Part 1: Part 1: Part 1: When a chemical reaction occurs Provide students with When teacher sees Follow directions on students at the point of something usually “What happens to handout working on their scientific Make observations of changes to have Properties when I explanation… new properties. combine chemical reaction substances?” Explain what they are What did you observe? Examples: handout seeing Bubbles, temperature Bubbles form Explain chemical set State their claim and change, not all Heat is given off up in front of give evidence from dissolved Solubility changes students their observations to Explain safety support their claim What is a claim? concerns Use scientific what you think is Tell students to knowledge to happening follow directions on connect the claim handout and make with the evidence observations, explain What evidence supports that? what they think is Part 2: happening, write a Students write down Part 2: claim, give evidence their questions and to support claim, and Tell students to read the post them questions that are posted Students read and give reasoning. and think about which 3 Part 2: might be testable and Tell students to write which might not be. down new questions Ask students to pick a brought up their question that they are exploration on interested in and go sentence strips and stand by it. (can be tape on wall different from original Facilitate separation group). of questions into testable/not testable categories (post grouping on wall) Looking at testable questions, group into similar type question groups Explore: Hands-on Learning, Contextualize Language, Use of Scaffolding, Use of Multiple Intelligences, Check for Understanding Description: Teacher’s Role discuss questionstestable/not testable Estimated Time 58 min Students’ Role Teacher Questions Explain: Listening, Speaking, Reading and Writing to Communicate Conceptual Understanding Description: Estimated Time 20 min Teacher’s Role Students’ Role Teacher Questions Evaluate: Thinking Maps, Summarize Lesson and Review Vocabulary, Variety of Assessment Tools Description: Assess learning goal Teacher’s Role Teacher Questions Check for understanding What is a chemical reaction? Concepts Concepts Estimated time 7 min Students’ Role Demonstrating what they learned about chemical 4 Concepts reactions What evidence can you use to determine if a chemical reaction occurs? Extend: Group Projects, Plays, Murals, Songs, Estimated Time Connections to Real World, Connections to other Curricular Areas Description: Students design a way to make a piece of chalk, large enough to write their name on the board. (engineering) OR Show me a new property using what you know about solubility. (make chalk) Teacher’s Role Teacher Questions Students’ Role Concepts Resources: Sample: Beauchamp, A., Kusnick, J., & McCallum, R. (2011). Success in science through dialogue, reading and writing. Davis, CA: Regents of California. Bybee Rodger (1997) Achieving Scientific Literacy: From Purposes to Practices 5