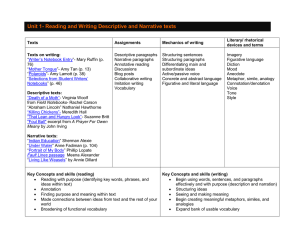
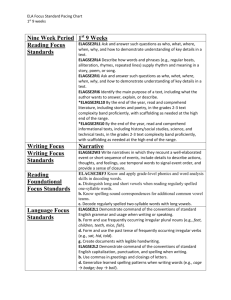
CLOSE READINGS
By: Kimberley Cooper
OBJECTIVE
After the presentation students will be able to define close reading and
demonstrate a close reading of a complex text with 90% proficiency.
After the presentation students will be able to translate what they think
about texts, and the author’s purpose, the structure, and the flow of texts by
creating a well-written essay analyzing the selection.
STANDARDS
Read closely to determine what the text says explicitly and to make
logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing
or speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.
Determine central ideas or themes of a text and analyze their
development; summarize the key supporting details and ideas.
Analyze how and why individuals, events, and ideas develop and
interact over the course of a text.
STANDARDS
Interpret words and phrases as they are used in a text, including
determining technical, connotative, and figurative meanings, and analyze
how specific word choices shape meaning or tone.
Analyze the structure of texts, including how specific sentences,
paragraphs, and larger portions of the text (e.g., a section, chapter, scene,
or stanza) relate to each other and the whole.
Assess how point of view or purpose shapes the content and style of a
text.
STANDARDS
Integrate and evaluate content presented in diverse formats and media,
including visually and quantitatively, as well as in words.*
Delineate and evaluate the argument and specific claims in a text, including the
validity of the reasoning as well as the relevance and sufficiency of the evidence.
Analyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to
build knowledge or to compare the approaches the authors take.
Read and comprehend complex literary and informational texts independently
and proficiently.
CLOSE READING
A close reading is a careful and
What is a close
reading?
Let’s examine what Dr.
Douglas Fisher (Professor
of Language and Literacy
Education in the
Department of Teacher
Education at San Diego
State University)
purposeful reading of a text.
Actually, it’s a careful and purposeful
rereading of a text.
It’s an encounter with the text where
students really focus on what the author
had to say, what the author’s purpose was,
what the words mean, and what the
structure of the text tells readers.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?featu
re=player_embedded&v=5w9v6-zUg3Y#!
CLOSE READING
How to do a close reading?
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a
dXdTXEzmzE
Consider these four elements
•
•
•
•
Language
Narrative
Syntax
Context
CLOSE READING
Language (diction
used to fit the audience, style
and purpose of the text)
What did the author repeat?
What was emphasized?
What kind of language is used?
• Formal/informal
• Slang
• Figurative language/mood words
What words are important to
understanding the theme/thesis?
CLOSE READING
Narrative (story)
Who is telling the story?
From what perspective (point
of view) is the story told?
How is the story told?
What motivates the narrator
to tell the story in this manner?
CLOSE READING
Does the author use Standard
Syntax (the order author’s
American English?
arrange their words to provide
Why would the author use
meaning/get a point across)
nonstandard syntax?
(grammar/sentence structure)
Who is the audience?
How does this writing style affect
the audience?
CLOSE READING
Context (happenings surrounding
What is the setting of the story?
What is the background of the
authorship)
author?
In what environment was the
story written? (what was happening
at the time the story was written?)
 0
0