Word - NERC
advertisement

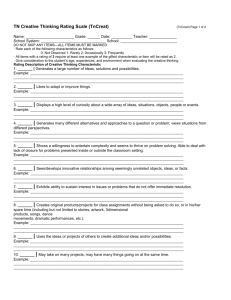
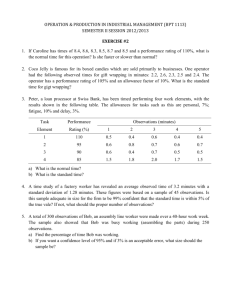
RISC Strategic Focus Exercise Introduction: NERC currently has a large number of activities and initiatives that have been identified, planned, or are underway. From those efforts, 41 specific activities were identified that were directly related to reliability risks. Those risks were then aggregated and grouped into eleven strategic areas. A table showing the aggregation, along with the source documents identifying the activity, is included at the end of this document. These eleven areas were then used to develop the exercise below. Please note that these are intended to be high-level strategic considerations, not specific tactical approaches to address a unique reliability risk. For example, there may be a number of ways in which a protection system misoperation may be averted – however, for the scope of this discussion, we would like to only focus on “misoperations” in general, rather than specifics (e.g., relay loadability, or SPS/RAS Interaction). Instructions: This exercise is meant to prioritize strategic areas for NERC activities. It is not intended to catalogue every risk to the Bulk Electric System. In this exercise, there are eleven statements of potential harm to reliability. Each of these statements corresponds to an area in which NERC currently has efforts. In order to create an overall context for how the RISC thinks about issues, please follow the instructions below to provide your input on these eleven areas. 1. First, evaluate the IMPACT of the issue to the reliability of the Bulk Electric System– either HIGH, MEDIUM or LOW a. When evaluating IMPACT, please do so by assuming there is no control on the issue or the control has failed (for example, when evaluating the impact of a hacker or terrorist attack as a risk to the BES, do not take into account the controls in place now or that will be in place after implementation of CIP v4 or v5) b. State your reasons for rating the IMPACT as you do – the reasons may be qualitative or quantitative but should be as clear as possible – this is a critical preparation step to our group discussion. c. When evaluating IMPACT, you may consider probability. If probability is considered, determine what you feel is medium or high probability, or likely to occur or an issue you deal with in normal operations/planning, and what you consider low probability. We have provided a column for you to check regarding this. 2. Second, PRIORITIZE your IMPACT analyses. After you have evaluated the IMPACT of each issue, then rank order the issues by IMPACT to the BES. NOTE: By the end of this step, you should have a list that shows you where the most resources either have been (if the issue has been addressed via controls or risk mitigation strategies) or should be (if the issues has not been fully addressed by controls or risk mitigation strategies) applied. 3. Third, evaluate what CONTROLS or other risk mitigation strategies s are in place to address the issue. a. List the controls/ risk mitigation strategies. b. Then rate the effectiveness of those controls/ risk mitigation strategies - NONE, FAIR, GOOD or EXCELLENT. c. State your reasons for evaluating the controls/ risk mitigation strategies as you do. d. Define any gap in a control/ risk mitigation strategies (you should do this for anything you rate FAIR – consider it for GOOD if you think the rating on the control/risk mitigation strategies needs to be higher than GOOD) 4. If there are any other potential harms you feel should be considered in the RISC strategic priority list, feel free to add them to the table and complete the exercise for them as well. However, please keep in mind this is not intended to catalog every risk to the Bulk Electric System. 5. Similarly, if one of the eleven provided should NOT be part of our strategic considerations, please note this as well. 6. Impact Rating Statement of Harm 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Protection Systems: A bad event becomes worse due to a protection system failing to operate correctly. Critical Infrastructure Protection: We have an event caused by a malicious attack by a hacker or terrorist. Workforce Capability and Human Error: We have an event because someone (e.g., an operator or a field technician) makes a mistake or has an error in judgment. Monitoring and Situational Awareness: We have an event due to someone (e.g., an operator or a field technician) not understanding the state of the system. Transmission Right of Way: We have an event due to a forced outage of part of the transmission system caused by a rightof-way incursion. Planning and Modeling: We have an event because our models and forecasts were inaccurate and did not predict the problem we experienced. Changes To and Within the Industry: We have an event because the world changed (e.g., environmental regulation, PHEVs, wind and solar, changing resource mix, etc...), and we were not prepared for that change. (High, Med, or Low) Reason for Impact Rating Probability Rating Priority (High, Med, or Low) (1 as highest, 10 as lowest) Control Rating Describe Control (None, Fair, Good, Excellent) Reason for Control Rating Define any Gap in Control Statement of Harm 8. Voltage and Reactive: We have an event because we are not able to maintain voltage stability. 9. Equipment Maintenance and Management: We have an event because we are not maintaining our equipment correctly or on schedule and something failed prematurely. 10. Generation Supply: We have an event because generation is inadequate during a frequency disturbance, and Underfrequency Load Shedding activated. 