File - Leaving Cert Biology
advertisement

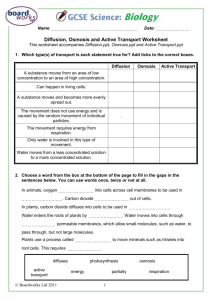
Chapter 8: Movement through cell membranes Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level Selective Permeability • Cell membranes are selectively permeable meaning they can control what enters and leaves the cell – Selective permeability is controlled by proteins embedded in the cell membrane Glucose transporter Glucose (in blood) Cell membrane (made of phospholipids) Glucose (in cell) Diffusion • Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration (i.e. down a concentration gradient) – E.g. oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse across the alveolus membranes from regions of relative high concentration to regions of relative low concentration Osmosis • Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration across a semi-permeable membrane – E.g. water is continuously moving across the membrane of an Amoeba by osmosis from the freshwater (high water concentration) to the interior of the cell (lower water concentration) Application of Osmosis • Osmosis is used by food industry for preservation of food – E.g. tinned fruit/vegetables are placed in a concentrated sugar (syrup) or salt solution – this causes any bacteria/fungi present to die due to water leaving the cells (Bacterial and fungal cells have a high water concentration relative to the syrup/salt solution) Turgor and Plasmolysis • Turgor is the pressure exerted by the cells contents on the cell wall of a plant cell H2O Roots H2O Leaf H2O Wilted leaf Turgor and Plasmolysis Experiment to demonstrate osmosis • Apparatus: Visking tubing, beakers, water, sucrose solution, balance • Method: set up as follows: Control Water Water Control Test 60% 60% sucrose sucrose 60% Water sucrose Experiment to demonstrate osmosis • Result: Visking tubes remained same weight Control Water Water Visking tube swelled Control Test 80% 80% sucrose sucrose 80% Water sucrose Experiment to demonstrate osmosis • Conclusion: – The two control Visking tubes did not change weight due to the fact that equal diffusion of water particles was occurring – i.e. osmosis was occurring in equal measure in both directions – The test Visking tube gained water by osmosis due to a water concentration gradient, i.e. water moved by osmosis from the beaker (high water concentration) into the Visking tube (low water concentration)