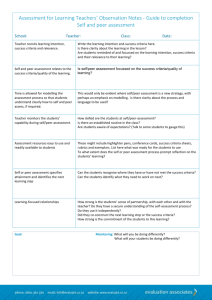
Checklist for designing and implementing self/peer
advertisement

Designing and Implementing Self and Peer Assessment/Evaluation/Feedback Why design and implement self and peer assessment? Falchikov (2007: 139) outlines a useful set of features where peer (and self) involvement in assessment is considered beneficial. These features: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Are designed to enhance learning; Require learners to take responsibility for their actions; Encourage a reflective approach to learning; Require students to identify and apply standards and criteria; Provide some degree of modelling and/or scaffolding; Involve learners in judging their performance or that of their peers – developing and using Sadler’s (1989 and 2005) evaluative expertise, providing, seeking and utilising feedback; 7. Allow learners to practise peer and self-assessment skills in a variety of contexts; 8. Allow fading of support so that learners may move nearer towards assessment autonomy. Checklist for designing and implementing self/peer assessment Once you have decided that your students and unit could benefit from having self and peer assessment tasks/activities, you might find the below list of questions helpful in designing and implementing your task. By answering these questions, you will have designed a plan to implement self and peer assessment task. For example, the following assessment task (described in grey below) is a team based activity where groups of five students are undertaking a project for which they will generate a report and deliver a presentation: Chie Adachi Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B © Deakin University 2015 Document last updated 8 February 2016 Page 2 of 4 # Questions Options Your reasons why and Actions 1 Is the task self- or peer- assessment or both? And why? SelfPeerBoth 2 Is the task aligned well with the intended learning outcomes? Both. Because both self and peer assessment allow students to critically analyse the standards and evaluate themselves and others fairly and accurately. Then students can compare their own ratings/feedback with peers. Yes, I have GLO7 team work aligned with one of my ULOs, therefore peer assessment is a good way to address this. 3 Is the task formative or summative assessment? Deakin Graduate Learning Outcome (GLO) Course Learning Outcome (CLO) Unit Learning Outcome (ULO) Formative Summative 4 Is this task an individual task or team/group task? Individual Team/group 5 What type of work is being evaluated? Written work Team/group work process/skills Team/group work product Knowledge Skills 6 7 Does the task require students to evaluate the KNOWLEDGE of team/group work? or the SKILLS of team/group work? *Note that team/group work SKILLS can only be assessed by people involved in that team/group work (often students themselves). What type of feedback will students give and receive? Qualitative (e.g. comments) Quantitate (e.g. Formative. This assessment involves team work work because students have to work collaboratively to achieve one mutual goal/task (i.e. project execution report and presentation) The evaluation of the process/skills of conducting team work. Actual skills of applying team work principles. Both qualitative and quantitative, but none of it will influence their grades as this task is formative. Chie Adachi Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B © Deakin University 2015 Document last updated 8 February 2016 Page 3 of 4 rating, marks) 8 What are the assessment criteria/rubrics? Feedback sheet (qualitative comments) Rubric (holistic vs analytic) Students Academics 9 Do I create the assessment criteria/rubrics or involve others (students or academic colleagues) to create them (together)? 10 What is the proportion of marks given to students to be responsible? And why? 0-100% 11 Are the individual marks given as well as group marks to students? If so, how are they calculated? 12 Are exemplars/examples of work provided? high/mid/low quality of work samples 13 What skills/knowledge do students need in order to do self and peer assessment/evaluation? Critical thinking Communication Self-management Team work 14 How am I going to facilitate students to learn about: - the assessment design - the rubric/assessment criteria/standards - team/group work Lecture Seminar Tutorial Handbooks/resources Readings Individual marks Group marks Both The first draft I did is an analytic rubric with much room to encourage students to give qualitative feedback, but I am intending to involve students to scrutinise this rubric and construct a rubric together. Students are involved in contributing to create the rubric descriptors because I want them to critically analyse the standards better and learn how to create a fair standard for assessing their peers. I have organised a time to do this exercise with my students in a seminar. 0%. This self and peer assessment is only an opportunity for formative feedback and peer learning. Their marking does not count towards the final grades in my unit. Individual marks are calculated based on the group marks I give – using SparkPlus. But they are given back to students only as formative feedback along with other qualitative feedback/comments. Students engage with three levels of sample work and practise marking against the rubric (high/mid/low quality of work) Students need high level critical thinking skills to understand the standards, apply them and make judgements about their own and their peers’ work. They also need the communication skills to effectively pass on the positive and constructive feedback to their peers. One-hour seminar is allocated to talk about the assessment design, rubric, and principles of team work. Chie Adachi Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B © Deakin University 2015 Document last updated 8 February 2016 Page 4 of 4 - 15 16 conflict resolutions among team members Will students get feedback on the feedback/marking that they give? If so, how? How do students know that they did a good job of self and peer assessment? Feedback on students’ self and peer feedback Comparison of their marking with their tutors/markers Yes, in a one hour tutorial, students will be given feedback by their tutors about their peer feedback responses. What are students supposed to do with the given self/peer feedback? Use the given feedback to improve their future work Students are invited to improve their work based on the given feedback before the final submission. Reference: Falchikov, N. (2007). The place of peers in learning and assessment. In D. Boud & N. Falchikov (Eds.), Rethinking assessment in higher education: Learning for the longer term (pp. 128-143). London: Routledge. Chie Adachi Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B © Deakin University 2015 Document last updated 8 February 2016