electricity revision and electrostatics
advertisement

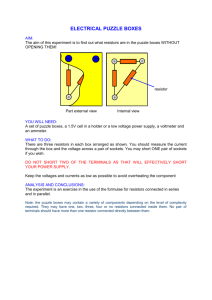
Tutorial Questions 1 to 8 Q = It V = IR Series Parallel I1 = I 2 = I 3 I = I + I2 VT = V1 + V2 + V3 V1 = V2 = V3 RT = R1 + R2 + R3 1 / RT = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 Short cut if resistors are identical, divide by the number of resistors Expt: For the 4 resistors 1. Measure resistance using an ohmmeter. 2. Find resistance using the colour code. Find tolerance. For the 33 resistor measure voltage and current then calculate resistance. ( The maximum current you can use is 0.25 A) Revision P = IV P = V2 ÷ R P = I2R E = Pt Vt Potential divider 2 1 0V Tutorial questions 9 to 20 V1 = R1 VT RT static electricity How is Static Electricity Produced? An atom will usually have the same number of positives and negatives This makes the atom NEUTRAL. Electron (-) Proton (+) Neutron Charging by rubbing TG (HSD) Electric Field – the space around a charge where electric forces can be detected. Field lines show the direction a positive charge would move in. The closer the lines the stronger the force. Electrical potential energy, Ew, is the work done in moving a charge from one point to another. + + + - - Ew = Fd Electrical potential difference, V, is the work done per unit charge. V = Ew÷ Q Therefore 1 V = 1 J/C One volt is when one joule of work is done in moving one coulomb of charge between two points. - A B - + + + Remember total energy is conserved. Work done in moving charge from B to A = Electrical potential energy at A = Kinetic energy at B QV = ½mv2 Tutorial Questions 1 to 8 on page 59 SAQ pages 1 to 8 Purple book Ex 4.7 Gains electrical Ep In battery chemical potential energy is changed to electrical energy. buzzer Loss of electrical Ep Bulb changes electrical energy to light and heat. Resistor changes electrical energy to heat. Heat is dissipated. Buzzer changes electrical energy to sound. Electromotive force, emf ( E ) = gain in electrical energy per unit charge ( in J/C ) Potential difference, pd (V) = loss in electrical energy per unit charge Read SAQ pages 13 and 16 Tutorial Qu 9 to 13