File - Nash, Rebecca
advertisement

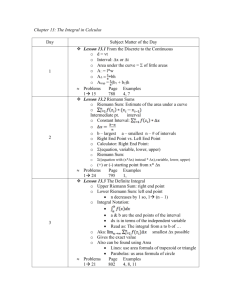
Rebecca Nash Calculus Chapter 5 Unit Plan Chapter 5: Integration Day Section Objective (s) Homework 1 5.1 PowerPoint Picture, quote, or significant achievement 2 5.4/5.5 Game Estimating Area History of Archimedes Circle based on inscribed polygons Left-side, right-side, and centered curve estimation Definition sigma notation/summations open form/closed form Partitions Notation Summation properties 3 5.1 Lecture & work time Display and Discuss Archimedes Find area by making polygons of area Recognize that the derivative of the area is the function of the line 4 5.2 Activity 5 5.2 Work stations 5.3 Flipped classroom Define Antiderivative Notation Addition and subtraction Simple Antiderivatives Constants exponents Using the table of integrals Initial value to find constant Integral curves U-Substitution Pg. 321 (14-16) Graph, estimate using right, left or centered rectangles from [0,3] with n=1, find actual area with stated lengths, show that the derivative of the area is the function of the line Pg. 330 (5,8,9,12-14) 6 Pg. 350 (1-6, 11-14, 1718) Pg. 330 (23-26,43-44, 5354, 61-64) Pg. 338-340 (1-4, 15-30, 69-74) 7 8 Quiz/intro to 5.5 5.5 Group work activity 9 5.6 Lecture & work time 10 5.6 Lecture & work time 11 Review for 5.1-5.6 Test on 5.15.6 12 Quiz Intro to Riemann Display and Discuss Riemann Notation From A to B B to A is the negative of A to B Constants Addition and subtraction Fundamental theorem of Calculus Point b – Point a Definite integral is a bounded indefinite integral Mean Theorem Divide integral by (b-a) to get mean Mean multiplied by (b-a) is the area Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Derivative of integral is the original function Integral of derivative gives rate of change Jeopardy Review Picture, quote, or significant achievement Pg. 360 (13-14, 19-22) Pg. 373 (1-3, 5-8, 13-18) Pg. 374-375 (57-60, 6364)