Stomata, Transpiration & Abscission
advertisement

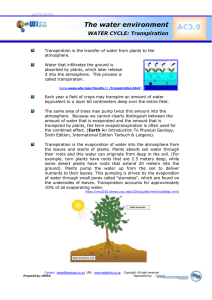
Controlled by guard cells Flaccid Little water Limp Turgid Fill with water Bend http://academic.kellogg.edu/herbrandsonc/bio111/animat ions/0021.swf Triggered by blue light Activates proton pump Yellow pigments located in membrane (?) H+ out, creates electrochemical gradient K+ diffuses in through ion channels, Cl- follows K+, Cl- accumulate in vacuoles, water moves in K+ concentration in guard cells decrease during day Sucrose increases, maintains osmotic pressure As sucrose concentration decreases, water leaves Pores close Blue Light Low CO2 concentration Water stress Hormones Abscisic acid Transpiration 99% of water plants take in is lost by evaporation Open stomata Rate of Transpiration affected by: Humidity Temperature Wind Guttation Liquid water forced out when transpiration negligible Allows water to move from roots to leaves Shedding of leaves Conifers lose needles yearround Deciduous trees Survive low temp of winter Water uptake inhibited Prevents continuous water loss by transpiration Controlled by hormones: Ethylene Essential organic compounds & minerals move to other parts of plant for storage Chlorophyll breaks down, other pigments seen Cork forms protective layer on stem side of abscission zone of petiole Enzymes dissolve middle lamella in abscission zone of petiole Leaf detaches in breeze