UNIT 2 INSIDE THE EARTH VOCABULARY LIST recycling
advertisement

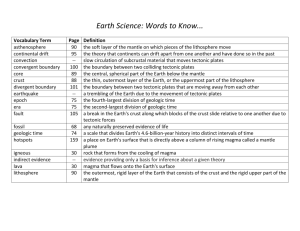
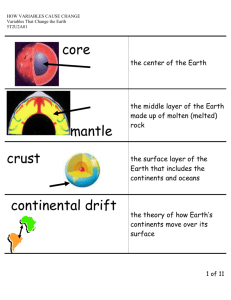
UNIT 2 INSIDE THE EARTH VOCABULARY LIST recycling - the process of recovering valuable or useful materials from waste or scrap; the process of reusing some items petroleum - a liquid mixture of complex hydrocarbon compounds; used widely as a fuel source natural gas - a mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons, located under the surface of the Earth, often near petroleum deposits, used as fuel nuclear energy - the energy released by a fission or fusion reaction; the binding energy of the atomic nucleus fission - process in which the nuclei of radioactive atoms are split into two or more smaller nuclei fusion - process in which the two or more nuclei are joined to form a larger nucleus chemical energy - the energy released when a chemical compound reacts to produce new compounds (hydrogen fuel cell) solar energy - the energy received by the Earth from the sun in the form of radiation wind power - the use of a windmill to drive an electric generator hydroelectric energy - electrical energy produced by falling water biomass - organic matter that can be source of energy gasohol - a mixture of gasoline and alcohol that is used as a fuel geothermal energy - the energy produced by heat within the Earth uniformitarianism - a principle that states that geologic processes that occurred in the past can be explained by current geologic processes catastrophism - a principle that states that geologic change occurs suddenly paleontology - the scientific study of fossils relative dating - any method of determining whether an event or object is older or younger than other events or objects superposition - a principle that states that younger rocks lie above older rocks if the layers have not been disturbed geologic column - an arrangement of rock layers in which the oldest rocks are at the bottom unconformity - a break in the geologic record created when rock layers are eroded or when sediment is not deposited for a long period of time fossil - the remains or physical evidence of an organism preserved by geological processes trace fossil - a fossilized mark that is formed in soft sediment by the movement of an animal index fossil - a fossil that is found in the rock layers of only one geologic age and that is used to establish the age of the rock layers geologic time scale - the standard method used to divide the Earth's long natural history into manageable parts extinction - the death of every member of a species crust - the thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle mantle - the layer of rock between the Earth's crust and core core - the central part of the Earth below the mantle lithosphere - the solid, outer layer of the Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle asthenosphere - the soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move mesosphere - the strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core tectonic plate - a block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle Continental Drift Theory - the hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up and drifted to their present locations Seafloor Spreading Theory - the process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies Plate Tectonics Theory-the theory that explain how large pieces of the Earth's outermost layer, called tectonic plates, move and change shape convergent boundary-the boundary formed by the collision of two lithospheric plates divergent boundary-the boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other transform boundary-the boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally compression - stress that occurs when forces act to squeeze an object tension-stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object folding - the bending of rock layers due to stress fault - a break in a body of rock along which one block slides relative to another uplift - the rising of regions of the Earth's crust to higher elevations subsidence - the sinking of regions of the Earth's crust to lower elevations earthquake - the quick and sudden movement of the earth caused when rock breaks seismology-the study of earthquakes deformation-the bending, tilting, and breaking of the Earth's crust; the change in the shape of rock in response to stress elastic rebound-the sudden return of elastically, deformed rock to its undeformed shape seismic wave - a wave of energy that travels through the Earth, away from an earthquake in all directions P-wave- a seismic wave that causes particles of rock to move in a back-and-forth direction S-wave - a seismic wave that causes particles of rock to move in a side-to-side direction Surface wave - a seismic wave that moves along the Earth's surface and produce motion mostly in the upper few kilometers of the crust - most destructive seismograph-an instrument that records vibrations in the ground and determines the location and strength of an earthquake seismogram - a tracing of earthquake motion that is created by a seismograph epicenter - the point on Earth's surface directly above an earthquake's starting point, or focus focus - the point along a fault at which the first motion of an earthquake occurs Richter Magnitude Scale - a scale used to measure the strength of an earthquake - 1 - 10 Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale - a scale used to measure the intensity of an earthquake I - XII gap hypothesis - a hypothesis that is based on the idea that a major earthquake is more likely to occur along the part of an active fault where no earthquakes have occurred for a certain period of time seismic gap - an area along a fault where relatively few earthquakes have occurred recently but where strong earthquakes have occurred in the past volcano- a vent or fissure in the Earth's surface through which magma and gases are expelled magma chamber - the body of molten rock that feeds a volcano vent - an opening at the surface of the Earth through which volcanic material passes shield volcano - built of layers of lava released from repeated nonexplosive eruptions cinder cone volcano - made of pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions composite volcano- most common type of volcano, form from explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material and quieter flows of lava crater - a funnel-shaped pit near the top of the central vent of a volcano caldera - a large, semicircular depression that forms when the magma chamber below a volcano partially empties and causes the ground above to sink lava plateau - a wide, flat landform that results from repeated nonexplosive eruptions of lava that spread over a large area subduction zone- a convergent boundary where one plate moves under the other plate, often causing volcanic activity rift zone - an area of deep crack that forms between two tectonic plates that are pulling away from each other (divergent boundary) hot spots - a volcanically active area of the Earth's surface far from a tectonic plate boundary