MBA115
advertisement

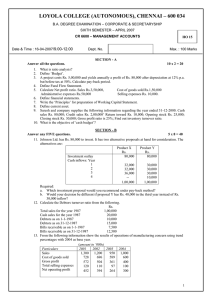
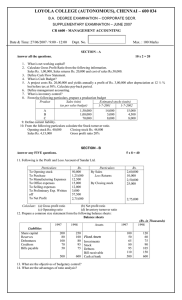
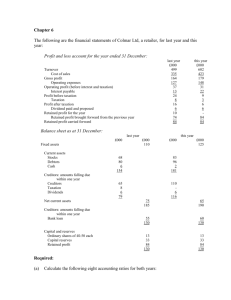
Writing anything except Roll Number on question paper will be deemed as an act of indulging in unfair means and action shall be taken as per rules. Roll No._________________ MBA Semester I MBA 115 – FUNDAMENTALS OF ACCOUNTING MODEL PAPER Time: 3 Hrs MM: 80 Note: 1. All Questions are compulsory in Section A. Section A carries 20 marks. 2. Attempt FIVE questions in all from Section B, selecting ONE question either A of B from each question. Answer of each question shall be limited upto 250 words. Each question carries 6 marks. 3. Attempt 3 questions in all from section C. Answer of each question shall be limited upto 500 words. Each question carries 10 marks. SECTION A Presented below are the balance sheets of R ltd, as at December 31, 2008 and 1. 2009 BALANCE SHEET ASSETS 2008 (Rs.) 2009 (Rs.) Cash and bank balances 6, 00, 000 4, 00, 000 Trade debtors 6, 50, 000 8, 00, 000 Inventory 15, 50, 000 14, 00, 000 Prepaid expenses 80, 000 65, 000 Land 18, 00, 000 15, 00, 000 Equipment 16, 00, 000 20, 00, 000 Accumulated depreciation(2, 50, 000) (3, 00, 000) equipment Building 25, 00, 000 25, 00, 000 Accumulated depreciation(5, 00, 000) (6, 00, 000) building 80, 30, 000 77, 65, 000 LIABILITIES Provision for taxation 1, 00, 000 1, 25, 000 Trade creditors 8, 00, 000 6, 50, 000 Debentures 22, 00, 000 20, 50, 000 Equity share capital 40, 00, 000 43, 00, 000 Retained earnings 9, 30, 000 6, 40, 000 80, 30, 000 77, 65, 000 Additional information: 1. Land was sold for cash at a profit of Rs. 50,000. 2. Dividends paid during the year Rs. 4, 50, 000. 1 3. 4. 5. 6. Net profits for the year Rs. 1, 60, 000. Equipment costing Rs. 6, 00,000 was purchased and paid by cash. In addition equipment costing Rs. 2, 00,000 with a book value of Rs. 40,000 was sold for Rs. 30,000 and cash was received. Debentures were redeemed at face value by issuing shares at par. Amount transferred to provision for taxation during the year Rs. 1,60,000. You are required to prepare a statement of cash flow for R ltd. For the year ended December 31, 2009. SECTION B 2. A Define management accounting. What are the main functions of management accounting? OR B Prepare the formats of trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet. Also mention the items. 3. A Following is the statement of an enterprise for the year ended on 31 march, 2010: Profit and loss account For the year ended on 31 march 2010 Profit and loss account For the year ended on 31 march 2010 Particulars To opening stock To purchases(credit) To gross profit Rs. 2,00,000 16,00,000 Particulars By sales By closing stock 18,00,000 36,00,000 Rs. 32,00,000 4,00,000 36,00,000 to office and admin expenses To selling expenses 4,00,000 By gross profit 18,00,000 2,00,000 By profit on sale of fixed assets 50,000 To other expenses To net profit 50,000 12,00,000 18,50,000 18,50,000 2 Balance sheet as on 31 march 2010 LIABILITIES Rs. ASSETS 2,00,000 equity 10,00,00 Land & shares of Rs. 5 each 0 building General reserve 6,00,000 Plant and machinery P&L a/c 4,00,000 Stock Sundry creditors 4,00,000 Sundry debtors Cash and bank B Rs. 7,00,000 5,00,000 6,00,000 4,00,000 2,00,000 24,00,00 24,00,000 0 Calculate: current ratio, liquid ratio, operating ratio, inventory turnover, average collection period, average payment period, earnings per share. Assume 360 days in a year. OR What do you understand by ratio analysis? Write all the operating ratios. 4. A What are the objectives of preparing cash flow statement? Prepare the format of cash flow statement. OR B The following are the summarized balance sheets of Al ltd. As on 31 December, 2004 and 2005 Liabilities 2004 2005 Assets 2004 2005 Cash at S.creditors 39,000 41,000 2500 2700 bank Bills payable 34,280 11,660 S.debtors 87,490 73,360 Bank 59,510 ---- Stock 1,11,000 97,300 overdraft Provision for Land and 40,000 50,000 1,48,500 1,44,250 taxation building Plant and Reserves 45,000 45,000 1,12,990 1,36,270 machinery Profit and 44,690 46,220 loss Share capital 2,00,000 2,60,000 4,62,480 4,53,880 4,62,480 4,53,880 The following additional information is obtained: 1. During the year ended 2005 an interim dividend of Rs. 26,000 was paid. 2. The assets of another company were purchased for Rs 60,000 payable in fully paid shares of the company. These assets consisted of stock Rs. 21,640 and machinery Rs. 38,360. In addition, sundary purchases of plant 3 were made totaling Rs. 5,650. 