Algebra II Pacing Guidance
advertisement

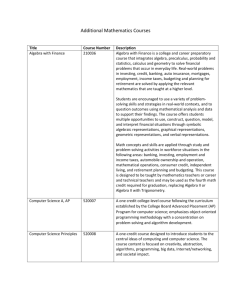
DRAFT Algebra II R Pacing Resources on Engageny.org Polynomial, Rational, and Radical Relationships September 2 –November 13 Algebra II R Checkpoint Assessment 1 Given week of November 9-13 Format: 15 MC, 1-2 pt open, 2- 4 pt open Functions November 16-February 5 Algebra II R Checkpoint Assessment 2 Given week of Jan 25-29 Format: 20 MC, 2-2 pt open, 2- 4 pt open, 1 -6 pt open Inferences and Conclusions from Data January 4 – April 15 Algebra II R Checkpoint Assessment 3 Given week of Apr 11-15 Format: 20 MC, 2-2 pt open, 2- 4pt open, 1 -6 pt open Trigonometric Functions Review April 18 – May 13 May 16-31 Building on their work with linear, quadratic, and exponential functions, students extend their repertoire of functions to include polynomial, rational, and radical functions. Students work closely with the expressions that define the functions and continue to expand and hone their abilities to model situations and to solve equations, including solving quadratic equations over the set of complex numbers and solving exponential equations using the properties of logarithms. The Mathematical Practice Standards apply throughout each course and, together with the content standards, prescribe that students experience mathematics as a coherent, useful, and logical subject that makes use of their ability to make sense of problem situations. DRAFT Algebra II Test Guide Algebra II Overview The content standards associated with Algebra II are based on the New York State Common Core Learning Standards for Mathematics and the PARCC Model Content Framework for Algebra II. The content standards define what students should understand and be able to do at the high school level; the Model Content Framework describes which content is included and emphasized within the Algebra II course, specifically. More information about the relationship between the NYS CCLS and the PARCC Model Content Frameworks can be found in this memo. For high school mathematics, the standards are organized at three levels: conceptual categories, domains and clusters. Algebra II is associated with high school content standards within five conceptual categories: Number & Quantity, Algebra, Functions, Geometry and Statistics & Probability. Each conceptual category contains domains of related clusters of standards. This chart shows the high school mathematics domains included in Algebra II, as well as the corresponding percent of credits on the Algebra II Regents Exam: DRAFT The Regents Examination in Algebra II test will mirror the organization of the standards: Major Clusters will account for a majority (51% - 65%) of the credits on the test, while Supporting Clusters (14% - 28%) and Additional Clusters (19% - 33%) will together constitute less than half the possible credits. DRAFT DRAFT Note: The Standards for Mathematical Practice form an important part of the Algebra II course, as well: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of structure. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. DRAFT For more information about the concepts and terms introduced in the Number and Quantity Domain, consult the Progression The Number System; High School, Number. DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT For more information about the concepts and terms introduced in the Algebra domain, please consult the High School Progression on Algebra. DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT For more information about the concepts and terms introduced in the Functions domain, please consult the High School Progression on Functions. DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT For more information about the concepts and terms introduced in the Statistics & Probability domain, please consult the High School Progression on Statistics and Probability.