SeasonsPPT
advertisement

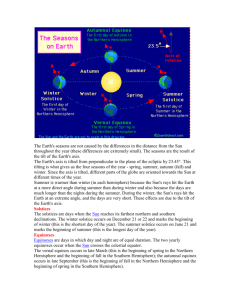
Seasons on Earth Butler Middle School 8th Grade Science Bob, Paul, Ms Adams, Oct 25, 2012 The Observed Data: 4 Seasons Autumn or Fall Winter Spring Summer We can explain the 4 seasons using Models of the Earth and Sun Scientific Model • Representation of an object for study and understanding (very common in Science) • Models can be physical and/or conceptual - Model leg in 7th grade life science - Computer model of a large weather system Spherical Earth Model Equator Earth rotates on N-S axis once per day Earth-Sun Model (evolved over 100’s maybe 1000‘s of years) Earth revolves around the sun once per year + a little bit Earth’s Orbital Plane Points to Polaris (North Star) to Polaris orbital plane 7 perpendicular to orbital plane Rotate and Revolve • Rotation: spinning like a top - Earth rotates on its axis once per 24hr - Causes day & night • Revolution: 1 object moving around a 2nd object - Earth revolves around sun once per year: 365 days + 1/4 day • Leap Year - Every 4 years February has an extra day • 4 years = (365 + 365 + 365 + 366) = 1461 days Comparing Diameters Earth Sun Sun ≈ 109 x Earth Sun illuminates Earth The Sun is a huge ball of fire - sends energy (light & heat) to the earth - 1/2 of earth is always illuminated - day - 1/2 of earth is always in the dark - night Energy distribution from Sun S slanted hit large area (cooler) U N direct hit small area (warmer) Energy distribution from Sun Understanding the Seasons • It’s all in the tilt • Summer: - Earth is tilted toward the sun, we get a more direct hit, so it’s warmer • Winter: • - Earth is tilted away from the sun, we get a slanted hit, so it’s cooler No tilt means 1 Season! Understanding Summer and Winter Summer in the North ☺ S ☺ night Winter in the North day ☹ ☹ U N South South From summer to winter earth revolves half-way around Sun Special Days Vernal Equinox March 20 Winter Solstice Dec 21 Summer Solstice June 21 Autumnal Equinox Sept 22 Earth Sun Model QuickTime™ and a H.264 decompressor are needed to see this picture.