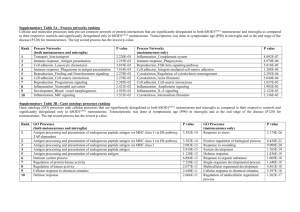
43 Study Guide 43.1 Name: 43.1 and Overview Vocabulary 1. A
advertisement

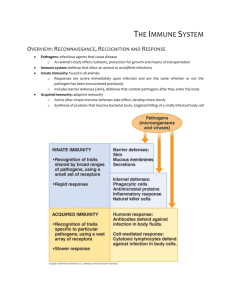
43 Study Guide 43.1 43.1 and Overview Vocabulary Name:__________________ 1.___________________ A defense found only in vertebrates which contains many receptors for recognizing molecules of particular pathogens 2. ___________________A defense that is active immediately upon infection and is the same whether or not the pathogen has been encountered previously 3. ___________________ Binds to fragments of molecules characteristic of a set of pathogens 4. ___________________Cells that circulate through body detecting abnormal surface proteins characteristic of some virus-infected cancerous cells 5. ___________________ Cellular ingestion and digestion of bacteria and other foreign substances 6. ___________________ Changes brought about by signaling molecules released upon injury or infection 7. ___________________ Enables an animal to avoid or limit many infections 8. ___________________ Enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls 9. ___________________ Important inflammatory signaling molecule 10. __________________Large phagocytic cell 11. __________________ Phagocytic cell which circulates in blood, and is attracted by signals from infected tissues, engulfs and destroys infecting pathogens 12. __________________Populate tissues such as skin that contact the environment, stimulating adaptive immunity against pathogens they encounter and engulf 13. __________________ Proteins that provide innate defense by interfering with viral infections 14. __________________ Roughly 30 proteins in blood plasma that circulate in an inactive state and are activated by substances on the surface of many microbes 15. __________________ Signaling molecules that enhance immune response 16. Discuss Recognition and response. 17. Discuss innate immunity of Invertebrates 18. Discuss immunity of vertebrates a. Barrier Defenses 1 b. Cellular Innate Defenses c. Inflammatory Response 19. Discuss evasion of innate immunity by pathogens 43.2 Vocabulary 1._____________________ An encounter with an antigen selects which lymphocytes will divide to produce a clonal population 2. _____________________Any substance that elicits a response from a B cell or T cell 3. _____________________ Display of the antigen fragment in exposed groove of MHC protein 4. _____________________ Host protein that displays the antigen fragment on the cell surface 5. _____________________Long lived cells that can give rise to effector cells in the same antigen is encountered later in the animal’s life 6. _____________________ Lymphocytes that originate in bone marrow and migrate to the thymus 7. ______________________Lymphocytes that remain and mature in the bone marrow 8. _________________ and ______________Make up Y shaped molecule that is an antigen receptor on B cells 9. ______________________Organ in the thoracic cavity above the heart 10. _____________________ Production of effector cells from a clone of lymphocytes during the first exposure to an antigen 11. _____________________Prolonged, faster, response of greater magnitude after being exposed again to the same antigen 12. _____________________ or _______________________ Secreted soluble form of the receptor on B cells 13. _____________________Short lived cells that take effect immediately against the antigen and any pathogens producing that antigen 14. _____________________ Small accessible portion of an antigen that binds to an antigen receptor 15. _____________________ Type of white blood cells (T cells and B cells) 16. Discuss how adaptive immunity, receptors provide pathogen-specific recognition. 2 a. Discuss antigen recognition by B Cells and antibodies b. Discuss antigen recognition by T Cells. c. Discuss B Cell and T Cell Development. 1. Discuss generation of B and T Cell diversity 2. Discuss origin and self-tolerance 3. Discuss proliferation of B Cells and T Cells 4. Discuss immunological memory 3 43.4 Vocabulary 1. __________________ Antigens that cause an exaggerated response 2. __________________Caused by the human immunodeficiency virus 3. __________________Disorder in which an immune system response to antigens is defective or absent 4. __________________When the immune system is active against particular molecules of the body 5.Discuss exaggerated, self-directed, and diminished immune responses. a. Discuss allergies b. Discuss autoimmune disease c. Discuss exertion, stress, and the immune system d. Discuss immunodeficiency diseases. 