3. Income tax paid during the year amounted to Rs.25,000. 4. The net profit for the year before tax was Rs62,530. Prepare the fund flow statement for the year 2005 and changes in working capital. 5. Define following costs with examples: i. Sunk cost ii. Prime cost iii. Opportunity cost iv. Expired cost 5. A Define following costs with examples: i. Sunk cost ii. Prime cost iii. Opportunity cost iv. Expired cos B OR M ltd. Manufactures three products P,Q and R. the unit selling prices of these products are Rs.100, Rs.80 and Rs.50 respectively. The corresponding unit variable costs are Rs.50, Rs.40, and Rs.20. the proportions (quantity wise) in which these products are manufactured and sold are 20%, 30% and 50% respectively. The total fixed costs are Rs. 14, 80,000. Given the above information, you are required to find out the overall break even quantity and the product wise break up of such quantity. 6. A What do you understand by the term “budgetary control”. Enumerate the steps involved in budgetary control system. OR B The following is an extract from the flexible budget of a service department in a manufacturing company: Flexible Budget Units Depreciation of equipment Power Supervision Wages 800 Rs. 600 250 350 60 1000 Rs. 600 275 375 60 1200 Rs. 600 300 400 60 4 Rent Consumable stores Repairs Heat and light Indirect salary 7. 8. 9. 250 150 200 80 400 2340 275 200 225 80 425 2515 325 250 275 120 475 2805 The budg eted activity was 1000 units of service. The actual activity and expenditure during the period were: units 900 Costs (Rs.): Depreciation of equipment 600; Power 302.5; supervision 382.5; wages 60; rent 262.5; consumable stores 180; repairs 220.5; heat and light 70; indirect salary 420. You are required to prepare a report for the variances from budget for each item of expenditure showing which are controllable by the departmental head. SECTION C State the nature of Management accounting and describe its importance. from the given information, make out a balance sheet of M ltd.with as many as details as possible: sales 18,00,000; total assets turnover 3 fixed assets turnover 5 current assets turnover 7.5 inventory turnover 20 debtors turnover 15 total assets to net worth 2.5 debt equity 1 current ratio 1 the summarized balance sheets of S ltd. As on 31-3-2010 and 2011 are given below: Liabilitie 2010 2011 Assets 2010 2011 s Share Fixed 4,50,000 4,50,000 4,00,000 3,20,000 capital assets General Invest 3,00,000 3,10,000 50,000 60,000 reserve ments P&L a/c 56,000 68,000 Stock 2,40,000 2,10,000 Debtor Creditors 1,19,000 92,000 2,10,000 4,55,000 s Provision for 75,000 10,000 Bank 1,00,000 1,55,000 taxation Mortgag -------2,70,000 e loan 5 10,00,00 12,00,00 12,00,000 10,00,000 0 0 Additional information: 1. Investments costing Rs. 8000 were sold during the year for Rs.8500. 2. Provision for tax made during the year was Rs.15, 000. 3. During the year, part of the fixed assets costing Rs 10,000 was sold for Rs.12, 000. 4. Dividend paid during the year amounted to Rs. 45,000. You are required to prepare a statement and sources and uses of cash. 10. Following particulars relate to a manufacturing factory for the month of march,2012: Variable cost per unit Rs.14 Fixed factory overhead Rs.5,40,000 Fixed selling overhead Rs. 2,52,000 Sales price per unit Rs.20 i. What is the break even point in amount and units? ii. How many units must be sold to earn a target net income of Rs. 60,000? iii. How many units must be sold to earn a net income of 25% of cost? iv. What should be the selling price per unit if the break even point is to be brought down to 1,20,000 units? 11. What is budgetary control? Discuss the various principles of budgetary control. 6