Earth notes completed
advertisement

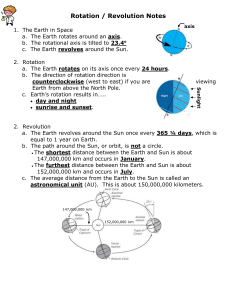
Astronomy Unit 1: Earth’s Motion and Time Guided Notes Name _______________________________________________ Period _____________ Date _________________________ A. The Day 1. Define Rotation ____Spinning on an axis (like a top)________________________________________ 2. Earth’s Rotation _Angled at 23.5 degrees , one rotation takes 24 hours or 1 day _________ 3. Evidence for Earth’s rotation 3a. __The Sun moves across the daytime sky_______ 3b. ___The Stars move across the nighttime sky__________ 4. Measuring night time __The Egyptians tracked 12 stars during the night.__________________ 5. Measuring day time :Ancient people built shadow clocks to measure time during the day._ 6. The 24 Hour Day _____________X- not doing this line_____________________________________ B. Measurement of Clock Time 7. Longitude lines _Imaginary lines drawn from pole to pole help with navigation and telling time.______________________________________________ 8. Degree longitude and time: 360 degrees in a circle and 24 hours in a day so…..15 degrees = 1 hour. 9. Time Zones _A geographical region sharing a standard time that is directly related to the Sun’s position. 10. Determining Boundaries : Based on convenience to people. Time zone boundaries are set by geography (mountains or rivers) or by politics (keep parts of countries or states together) C. The Year 11. Define Revolution: The motion of one object around another. The Earth revolves around the Sun. 12. Earth’s Revolution: The Earth rotates 365.25 times for each revolution around the Sun. D. Evidence for Revolution 13. Seasonal stars are Stars that are seen only during certain seasons. They are blocked by the sun during other times of the year. 14. circumpolar stars are seen all year round. They appear in different orientations at different times of the year. 15. Size of the Sun appears different throughout the year. The orbit of the Earth is not a perfect circle. January: 147 million km away, July 152 million km away. Sun looks bigger in winter. E. Seasons 16. Most Important Reason for Seasons is that Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted 23.5 degrees. The Results: A. Longer days = more sunlight when tilted towards the Sun.____________ B. _Higher angle of incoming Sunlight = higher intensity light when we are tilted towads the Sun.___________________________________ C. The end result is higher surface temperatures. (Summer)____________ 17. Supporting reasons for seasons A. _The direction of the tilt does not change.______________ B. The Earth revolves around the Sun._______________________ The Result : As Earth revolves we tilt towards and away from the Sun in an annual pattern. 18. Seasons are ____NOT___ related to __Earth’s distance from the Sun. ____ We are actually ____________CLOSER__________ to the _______SUN__________ in ______Winter________ F. Earth’s Position During the Seasons 19. Summer Solstice is on June 22. Longest day of the year, we are tilted towards the Sun. Daylight gets shorter after this date. Sun shines directly overhead at the Tropic of Cancer. 20. Winter Solstice is on December 22. Shortest daylight of the year, we are tilted away from the Sun. Daylight gets longer after this date. Sun shines directly overhead at the Tropic on Capricorn. 21. Spring Equinox: Both North and South Hemispheres experience 12 hours of daylight. Sun passes directly over the equator. 22. Fall Equinox: same as 21. Equinox means equal dark. (solstice means the standing still of the sun, or the turning point, half way between the equioxes)