11. High-Impact, Low Probability: We have a long-term BES outage because a HighImpact, Low Probability event occurred and we were not prepared. Impact Rating Reason for Impact Rating Probability Rating Priority Describe Control Control Rating Reason for Control Rating Define any Gap in Control Current NERC Priority Areas and Activities State of Reliability 2012 Protection Systems 1. Misoperations of relay protection and control systems Description and notes 2. Misoperations of Protection systems that take corrective action (i.e., not simply take a line out of service) System Protection Schemes/Remedial Action Schemes 3. Backup Protection Applications 4. Reliability of Protection Systems 5. Relay Loadability Critical Infrastructure Protection 6. Critical Infrastructure Protection 7. Cyber Security Workforce Capability and Human Error 8. Human error 9. Ambiguous or incomplete voice communications 10. Support Personnel Training Monitoring and Situational Awareness 11. Disturbance Monitoring Failures to trip or improper trips, as well as slow trips 12. Project 2012-01 Equipment Monitoring and Diagnostic Devices Proactively identifies equipment likely to fail 13. Real-time Reliability Monitoring and Analysis Capabilities Assists the system operator in maintaining situational awareness Transmission Right of Way Provides detailed information on system conditions and events through use of monitoring devices with sub-second sampling rates Description and notes 15. Right-of-Way Maintenance Reducing likelihood of transmission line faults Planning and Modeling Description and notes 14. Project 2009-04 Phasor Measurements x Presidents Top Priorities OC Strategic Plan 20122016 PC Strategic Plan x x x Special Assessment (various) Reliability Standards Development Plan 20112013 x x Secondary protection systems designed to perform if primary protections fail Identification and mitigation of single points of failure in protection systems Improper trips due to oversensitivity that remove needed resources prematurely Description and notes Identification and protection of critical infrastructure from physical attack Identification and protection of critical infrastructure from cyber attack Description and notes Mistakes in performance that result in negative outcomes Communication practices that can result in misunderstanding and error Ensuring key support personnel have appropriate levels of competency Description and notes Ensures equipment is in place for monitoring and recording disturbance events Long Term Reliability Assessment 2011 x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x Current NERC Priority Areas and Activities 16. System Modeling Improvement and Coordination 17. Load Forecasting Improvements and Coordination Changes To and Within the Industry 18. Climate change 19. Environmental Regulations and Impacts to BPS Reliability 20. Post-recession Demand Growth State of Reliability 2012 Ensuring models are adequate predictors of system performance Ensuring load forecasts are adequate predictors of system demand Description and notes 27. Under voltage Load Shedding Mitigating risk of voltage collapse 28. Voltage and Reactive Issues Specifying minimum criteria for voltage and reactive planning Equipment Maintenance and Management Description and notes Equipment failing prematurely or entities not taking action to prevent failure Mitigating the risk of older equipment failing or having known vulnerabilities Description and notes Ensuring generators perform as expected, or sufficient margin exists to address deviation Verifying new resources are meeting minimum requirements to support the BES Coordinating generation control systems to ensure goal alignment Coordination of the control systems for boiler and turbine to be complementary Ensure appropriate balance is maintained 23. Integration of new technologies 24. Changing Resource Mix 25. Integration of Variable Gen 26. Increased Dependence on Natural Gas Generation 29. Equipment failure 30. Obsolescence Review Generation Supply 31. Generator Performance 32. Interconnection Criteria for Frequency Support and Response 33. Generator Control Coordination 34. Mechanical System Coordination 35. Risks associated with Frequency x PC Strategic Plan Special Assessment (various) x Reliability Standards Development Plan 20112013 x x x Impact of environmental regulation on the generation portfolio Voltage and Reactive 22. Smart Grid Presidents Top Priorities OC Strategic Plan 20122016 Threats associated with drought, weather volatility, etc… Potential for rapid demand increases Impact of load reduction (including DR performance), as opposed to raising generation Risks of adverse control (e.g., cyber threat) and changes in demand behavior Impact of Plug-in Hybrids, distributed generation, storage technology, etc.. Decreasing reliance on coal, and the impact on voltage and reserves Increased support for wind and solar, and addressing their inherent variability Risk associated with gas curtailment, as well as common mode failure of a pipeline Description and notes 21. Demand response Long Term Reliability Assessment 2011 x x x x x x x x x x x x x x X x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x Current NERC Priority Areas and Activities 36. Reserves 37. Automatic Generation Control High-Impact, Low Probability 38. Severe Weather Events 39. Geomagnetic Disturbance 40. Tracking of Spare Equipment 41. Preparedness for HILF State of Reliability 2012 Long Term Reliability Assessment 2011 Presidents Top Priorities OC Strategic Plan 20122016 PC Strategic Plan Special Assessment (various) Verify appropriate levels of reserves are being identified and carried Specifying minimum criteria for regulation and metering Description and notes Threats from tornadoes, ice storms, hurricanes, extreme cold, extreme heat) Catastrophic BES failure through Ground-Induced Currents and associated equipment failure Faster recovery from events and equipment failures Identifying events and developing mitigation and recovery strategies Reliability Standards Development Plan 20112013 x x x x x x x x x x