Problem HY.2 Questions
advertisement
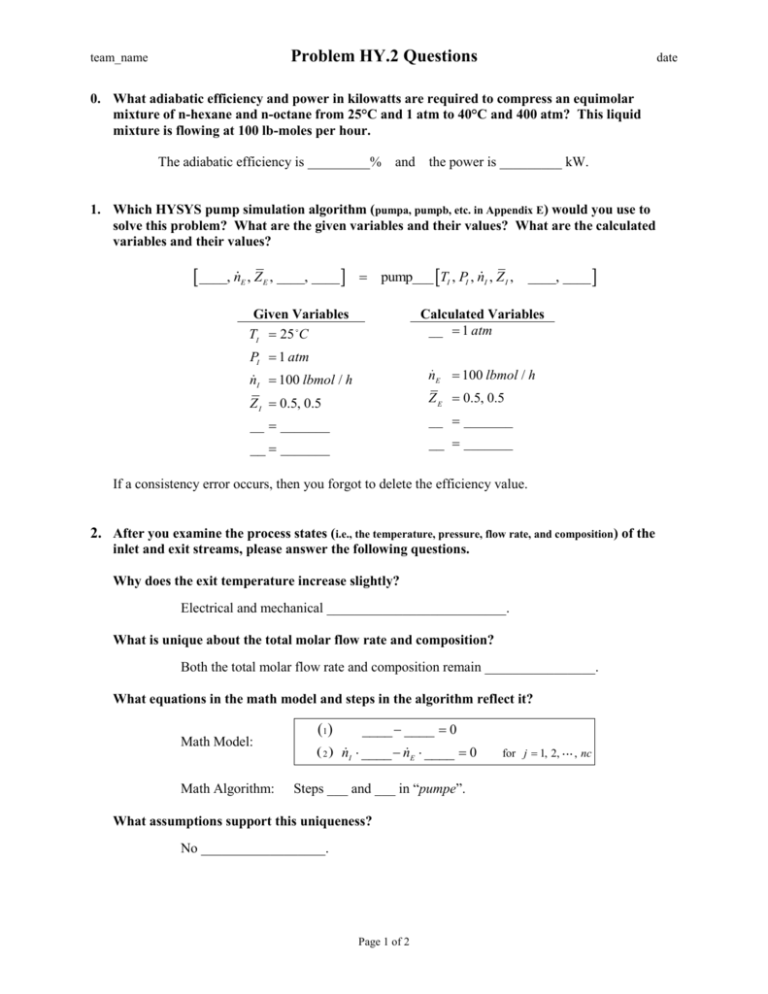
Problem HY.2 Questions team_name date 0. What adiabatic efficiency and power in kilowatts are required to compress an equimolar mixture of n-hexane and n-octane from 25°C and 1 atm to 40°C and 400 atm? This liquid mixture is flowing at 100 lb-moles per hour. The adiabatic efficiency is _________% and the power is _________ kW. 1. Which HYSYS pump simulation algorithm (pumpa, pumpb, etc. in Appendix E) would you use to solve this problem? What are the given variables and their values? What are the calculated variables and their values? ____, n E , Z E , ____, ____ pump___ TI , PI , nI , Z I , Given Variables TI 25 C ____, ____ Calculated Variables __ 1 atm PI 1 atm nE 100 lbmol / h nI 100 lbmol / h Z E 0.5, 0.5 Z I 0.5, 0.5 __ _______ __ _______ __ _______ __ _______ If a consistency error occurs, then you forgot to delete the efficiency value. 2. After you examine the process states (i.e., the temperature, pressure, flow rate, and composition) of the inlet and exit streams, please answer the following questions. Why does the exit temperature increase slightly? Electrical and mechanical __________________________. What is unique about the total molar flow rate and composition? Both the total molar flow rate and composition remain ________________. What equations in the math model and steps in the algorithm reflect it? Math Model: Math Algorithm: 1 ____ ____ 0 2 nI ____ nE ____ 0 Steps ___ and ___ in “pumpe”. What assumptions support this uniqueness? No __________________. Page 1 of 2 for j 1, 2, , nc Problem HY.2 Questions team_name date What are the operating conditions that would invalidate each assumption? Assumption Invalidation continuous process steady state no chemical reaction neglect KE change neglect PE change 5. adiabatic 6. incompressible liquid _____ inlet or outlet stream total flow out is less than the __________ a chemical reaction _____ within the pump inlet and outlet pipe diameters are _______ inlet and outlet pipe heights are _________ significant heat ______ to the surroundings when liquid is significantly ____________ 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. What is the ideal work expressed in units of horsepower? Wideal ___ 100 1 hp 1000 W _____ 100 _____ W 1 kW Wideal ______ kW ______ hp 4. In the math algorithm, what variables are only functions of the material state ( i.e., the temperature, pressure, and composition) of the liquid? I , _____, and _____ 5. What does the assumption of “adiabatic process” imply? Is this a valid assumption? No ______________ to the surroundings. Yes, its value is small compared to the work term. 6. What is the energy relative imbalance (%RIB)? Show your calculations. The energy %RIB equals 100*(energy flow in – energy flow out) / (energy flow in). % RIBEB ___________ Ein 100 _________ kJ/h - _________ kJ/h _________ kJ/h 100 _________ kJ/h % RIBEB _________ % RIBEB Each energy flow value was obtained by copying it from HYSYS and pasting it here. In the HYSYS software, the Mass/Energy Balance page within the Flowsheet/Flowsheet Summary menu provides the relative imbalances for material and energy. Page 2 of 2