Components of the Literacy Framework
advertisement
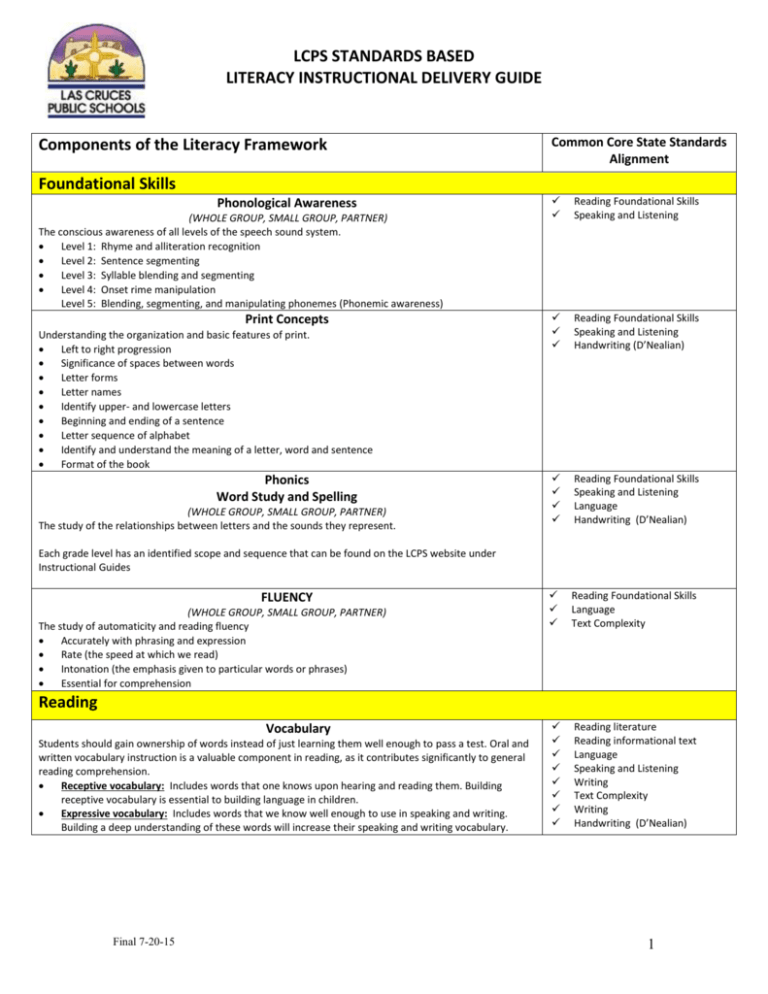
LCPS STANDARDS BASED LITERACY INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY GUIDE Components of the Literacy Framework Common Core State Standards Alignment Foundational Skills Phonological Awareness (WHOLE GROUP, SMALL GROUP, PARTNER) The conscious awareness of all levels of the speech sound system. Level 1: Rhyme and alliteration recognition Level 2: Sentence segmenting Level 3: Syllable blending and segmenting Level 4: Onset rime manipulation Level 5: Blending, segmenting, and manipulating phonemes (Phonemic awareness) Print Concepts Understanding the organization and basic features of print. Left to right progression Significance of spaces between words Letter forms Letter names Identify upper- and lowercase letters Beginning and ending of a sentence Letter sequence of alphabet Identify and understand the meaning of a letter, word and sentence Format of the book Phonics Word Study and Spelling (WHOLE GROUP, SMALL GROUP, PARTNER) The study of the relationships between letters and the sounds they represent. Reading Foundational Skills Speaking and Listening Reading Foundational Skills Speaking and Listening Handwriting (D’Nealian) Reading Foundational Skills Speaking and Listening Language Handwriting (D’Nealian) Reading Foundational Skills Language Text Complexity Reading literature Reading informational text Language Speaking and Listening Writing Text Complexity Writing Handwriting (D’Nealian) Each grade level has an identified scope and sequence that can be found on the LCPS website under Instructional Guides FLUENCY (WHOLE GROUP, SMALL GROUP, PARTNER) The study of automaticity and reading fluency Accurately with phrasing and expression Rate (the speed at which we read) Intonation (the emphasis given to particular words or phrases) Essential for comprehension Reading Vocabulary Students should gain ownership of words instead of just learning them well enough to pass a test. Oral and written vocabulary instruction is a valuable component in reading, as it contributes significantly to general reading comprehension. Receptive vocabulary: Includes words that one knows upon hearing and reading them. Building receptive vocabulary is essential to building language in children. Expressive vocabulary: Includes words that we know well enough to use in speaking and writing. Building a deep understanding of these words will increase their speaking and writing vocabulary. Final 7-20-15 1 LCPS STANDARDS BASED LITERACY INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY GUIDE LISTENING COMPREHENSION INTERACTIVE READ ALOUD (WHOLE GROUP in close proximity to the teacher) Interactive Read Aloud model with COMPLEX TEXT Fluent reading with prosody – expression, intonation, and phrasing Active Listening Comprehension strategies through “Think Aloud” Close reading strategies are modeled READING LANGUAGE COMPREHENSION SHARED READING/CLOSE READING Shared reading is reading with children using COMPLEX TEXT (WHOLE GROUP-Skilled and strategic reading by the teacher is done in an engaging setting where the learning and reading knowledge is shared, supported and practiced. Text is seen by all: big book, shared text, transparency, chart, etc.) Reading Literature Reading Informational Text Speaking and Listening Text Complexity Handwriting (D’Nealian) Writing: Reader’s Response Reading Literature Reading Informational Text Speaking and Listening Language Text Complexity Handwriting (D’Nealian) Writing: Responding to Text Dependent questions Reading Literature Reading Informational Text Reading Foundational Skills Speaking and Listening Handwriting (D’Nealian) Writing: Responding to Text Dependent questions K-1 shall focus on a Shared Reading experience that will focus on: Interacting with text in applying reading (decoding) strategies Rereading confusing parts to reinforce understanding of text. Reading with a pencil (annotating text) to help remember text. Identifying and clarifying confusing words or parts – application of phonic skills Discussing the text with others. Responding to text-dependent questions. 