6.Discuss evolutionary adaptations of pathogens that underlie immune system avoidance. a. Discuss antigenic variation 4 b. Discuss latency. c. Discuss attack on the immune system: HIV. 7. Discuss Cancer and immunity 45.1 and Overview Vocabulary 1.______________________ A hormone also called adrenaline 2. ______________________Chemicals that are released into the external environment Ductless organs 3. ______________________ Functions in the body as both a neurotransmitter and local regulator 4. ______________________Group of local regulators made of modified fatty acids 5. ______________________ Molecules that act over short distances and reach their target cells solely by diffusion 6. ______________________ Molecules that diffuse a very short distance to bind to receptors on target cells 7. ______________________ Molecules that diffuse from nerve cell endings into the blood stream and travel through bloodstream to target cells 8. ______________________ Network of specialized cells-neurons-that transmit signals along dedicated pathways 9. ______________________ One of two basic systems of communication and regulation throughout the body 10. _____________________ Series of changes in cellular proteins that converts the extracellular chemical signal to a specific intracellular response 11. _____________________ Signaling in which target cells is the secreting cell 12.______________________Signaling in which target cells lie near secreting cell 13. ______________________Stimulate cell proliferation and differentiation 14. _____________________ Stimulates the growth of adult cells, the programmed death of larval cells, and behaviors that bring about motionless pupal stage 15. ______________________Type of molecule (means to excite) 16. Discuss the body’s long-distance regulators 5 17. Discuss how hormones and other signaling molecules bind to target receptors, triggering specific response pathways. A. Discuss intercellular communication 1. Discuss Endocrine signaling 2. Discuss paracrine and autocrine signaling 3. Discuss synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling. 4. Discuss signaling by pheromones B. Discuss Endocrine tissues and organs. C. Discuss Chemical Classes of Hormones D. Discuss Cellular Response and Pathways 1. Discuss the pathway for water soluble hormones 6 2. Discuss the pathway for lipid-soluble hormones E. Discuss multiple effects of hormones. F. Discuss Signaling by Local Regulators G. Discuss coordination of neuroendocrine and endocrine signaling. 45.2 Vocabulary 1. _________________ Disease caused by a deficiency of insulin or decreased response to insulin in target tissues 2. _________________ Gland located behind the stomach 3. _________________ Hormone that promotes release of glucose into blood from energy stores such as liver glycogen, increasing blood glucose concentration 4. _________________ Hormone that triggers uptake of glucose from blood into body cells decreasing blood glucose concentration 5. _________________ Loop in which response reduces initial stimulus 6. _________________ Neurohormone that when circulating stimulates mammary glands to secrete milk 7. _________________ Reinforces stimulus leading to a greater response 8. Discuss how feedback regulation and antagonistic hormone pairs are common in endocrine systems. A. Discuss simple hormone pathways 7 B. Discuss feedback regulation C. Discuss Insulin and glucagon: Control of blood glucose 1. Discuss target tissues for insulin and glucagon 2. Discuss Diabetes Mellitus 47.3 Vocabulary 1.____________________ A block of mesodermal tissue located underneath the ectoderm where the posterior side of the bud is attached to the body 2. ____________________Can develop into different cell types of that species 3. ____________________ Development of an animal’s spatial organization 4. ____________________ Diagrams showing the structures arising from each region of an embryo 8 5. ____________________ Process by which a cell or group of cells becomes committed to a particular fate 6. ____________________ Results in specialization in structure and function 7. ____________________ Tells a cell where it is with respect to the animal’s body axes 8. ____________________ Thickened area of ectoderm at the tip of the bud 9. Discuss how cytoplasmic determinants and inductive signals contribute to cell fate specification 10. Discuss fate mapping. a. Discuss axis formation b. Discuss restricting developmental potential 11. Discuss Cell Fate Determination and pattern formation by inductive signals. a. Discuss the “Organizer” of Spemann and Mangold. b. Discuss the formation of the vertebrate limb c. Discuss cilia and cell fate 9 10