Standard 3 Review Worksheet
advertisement

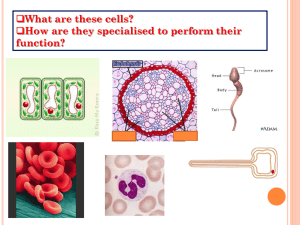
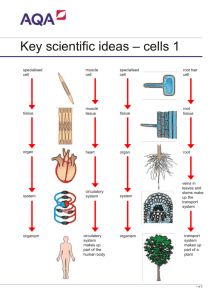
Name ______________________________________ Period _______ Standard 3.1 Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures and perform specific life functions. Objective 1: Observe and describe cellular structures and functions. Living things are made of smaller structures whose functions enable the organisms to survive. The basic unit of structure in all living things is the cell. Cells combine to form tissues that combine to form organs. While all cells have common structures, there are differences between plant and animal cells. Cell details are usually visible only through a microscope. a. Use appropriate instruments to observe, describe, and compare various types of cells. 1. Identify the parts of a microscope (eye piece, coarse adjustment, fine adjustment, stage, arm, base, objective lenses, nosepiece, light source) 2. Recognize cell wall, nucleus and cytoplasm of various types of cells. 3. ____________________________ developed first microscope. 4. ____________________________ was first to see and name cells using his microscope. b. Observe and distinguish the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, chloroplast, and cytoplasm of cells. 1. Cell: Basic unit of all ____________________________ things. a. Two types of cells: b. _____________________________: Don’t have membrane-bound nucleus. c. _____________________________: plant and animal cells, have membrane-bound organelles 2. Recognize key ____________________________ in various cells (cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, chloroplast, cytoplasm, vacuole). 3. Plant Cells: Label the parts of the cell. Circle the names of the parts that are unique to a plant cell. 4. Animal Cells: Label the parts of the cell. Circle the names of the parts that are unique to an animal cell. c. Differentiate between plant and animal cells based on cell wall and cell membrane. 1. ____________________________ cells have cell walls, ____________________________ cells do not have cell walls. 2. Both plant cells and animal cells have ____________________________. d. Model the cell processes of diffusion and osmosis and relate this motion to the motion of particles. 1. ____________________________ is particles moving from a higher concentration to a ____________________________ concentration. 2. ____________________________ is water moving from a higher concentration to a lower concentration across a ____________________________ to maintain the correct balance in a cell. 3. Examples: a. Diffusion: _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ b. Osmosis: _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ e. Gather information to report on how the basic functions of organisms are carried out within cells (e.g., extract energy from food, remove waste, produce their own food). 1. Describe the functions of the following cell parts: a. Nucleus: _________________________________________________________________________ b. Vacuole: _________________________________________________________________________ c. Chloroplast: ______________________________________________________________________ d. Cell membrane: ___________________________________________________________________ e. Cell wall: _________________________________________________________________________ Standard 3.2 Students will understand that the organs in an organism are made of cells that have structures and perform specific life functions. Objective 2: Identify and describe the function and interdependence of various organs and tissues. a. Order the levels of organization from simple to complex (e.g., cell, tissue, organ, system, organism). Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems, organ systems make organisms Cells are the most _____________________________, organisms are most _____________________________ Levels of Organization, from least complex to most complex: cells-_____________________________organs-_____________________________- organism Cell: Basic unit of all living things. a. Two types of cells: b. _____________________________: Don’t have membrane-bound nucleus. c. _____________________________: plant and animal cells, have membrane-bound organelles Tissue: Group of the same kind of cells working together. a. Four types of tissue: _____________________________, _____________________________, _____________________________, _____________________________ Organ: Structure composed of two or more types of _____________________________ working together. o Examples include the stomach, intestines, heart, lungs, skin, bones, kidneys and liver. Organ system: Group of organs that work together to do a certain job. o _____________________________System: Made up of skin, hair. Provides exterior protection. o _____________________________System: Made up of lungs, trachea, and diaphragm. Takes in oxygen, releases carbon dioxide. o _____________________________System: Made up of stomach, intestines. Breaks down nutrients. o _____________________________System: Made up of skeleton. Provides structure and support. o _____________________________System: Made up of muscles. Movement. o _____________________________System: Made up of brain, sense organs, nerves. Carry and interpret messages o _____________________________System: Made up of: thyroid, pituitary. Regulate hormones o _____________________________System: Made up of: heart, arteries. Circulates blood. o _____________________________& Lymphatic System: Made up of: Appendix, lymph nodes. Maintain health. o _____________________________System: Made up of: testes, ovaries. Produce offspring o _____________________________System: Made up of: kidney, colon. Remove waste. Organism: Individual living thing that may be made up of two or more _____________________________systems. o Characteristics of life include movement, growth and development, reproduction, use of energy, cellular structure and chemical makeup, response to stimuli, get rid of wastes. b. Match a particular structure to the appropriate level (e.g., heart to organ, muscle to tissue). Common organs are heart, lung, skin, kidney. Cells are _____________________________cell, nerve cell, plant cell, muscle cell. Organ systems (digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system). Match the term at left to the level of organization: Red Blood Cell Epithelial Liver Dog Respiratory System Organism Organ Cell Organ System Tissue b. Relate the structure of an organ to its component parts and the larger system of which it is a part. _____________________________are made of individual organs that work together towards a common function Organ systems work together for survival of organism Example: circulatory system: heart, veins, arteries, and blood c. Describe how the needs of organisms at the cellular level for food, air, and waste removal are met by tissues and organs (e.g., lungs provide oxygen to cells, kidneys remove wastes from cells). _____________________________provide oxygen to cells, remove carbon dioxide from body _____________________________remove wastes from cells _____________________________breaks down food to provide nutrients to cells _____________________________protects organism from outside, sweat removes wastes through the pores