File - Keswick Biology
advertisement

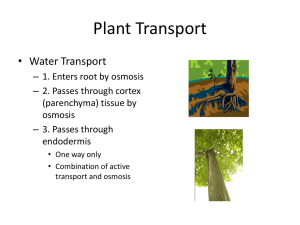
1 – Exchange of Materials 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Define osmosis Define active transport Give 3 biological examples of where osmosis or active transport would take place Define isotonic How do isotonic drinks help to rehydrate cells after exercise? (Remember to refer to the processes e.g. diffusion/active transport/osmosis) 6. What 3 features of the lungs make them a good surface for gas exchange? 7. Describe the process of ventilation (including named muscles) 8. How does an ‘iron lung’ work as a breathing aid? 9. How is ‘iron lung’ ventilation different to a positive breathing aid 10. What features of healthy lung function are mimicked by an artificial breathing aid? 11. What feature increases the surface area of the small intestine? 12. Give an example of where each of the following would be used in a plant (a) diffusion (b) osmosis and (c) active transport 13. Why do leaves have stomata which open and close? 14. What feature increases the surface area of the root of a plant? 15. Define transpiration 16. What factors affect the rate of transpiration? 17. How can you measure the rate of transpiration? 2 – Transport of Materials 1. Which 2 transport tissues are found in plants and what do they transport? 2. What are the four main blood vessels entering and leaving the heart? Where does each one take blood from and to? 3. Why is the heart referred to as a ‘double pump’? 4. What is the function of valve in the heart? 5. Name 2 main differences for arteries, veins and capillaries? 6. What is atherosclerosis and how can it be treated? 7. What are the four main components of blood and what is the function of each? 8. Describe 3 adaptations of a red blood cell for its function 9. Describe 3 key differences between donor blood and artificial blood 10. What is artificial blood usually made from? 3 – Homeostasis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Define homeostasis What is the difference between urea and urine? Describe the process of ‘selective reabsorption’ in the kidney Which blood vessel brings blood to the kidney? Draw a diagram to illustrate how a dialysis machine would filter human blood 6. Explain why dialysis fluid contains the same concentrations of useful substances (e.g. glucose and mineral ions) 7. Explain why immunosuppressant drugs are essential for the recipient of an organ donation 8. Why do organ donations have to be carefully matched to the patient? 9. Where is blood temperature monitored? 10. Describe the effects coordinated by the body in response to a rise in temperature 11. Describe the effects coordinated by the body in response to a fall in temperature 12. Who is most at risk of hyperthermia and dehydration or of hypothermia? 13. Explain how the body responds to a rise in blood glucose levels 14. Explain how the body responds to a fall in blood glucose levels 15. Define: glycogen, glucagon, glucose and insulin 16. What is type 1 diabetes? 17. How does type 2 diabetes differ from type 1 diabetes? 18. Why is insulin not usually an effective treatment for a type 2 diabetic? 4 – Humans & the Environment 1. Describe 6 implications of the recent ‘population boom’ 2. How do people reduce the amount of land available for animals and plants? 3. Name all the major air pollutants (and their source) 4. Name all the major water pollutants (and their source) 5. What is bioaccumulation? 6. What is eutrophication? 7. What is the mineral in fertilisers which causes eutrophication? 8. Describe the social and economic reasons for deforestation 9. What is ‘slash and burn’ clearance and why is it an issue? 10. Define biodiversity 11. Define carbon sink 12. What are the 2 main sources for rising atmospheric methane levels?# 13. Why are peat bogs important? (*Use GCSE bitesize) 14. Why are peat bogs being destroyed? (*Use GCSE bitesize) 15. What is the greenhouse effect? 16. Why do some people argue that global warming is not man-made? 17. Describe 3 reasons for the current increase in greenhouse gases 18. Clearly explain 6 biological implications of global warming 19. Describe how biodiesel is synthesised 20. Explain what is meant by the term carbon neutral 21. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using biodiesel as a fuel 22. Describe how biogas is synthesised 23. Explain how microorganisms are used in the synthesis of biodiesel and biogas 24. Explain why a vegetarian diet is more energy efficient than a meat eaters 25. Explain 4 ways in which energy can be wasted as it moves along the food chain 26. Describe 3 ways in which energy wastage is minimised in intensive farming 27. Explain some of the reasons why some people are opposed to intensive farming 28. What is a food mile? 29. Define sustainable 30. What is a fishing quota? 31. Explain how mycoprotein is synthesied 32. Why is mycoprotein considered to be a sustainable food source? 33. Can you suggest any ways in which reservoirs can cause environmental problems?