Earth`s Terms Test PLATE TECTONICS Crust – the thin and solid
advertisement

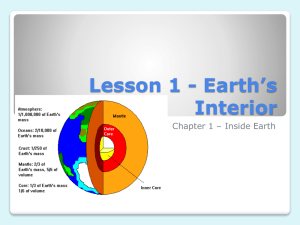
Earth’s Terms Test PLATE TECTONICS Crust – the thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth, above the mantle Mantle – the layer of rock between the Earth’s crust and core Core – the central part of the Earth below the mantle Lithosphere – the solid, outer layer of the Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle Asthenosphere – the soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move Mesosphere – the strong, lower part of the mantle between the Asthenosphere and the outer core Tectonic Plate – a block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle Continental Drift – the hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations Sea Floor Spreading – the process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies Plate Tectonics – the theory that explains how the tectonic plates move and change shape Convergent Boundary – the boundary formed by the collision of two ltihospheric plates Divergent Boundary – the boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other Transform Boundary – the boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally Compression – the stress that occurs when forces act to squeeze an object Tension – stress that occurs when forces act to stretch an object Folding – the bending of rock layers due to stress Fault – a break in a body of rock along which one block slides relative to another Uplift – the rising of regions of the Earth’s crust to higher elevations ROCK CYCLE Weathering – when rocks are broken down into smaller fragments Erosion – when rock fragments are moved by some force of nature Deposition – when rock fragments are laid down in a new location Igneous rock – formed by cooling and hardening of hot liquid rock Sedimentary rock – formed when sediments are pressed and cemented together Metamorphic rock – formed when rocks are changed by heat and pressure EARTHQUAKE P waves – a seismic wave that compresses and expands rock, fastest wave S waves – a seismic wave that causes rock to move in a side-to-side direction Surface waves – these seismic waves travel more slowly, but are more destructive Seismic waves – a wave of energy that travels through the Earth, away from an earthquake in all directions Seismology – the study of earthquakes Seismologist – someone who studies earthquakes Seismogram – the print out of earthquake activity, shows the p, s, and surface Waves Seismograph – an instrument that records seismic waves Focus – the point inside the Earth where the earthquake begins Epicenter – the point on the Earth’s surface directly above an Earthquake’s starting point, or focus Fault – a break in a body of a rock in which one block slides relative to another Elastic rebound – the sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed shape Deformation – the bending, tilting, and breaking of the Earth’s crust Richter scale – measures earthquake intensity on a scale of 1-10 Mercalli intensity scale – measures earthquake intensity and the amount of damage caused by an earthquake Earthquake – the shaking of the ground Aftershock – minor shocks following the main shock of an earthquake Tsunami – a large wave that results from large-scale seafloor displacements associated w/ large earthquakes VOLCANO Volcano – a vent or fissure in the Earth’s surface through which magma and gases are expelled Vent – an opening at the surface of the Earth through which volcanic material passes Magma Chamber – the body of molten rock that feeds the volcano Crater – a funnel shaped pit near the top of the central vent of a volcano Caldera – a crater that forms when the ground sinks around the vent Rift Zone – area of deep cracks that forms between two tectonic plates that are pulling away Hot spot – a volcanically active area of Earth’s surface far from a tectonic plate boundary Ring of Fire – an area of volcanic activity that borders the pacific plate Shield Volcano – built by layers of lava, non explosive eruptions Cinder Cone Volcano – pyroclastic material, steep slopes, moderately explosive Composite Volcano – explosive eruptions and quiet flows Lava – liquid magma that flows from a volcanic vent