2-5 shall focus on a Close Reading experience that will focus on: Rereading confusing parts to reinforce understanding of text. Reading through a close reading lenses to comprehend text and develop a new understanding of text Read closely for text evidence (specific details, characters actions and thoughts, settings, time periods, and relationships Use reading patterns to determine how details fit together Use reading patterns to think about characters feelings, traits, relationships within themes and lessons Annotate text with ideas and thoughts Discussion of text and close reading lenses with others Responding to text-dependent questions. GUIDED READING EARLY CONCEPTS (SMALL GROUP with similar needs/instructional level) Pre-A level – describe pictures using complete sentences, one-to-one matching, using picture to decode a word, understand the concept of a word, match sounds to letters Emergent – forming letters, practicing letters and sounds, hear sounds in sequence, spacing between words during writing GUIDED READING COMPREHENSION Early – monitor and checking for meaning, visual match to words, decoding, rereading, fluency, retelling, read/write sight words and phonetic principles Transitional - self-monitoring, decoding multisyllabic words, increasing fluency, expanding vocabulary, improving comprehension (Teacher should be teaching with leveled reader and complex text) Fluent- increasing vocabulary, using a variety of comprehension strategies (Teacher should be teaching with complex text) Final 7-20-15 2 LCPS STANDARDS BASED LITERACY INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY GUIDE CENTERS As students are in Guided Reading with the teacher, the remaining students are divided into groups (typically based on their guided reading level) and rotated through centers that support through collaborative and independent practice of reading skills. Typical centers are: Independent Reading or Writing with Complex Text Response to Reading of Complex Text Phonics Wordy Study practice Content Area/Research Station Daily 5 workstations Reading Literature Reading Informational Text Reading Foundational Skills Speaking and Listening Language Complex Text Writing o Text Types and Purposes o Research to Build and Present Knowledge o Production and Distribution of Writing Language: Conventions of Standard English Speaking and Listening Responding to Complex Text Handwriting (D’Nealian) WRITING Text Types and Purposes and Research to Build and Present Knowledge Narrative, Informative/Explanatory (to include research topics) and Opinion TEACHER WRITING and/or INTERACTIVE WRITING Teacher Writing Modeling the genre of writing. Modeling the thought process of writing. The teacher is “thinking aloud” while writing. Text is seen by all Modeling the writing process (each step at different times) o Writing process Brainstorming and Draft (Plan and talk, genre organizer) Edit (Punctuation time) Revise (Talk and Write) Publish Not an interactive time between teacher and student Teacher models “what good writers do” Interactive Writing Collaborative learning and discussion of genre of writing. Collaborative learning and discussion about the process of writing. Text is seen by all AND created by all Interacting with the writing process (each step at different times) o Writing process Brainstorming and Draft (Plan and talk, genre organizer) Edit (Punctuation time) Revise (Talk and Write) Publish Collaborative learning that uses discussion and negotiation to create pieces of writing as a productive group Students are practicing what “what good writers do” Range of Writing: Narrative, Informative/Explanatory (to include research topics) and Opinion. PARTNER AND INDIVIDUAL WRITING Final 7-20-15 Writing o Text Types and Purposes o Research to Build and Present Knowledge 3 LCPS STANDARDS BASED LITERACY INSTRUCTIONAL DELIVERY GUIDE o (Whole group, Individual) Partner Writing Collaborative learning and discussion of genre of writing. Collaborative learning and discussion about the process of writing. Text is seen and created by partners Interacting with the writing process (each step at different times) o Writing process Brainstorming and Draft (Plan and talk, genre organizer) Edit (Punctuation time) Revise (Talk and Write) Publish Collaborative learning that uses discussion and negotiation to create pieces of writing as a productive partners Students are practicing what “what good writers do” Production and Distribution of Writing Comprehension Vocabulary Language: Conventions of Standard English Speaking and Listening Handwriting (D’Nealian) Independent Writing Independent thinking about the genre of writing. Applying the process of writing. Text is created individually Applying the writing process (each step at different times) o Writing process Brainstorming and Draft (Plan and talk, genre organizer) Edit (Punctuation time) Revise (Talk and Write) Publish Students are applying what “what good writers do” PUBLISHING AND SHARING Whole group, small group, partners and individuals should create final pieces of writing for publishing Published writing that indicates the author should be added to the classroom library Groups and individuals should always share their published work by presenting it to the class prior to adding the text to the library. Ways to share: Digital (ibook, power point, scanned booklet, etc.) Small group Whole group Parent nights Classroom across classroom sharing Final 7-20-15 Language Speaking and Listening Writing: Production and Distribution Handwriting (D’Nealian) 4