Topic 3: The Cell - Structure - Jefferson County School District
advertisement

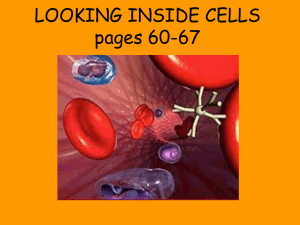
Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence Course: Biology I Course Code: 2000310 Quarter: 1C Topic(s) of Study: Cell Structure Bodies of Knowledge: Nature of Science and Life Science Big Idea(s): 1: The Practice of Science, 2: The Characteristics of Scientific Knowledge, 3: The Role of Theories, Laws, Hypotheses, and Models, 14: Organization and Development of Living Organisms Essential Questions: How does the history of the cell theory relate to the process of science? How does the structure of plant and animal organelle structure relate to their function? How do scientists design an investigation to answer a scientific question and communicate their findings? NGSSS SC.912.L.14.1 Describe the scientific theory of cells (cell theory) and relate the history of its discovery to the process of science. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.912.L .14.2 Relate structure to function for the components of plant and animal cells. Explain the role of cell membranes as a highly selective barrier (passive and active transport). Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.912.L.14.3 Compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells. Compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.912.L.14.4 Compare and contrast structure and function of various types of microscopes. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.912.N.1.1 Define a problem OUTLINE OF CONTENT (CONCEPT/SKILLS) OBJECTIVES I Cell theory A. The cell is the unit of structure, physiology, and organization in living things. B. The cell retains a dual existence as a distinct entity and a building block in the construction of organisms. C. All cells only arise from pre-existing cells D. Was developed using the several processes of science over many years. It was modified as microscopes were improved and knowledge increased. II Animal cell components: structure related to function A. Nucleus – information hub and DNA storage 1. Nucleolus - Identify and describe the components of the theory of cells (cell theory) using a graphic organizer. (I) Describe how the history of the theory of cells (cell theory) relates to the process of science using a graphic organizer. (I) Compare and contrast active and passive transport as related to the cell membrane using a graphic organizer and analyzing a video or images. (II, III) Explain how the structure of plant cell organelles relates to their function by constructing a model. (III) Compare and contrast the general structures of animal and plant cells by viewing prepared slides and constructing a model. (II, III) Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by viewing prepared slides. (IV, V) Compare and contrast structure and function of various types of microscopes. (VI) Objectives below are from Quarter 1A and should be embedded in this topic of study. Describe the role consensus plays in 1 Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence based on a specific body of knowledge, for example: biology, chemistry, physics, and earth/space science, and do the following: Cognitive Complexity: High 1. pose questions about the natural world, 2. conduct systematic observations, 3. examine books and other sources of information to see what is already known, 4. review what is known in light of empirical evidence, 5. plan investigations, 6. use tools to gather, analyze, and interpret data (this includes the use of measurement in metric and other systems, and also the generation and interpretation of graphical representations of data, including data tables and graphs), 7. pose answers, explanations, or descriptions of events, 8. generate explanations that explicate or describe natural phenomena (inferences), 9. use appropriate evidence and reasoning to justify these explanations to others, 10. communicate results of scientific investigations, and 11. evaluate the merits of the explanations produced by B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. Contains RNA for protein manufacture 2. Nuclear membrane Surrounds nucleus, composed of two layers,numerous openings for nuclear traffic a. Passive transport b. Active transport Cytoplasm – gel like substance that contains all organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum – transport system of the cell Ribosomes – site for protein synthesis Mitochondria – power house of cell where sugars are broken down for cellular respiration Golgi Bodies – sorts, modifies and packs macromolecules to be used within or outside the cell Vacuoles - Membranebound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal. Lysosome - Digestive 'plant' for proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates Cell Membrane - Outer membrane of cell that controls cellular traffic the historical development of a theory in biology. Give examples of how advances in technology have affected scientific theories and laws. Compare and contrast the terms that describe examples of scientific knowledge such as: theory, law, hypothesis, and model. Distinguish between a scientific theory and a general claim. Distinguish between laws and theories by understanding that laws describe the what and theories explain the why. 2 Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence others. SC.912.N.1.3 Recognize that the strength or usefulness of a scientific claim is evaluated through scientific argumentation, which depends on critical and logical thinking, and the active consideration of alternative scientific explanations to explain the data presented. Cognitive Complexity: Low SC.912.N.1.4 Identify sources of information and assess their reliability according to the strict standards of scientific investigation. Cognitive Complexity: High SC.912.N.1.6 Describe how scientific inferences are drawn from scientific observations and provide examples from the content being studied Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.912.N.2.1 Identify what is science, what clearly is not science, and what superficially resembles science (but fails to meet the criteria for science). Cognitive Complexity: High III Plant cell components: structure related to function (same as for animals with some additional organelles) A. Cell membraneouter membrane of the cell that controls cellular traffic B. Cell wall - Outer membrane of cell that controls cellular traffic and contains proteins that span through the membrane and allow passage of materials C. Chloroplasts – Contain green chlorophyll where photosynthesis takes place IV Prokaryotic Cells A. Lack a membranebound nucleus B. Have few internal structures C. Don't have a membrane-bound nucleus and instead of having chromosomal DNA, their genetic information is in a circular loop called a plasmid. SC.912.N.3.1 Explain that a scientific theory is the culmination of many scientific investigations drawing together all the current evidence V Eukaryotic Cells concerning a substantial range of A. Have a membranephenomena; thus, a scientific bound nucleus theory represents the most B. contain many powerful explanation scientists internal membranehave to offer. Cognitive bound organelles Complexity: High 3 Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence SC.912.N.3.4 Recognize that theories do not become laws, nor do laws become theories; theories are well supported explanations and laws are well supported descriptions. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate VI Microscopes A. Compound B. Light C. Electron LA.910.2.2.3 The student will organize information to show understanding or relationships among facts, ideas, and events (e.g., representing key points within text through charting, mapping, paraphrasing, summarizing, comparing, contrasting, or outlining); LA.910.4.2.2 The student will record information and ideas from primary and/or secondary sources accurately and coherently, noting the validity and reliability of these sources and attributing sources of information; MA.912.S.1.2 Determine appropriate and consistent standards of measurement for the data to be collected in a survey or experiment. MA.912.S.3.2 Collect, organize, and analyze data sets, determine the best format for the data and present visual summaries from the following: bar graph s line graphs stem and leaf plots circle graph s histograms box and whisker plots scatter plots 4 Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence cumulative frequency (ogive) graphs 5