competency and indonesian qualification framework based syllabus
advertisement

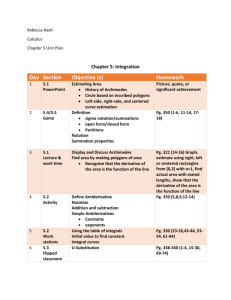
COMPETENCY AND INDONESIAN QUALIFICATION FRAMEWORK BASED SYLLABUS Course Title : Mathematical Economics Coordinator : Prof. Dr. D.S. Priyarsono Course Code : EKO 202/3 (2-3) Semester : even/4 Prerequisite Course : Introduction to Mathematics (MAT 100), Calculus (MAT 103) Short Description : This course is designed to provide knowledge on the concepts, techniques, and problems of mathematics related to economics and its applications. Learning Outcome : After completing this course, students are expected to be able to understand and explain the concept and technique of mathematics and be able to solve mathematics problems, particularly multivariable calculus and dynamics that are commonly used in economic analyses. WEEK 1 EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOME Students can explain matrix and vector, matrix operation, idempotent matrix, partitioned matrix, kronecker products, transpose and inverse INDICATOR 1) Explain matrix and vector 2) Explain matrix operation 3) Explain idempotent matrix 4) Explain partitioned matrix 5) Explain kronecker TOPIC (TEACHING MATERIAL) LEARNING METHOD TIME ALLOCATI ON The concepts and definitions of matrix and vector, matrix operation, partitioned matrix, kronecker products, the concept, definition, and use of matrix transpose and inverse, application examples Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) LEARNIN G SOURCE ASSESSMEN T CRITERIA SCORE WEIGH T (%) (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% products 6) Explain transpose and inverse 2 Students can explain determinant and the basic characteristic of determinant, vector and characteristic root, linear combination and rank, linear equation system, cramer’s rule, and application in economic model 1) Explain determinant and the basic characteristics of determinant, 2) Explain vector and characteristic root 3) Explain linear combination and rank 4) Explain linear equation system 5) Explain cramer’s rule 6) Explain application in economic model 1) Explain linear differential equation order 1 and 2 2) Explain linear difference equation order 1 and 2 3 Students can explain linear differential equation order 1 and 2 and linear difference equation order 1 and 2 4 Students can explain the 1) Explain the characteristics of characteristics of comparative statics, rate comparative statics of change and derivative, 2) Explain rate of derivative and slope of change and Explain the concept and basic characteristics of determinant, vector and characteristic root, explain rank, linear equation system, cramer’s rule as well as the use in solving economic problems. Explain the concept and function of linear differential equation order 1 and 2 and linear difference equation order 1 and 2 Explain the concept of comparative statics and rate of change as well as the illustration. Derivative, derivative and slope of Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Illustratio n, discussio n, and quiz Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% (1), (2). Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and 2.5% curve, the concept of derivative limit and continuity and 3) Explain derivative differentiation function and slope of curve 4) Explain the concept of limit 5) Explain continuity and differentiation function 1) Explain differentiation rule for one-variable function 2) Explain differentiation rule for two or more of the same variable function 3) Explain differentiation rule with different variable functions 4) Explain partial differentiation 5) Explain comparative and static analysis application 6) Explain Jacobian determinant 5 Students can explain differentiation rule for one-variable function, differentiation rule for two or more of the same variable function, differentiation rule with different variable functions, partial differentiation, comparative and static analysis application, and Jacobian determinant 6 Students can explain 1) Explain differential differential, total 2) Explain total differential, differential differential curve. Outline the concept methods, of limit and requirement Tutorial for continuity and differentiation in limit There are several types of differentiation rules, namely the differentiation rules for one-variable function, two or more of the same variable function, different variable function, and partial differentiation (50’x3) Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) The lesson on partial Illustratio derivative allows students n, to do simple comparative discussio Lecture: 1x (50’x2) individual task (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% (1), (2). Written test, Students’ 2.5% 7 rules, total derivative, 3) Explain differential derivative of implicit rules function, and 4) Explain total comparative statics with derivative general function model 5) Explain derivative of implicit function 6) Explain comparative statics with general function model 1) Explain optimum value and extreme Students can explain value optimum value and 2) Explain first extreme value, first derivative test derivative test, second 3) Explain second and and more derivative, and more derivative second derivative test. 4) Explain second derivative test statical problems, but in the models containing general function, because short and explicit solution cannot be obtained, so total differentiation is needed. n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) The most common criteria in the economy usually maximize (profit) and minimize (cost) of a goal. Optimum value is obtained by conducting derivative test on a function. Illustratio n, discussio n, and quiz methods, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) activeness and individual task (1), (2). Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% MID-TEST/UTS (40%) 8 Students can explain exponential characteristics and functions, natural exponential functions and growth issues, the concept and functions of logarithm, and derivative of exponential functions. 1) Explain exponential characteristics and functions 2) Explain natural exponential functions and growth issues 3) Explain the concept of logarithm 4) Explain logarithm functions 5) Explain derivative of exponential functions and This chapter introduces new topic, which is the use of exponential functions. Exponential functions and logarithm functions have close relationship, particularly in regard to growth issues and the dynamics of the economy and more specifically in optimization issues with time variable logarithm functions 9 Students can explain first derivative condition, second derivative condition, square form, and characteristic root. 1) Explain first derivative condition 2) Explain second derivative condition 3) Explain square form 4) Explain characteristic root 1) Explain objective function with more than two variables 2) Explain the second derivative relationship with concave and convex. 3) Explain the application in economics. 10 Students can explain objective function with more than two variables, the second derivative relationship with concave and convex, application in economics. 11 1) Students can explain the method of Lagrange multipliers, second derivative condition, and 2) bordered hessian. Explain the method of Lagrange multipliers lagrangian Explain second derivative condition The use of first and second derivatives surfaces because in the previous chapter optimization is only with one preference variable. So, a method is developed to obtain the extreme value of an objective function that involves two or more preference variables. Therefore, we can handle problems such as multiproduct companies. Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Explain objective function with two variables. The concept of concave and convex can be used to determine the extreme value of a function. This characteristic can be obtained through second derivative test. Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) This chapter discusses the limitation of constraint (for example production quota) where there is a relationship between variables. The new Illustratio n, discussio n, and quiz methods, Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% (1), (2). Written test, Students’ activeness and individual 2.5% 3) Explain bordered hessian 12 13 Students can explain quasy concave and quasy convex, maximum satisfaction and consumer’s demand, and comparative statics analysis. Students can explain integral basic rules, definite integral, indefinite integral, economic application of integral, and Domar’s growth model 1) Explain quasy concave and quasy convex 2) Explain maximum satisfaction and consumer’s demand 3) Explain comparative statics analysis 1) Explain integral basic rules 2) Explain definite integral and indefinite integral 3) Explain the economic application of integral 4) Explain Domar’s growth model optimum level that fulfils production quota requirement is constrained optimization. The solution is through the method of Lagrange multipliers, second derivative, and bordered hessian. The understanding on quasy concave and quasy convex of objective function eliminates the need to check second order requirement. After that, examples of problems are given about maximum satisfaction and consumer’s demand in simple cases (two-good case) until more complex cases. Integral calculus is known as primitive function (basic function) or anti derivative. In the lecture, integral basic rules are introduced and then it continues to integral operation rules. Definite integral is the integral that has specific numeric value (has top and bottom limits), whereas indefinite integral is the contrary. Tutorial task Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) Illustratio n, discussio n, and individual task methods, Tutorial Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% 14 Students can explain non linear programming, Kuhn-Tucker condition, Kuhn-Tucker condition interpretation, constraint qualification, concave programming, and quasy concave programming 1) Explain non linear programming, 2) Explain KuhnTucker condition 3) Explain KuhnTucker condition interpretation 4) Explain constraint qualification, 5) Explain concave programming 6) Explain quasy concave programming This chapter discusses two main topics. The first is non linear programming, which is the extension of controlled optimization technique marked with the involvement of inequality constraint into the problems. The second is the review of classic controlled optimization to discuss several new topics Illustratio n, discussio n, and quiz methods, Tutorial FINAL TEST/UAS (40%) ASSIGNMENT/QUIZ (20%) Reading Sources: (1) Chiang. 2005. Fundamental methods of Mathematical Economics. McGraw-Hill. (2) Sydsaeter, K. & P.J. Hammond, 2005. Mathematics for Economic Analysis. Prentice Hall. Lecturer Team: - Prof. Dr. D.S Priyarsono (K) - Dr. Toni Bahtiar - Dr. Sri Mulatsih - Dr. Yusman Syaukat Lecture: 1x (50’x2) Tutorial: 1x (50’x3) (1), (2) Written test, Students’ activeness and individual task 2.5% - Ir. Farida Hanum, M.S - Ir. Doni Citra Lesmana, M.Sc - Novindra, S.P, M.Si - Andromeda, M.Si - Dicky Firmansyah, M.Si - Indra, M.Si - Izzudin, M.Si - Perdana, S.E ASSESSMENT FORMAT : Exam and Assignment Mid-test (UTS) : 40 % Final test (UAS) : 40 % Assignment/Quiz : 20 %