F212- -Cell_Specialisation
advertisement

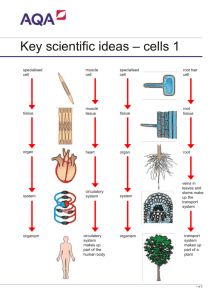
What are these cells? How are they specialised to perform their function? CELL SPECIALISATION Define terms differentiation & specialisation -erythrocytes, neutrophils, epithelial cells, sperm cells, palisade cells, root hair cells, xylem, Phloem & cambium Which organism has the highest surface area to volume ratio? The single celled Amoeba Polar bear or other multi cellular organism Which organism has the highest surface area to volume ratio? The single celled Amoeba 12:8 = 3:2 Polar bear or other multi cellular organism 20:25 Single celled organisms Large s/a: volume All cells exposed to environment Effective exchange surface-for what? All cells perform all functions Multi-cellular organisms Smaller s/a: volume Not all cells in contact with external environment Therefore: Specialised cells to perform different functions Young cell Cell division Cell growth Cell specialisation What is Differentiation When a cell becomes specialised to carry out a particular job/function What categories of differentiation are there? Change number of particular organelle e.g. muscle cell Change the shape of the cell e.g. root hair cell Change some of the contents of the cell e.g. RBC ALL 3!! Mature cell -Unlikely or unable to divide again In your group, split the cells between you. Research your cell. Later you will need to explain your findings to the rest of the group Specialised Cell Erythrocyte Neutrophil Sperm cell Palisade Cell Root hair cell Guard Cell Ciliated Epithelium How the cell is specialised for its function What are tissues, organs and organ systems? Write a definition and an example of the following on the yellow post-its and stick under the appropriate heading: Tissue Organ Organ system . What are tissues, organs and organ systems? Cells make up TISSUES, groups of the same kind of cells performing a common function e.g. xylem and phloem in plants, muscle tissue in animals Groups of different types of tissues are arranged together to form organs e.g. the stomach consists of mucus membrane tissue, muscle tissue, etc Organs are grouped into systems e.g. respiratory system, reproductive system. organ systems consist of a number of organs working together to perform an overall life function . GROUP ESSAY In this question, one mark is available for the quality of spelling, punctuation and grammar. Below is a picture of blood showing both red and white blood cells. Describe how red blood cells, such as those shown in the picture are adapted for their function. (Allow one lined page). [6] Quality of Written Communication [1] [Total 7 marks] Think about the other side of the course too!! 1 haemoglobin/haem, carries oxygen/AW; 2 detail of no. of oxygen molecules carried; 3 small size/large SA:V ratio, so haemoglobin never far from cell surface/AW; 4 flexible/elastic/stretchy/changes shape/AW; 5 small size/‘stretchiness’/AW, allows red cells to, fit/squeeze, into capillaries; 6 biconcave/AW [A ‘dimpled’], gives, increased/AW, surface area relative to volume (for diffusion); 7 no nucleus to maximise room for, haemoglobin/oxygen/AW; 8 contain carbonic anhydrase; 9 describe, the reaction catalysed by carbonic anhydrase/role in maintenance of diffusion gradient/AW; 10 transport of carbon dioxide as carbamino-haemoglobin/CO2 combines with Hb; 11 ref buffering effect; 12 AVP; e.g. further detail of oxygen carriage variable oxidation state of Fe idea that small size allows them to be close to tissue or cells lack of, other/named, named organelles, also increases room for Hb/O2 max 6 13 QWC – legible text with accurate spelling, punctuation and grammar; 1[7]