Water Properties Worksheet: Adhesion, Cohesion & Polarity
advertisement

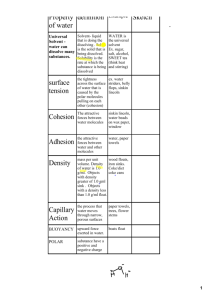
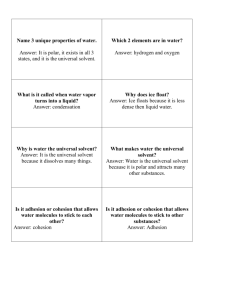
Analyze Water Properties. Name: 1. How does the colored water get into the leaves? Through capillary action. Adhesion & Cohesion. 2. What properties of water allow for this to happen? Adhesion (attracted to other polar molecules) & cohesion (attracted to itself) 3. Why is this important for life? Plants give off oxygen, but need water to live. Without living plants we could not live as we need the oxygen they give off. So, getting water to the leaves, where photosynthesis and oxygen production takes place, is vitally important to all organisms that need oxygen. 4. Why doesn’t oil & water mix? Water is polar, but oil is non-polar & inherently hydrophobic. Being hydrophobic causes oil to run away, so to speak, from water. 5. What property of water creates this scenario? Basically, water being polar causes this to happen. 6. Why is this important for life? Membranes surround all cells and their properties are very important to how our biological systems work. Since they are repelled by water, they are forced to spontaneously form in our water-based bodies. 7. What property allows water to bead up? Cohesion & surface tension. 8. Why is this important for life? Ultimately, surface tension relates to the cohesive properties of water. This is important because it keeps water in fluid form rather than evaporating into the atmosphere. 9. Why can water dissolve so many particles? Because it’s polar. The polar interactions from water with other polar molecules interferes with the solute’s cohesive properties (the attraction to itself that keeps it held together). This breaks the solute down and causes it to be dispersed in the water evenly… dissolved. 10. What property allows water to do this? The polarity of water allows is to be an effective solvent. 11. Why is this important for life? Chemical reactions are much more likely to be completed in aqueous (fluid, specifically water-based) solutions. Considering life is literally a series of complex chemical reactions, life has taken hold and persists best when water is involved. 12. Water will bead up on wax paper but spread out on glass. Explain this. Wax is a lipid, so non-polar. Water doesn’t interact well with non-polar substances so is more likely to interact with itself through cohesion. Glass, on the other hand, is slightly polar so water will interact with itself to an extent, but more with the glass, spreading out in the process. 13. Why does water resist vaporization? Vaporization is caused when molecules in a fluid absorb enough energy to escape the cohesive bonds (hydrogen bonds) that hold in suspension. There are many hydrogen bonds in fluid water that are stronger than the energy absorbed that would otherwise energize the molecules, sending it into the vapor state. 14. Why is this important for life? This property keeps water more likely in its fluid state, maintaining more water in fluid form making it available to be a medium for chemical reactions that support life. 15. How does water react to changes in temperature? Does water heat up quickly or slowly? Due to water’s high capacity to absorb heat and dissipate this in its hydrogen bonds, water resists boiling more than most fluid. 16. Why is this important for life? This helps organisms maintain homeostasis, resisting temperature changes that would otherwise disrupt the natural efficiency of molecules of enzymes, which are temperature-dependent. 17. Draw 10 water molecules, properly oriented, hydrogen bonded to one another. Either using space-filling models (shown left) or structural formulas (right), hydrogen bonds are represented by dashed lines spanning the distance between the negative pole of the oxygen to the positive pole of hydrogen. 18. Some adult insects are unable to swim but are able to walk on top of water. What characteristic of water enables these insects to walk on top of water? A. pH C. atomic bonds B. solvent properties D. surface tension 19. Which term refers to water’s attraction to other substances that have full or partial electrical charges? A. polarity D. solvent B. adhesion E. density C. cohesion 20. Which term refers to water having partial positive charges and a partial negative charge? A. cohesion D. good solvent B. surface tension E. adhesion C. polarity 21. Which term refers to water’s attraction to different substances? A. polarity D. good solvent B. cohesion E. adhesion C. surface tension 22. Which term refers to the fact that water can dissolve polar molecules like sugar or ionic substances like salt? A. surface tension C. polarity B. high heat capacity D. cohesion 23. Which part(s) of a water molecule has/have a partial positive charge? A. the two hydrogen (H) atoms C. the one hydrogen (H) atom B. the two oxygen (O) atoms D. the one oxygen (O) atom 24. Which characteristic of water allows a paperclip to remain “floating” on water when the paperclip is gently placed on top of the water (even though paperclips are denser than water)? A. adhesion D. nonpolar B. surface tension E. inorganic C. solvent properties 25. Plants need to move water from their roots to their leaves in order to perform photosynthesis. The tube system that moves the water is called xylem. What property of water allows water to move up the xylem into the leaves? A. Evaporation C. Specific Heat B. Three phases of water, solid, liquid, or D. Capillary Action gas 26. Water has a high specific heat capacity; this means that it takes a lot of energy to change the temperature of water. Which of the following explains why this is important to life? a. Allow water to boil faster than other substance such as oil. b. Helps organisms to maintain a constant internal temperature. c. Helps organisms maintain an osmotic balance. d. Helps organisms transport substance throughout the organisms.