PS_Module 4 Study Guide
advertisement

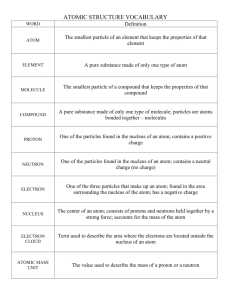
Physical Science Honors – Module 4 Test – Study Guide Vocabulary to Know Physical properties Solid Chemical properties Liquid Physical change Gas Chemical change Plasma Law of conservation of mass State of matter Atomic theory Phase change Atom Kinetic theory of matter Nucleus Freezing Proton Evaporation Neutron Condensation Electron Melting Electron cloud Heat of fusion Atomic number Heat of Vaporization Mass number Pure substance Ion Element Isotope Compound Periodic table Mixture Period Homogeneous mixture Group Heterogeneous mixture Module 1 Concepts 1. Recognize that matter is made of particles in constant motion. 2. Identify the four states of matter. 3. Differentiate between the arrangement of particles in solids, liquids, and gases, and plasma. 4. Explain why adding energy to of removing energy from matter can cause it to change phase. a. How does a liquid change into a gas? Into a solid? b. How does a solid change into a liquid? c. How does a gas turn into a liquid? 5. Distinguish elements, compounds, and mixtures. a. H2O b. Helium (He) c. Chex mix d. Kool-aid 6. Compare and contrast pure substances to mixtures. 7. Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. 8. Identify and compare physical and chemical properties of matter. 9. Identify and compare physical and chemical changes. a. 4 characteristics of a chemical change: b. Toasting a marshmallow c. Cutting paper d. Digesting food e. Painting wall 10. Explain how the law of conservation of mass applies to both physical and chemical changes. 11. Describe the development of the modern atomic theory over time. 12. Describe the structure of atoms. a. Where is most of the mass located in the atom? b. What is the atom mostly made of? c. What is the charge of the nucleus of the atom? d. What particles are found in the electron cloud? e. What are the charges of subatomic particles? 13. Compare the atomic number and mass number of different atoms. 14. Describe energy levels 15. Differentiate among atoms, ions, and isotopes. a. Adding/Removing a proton b. Adding/Removing a neutron c. Adding/Removing an electron 16. Explain how the periodic table is organized. a. How was the first periodic table constructed? b. How did this change later when more was learned about the atom? c. Where are metals, nonmetals, and metalloids located? 17. Describe trends that are found on the periodic table. a. Which atom has greater atomic radius, Li or Be? b. Which atom has greater ionization energy, Al or c. Which atom has greater electronegativity, Mg or F? 18. Use the periodic table to obtain information about elements and atoms. a. How can you tell how many shells an atom has for its electrons? b. How can you figure out how many valance electrons an atom has?