InstructionalDesign 290813v3
advertisement

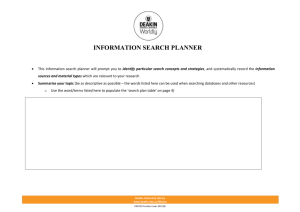
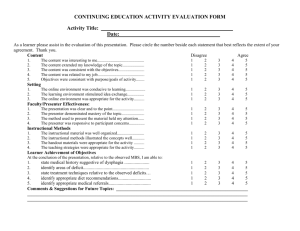
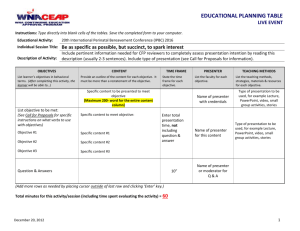
[Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 USING INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN TO PLAN YOUR UNIT Dr Yiong Hwee Teo Learning Innovations 23 Oct 2013 Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B MY BACKGROUND Educator (27 years); BSc(Hons‐Physics)‐Singapore; MEd (Boston U); PhD (Monash U) Portfolios include: • Physics Teacher/high school • Educational Television Producer, Media Specialist, Instructional Designer • Asst Director/Media Development • Asst Director/IT Training – Developed and implemented Singapore’s ICT Masterplans 1‐3; Trained 24,000 teachers how to use technology in teaching and learning • Uni Lecturer – Nanyang Technological University; Monash U; ACU, Deakin U Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 1 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 AGENDA • ADDIE introduction –Needs Assessment • Analysis • Design • Development • Implementation • Evaluation Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B A GENERIC INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN MODEL: ADDIE A Analysis Answers: What is the Performance Goal? D Design Answers: How will Learners accomplish the Performance Goal? D Development Meeting the Objectives I Implementation Delivering the Solution E Evaluation Ensuring Quality Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 2 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 NEEDS ASSESSMENT • What do you want the learners to be able to perform? • What can they perform now? • What are the performance gaps? • Can these performance gaps be addressed by training? • If yes, use ADDIE to develop training package Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B • Needs Assessment NEEDS ASSESSMENT Mager & Pipe, (1984) Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 3 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 NEEDS ASSESSMENT refer to flowchart by Mager & Pipe, (1984) • Question 1: In your workplace, are there performance gaps of colleagues which cannot be addressed by training? • Question 2: In your teaching, are there performance gaps of your students which cannot be addressed by training? Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B ANALYSIS: GOAL • Determine whether there is an instructional problem; then establish goal • A goal is a starting point from which teaching/learning activities are derived • A goal is a general statement of desired instructional outcome that usually can be broken down into a variety of much more specific behaviours Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 4 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 ANALYSIS: GOAL Examples: – Grade 7 students should be able to write an essay of no more than 500 words – Students studying Computer Applications should be able to use MS Office to perform office tasks – Front‐line personnel will demonstrate courteous, friendly behaviour while greeting customers Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B ANALYSIS: GOAL (ACTIVITY) Classify instructional goals by learning domain 1. Open & maintain a cheque account A. Psychomotor skill 2. Name parts of the human body using common terms B. Intellectual skill 3. Separate an egg yolk from C. Verbal Information the egg white, using the D. Attitude shell as a tool 4. Choose to behave safely while flying on airplanes Duration: 5 mins Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 5 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 ANALYSIS • Given a goal, the next step is to perform learner analysis, content analysis and task analysis Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B LEARNER ANALYSIS • What are the characteristics of your learners that you will consider? – General Background and experiences • Age, grade, sex, general experience with world they live in – Knowledge Factors • Prior knowledge, literacy level, level of IT skills – Psychological Factor • Motivational level, ability, learning style (verbal, visual, kinesthetic) – Social Factors • Cultural background, readiness for pair/group work Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 6 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 LEARNER ANALYSIS (THINK‐PAIR‐SHARE ACTIVITY) For the goal, “Students studying Computer Applications should be able to use MS Office to perform office tasks”, state how the following learner characteristics will affect your instruction: – General Background and experiences • Age, grade, sex, general experience with world they live in – Knowledge Factors • Prior knowledge, literacy level, level of IT skills – Psychological Factor • Motivational level, ability, learning style (verbal, visual, kinesthetic) – Social Factors • Cultural background, readiness for pair/group work Duration: 5 mins Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B CONTENT ANALYSIS Breaking subject matter into smaller and instructionally useful units • To identify and isolate single idea or skill units for instruction • To act as an objective decision rule for including or excluding topics from instruction Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 7 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 CONTENT ANALYSIS (EXAMPLE) Goal: Name parts of human body Parts of head 1.0 1.1 scalp 1.2 hair 1.3 ear 1.4 forehead 1.5 eyebrows 1.6 eyes 1.7 eyelids 1.8 cheeck 1.9 … Parts of Arm 2.0 2.1 armpit 2.2 upper arm 2.3 elbow 2.4 forearm 2.5 wrist Parts of Hand 3.0 3.1 back 3.2 palm 3.3 finger 3.4 thumb 3.5 knuckle 3.6 fingertip 3.7 fingernail Parts of trunk 4.0 4.1 shoulder 4.2 collarbone 4.3 chest 4.4 breast 4.5 rib cage 4.6 waist 4.7 … Parts of leg 5.0 5.1 thigh 5.2 knee 5.3 calf 5.4 shin 5.5 ankle Parts of foot 6.0 6.1 heel 6.2 arch 6.3 sole 6.4 toe 6.5 toe joint 6.6 toe nail Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B TASK ANALYSIS • Definition: An intensive examination of how people perform work activities Purpose • To determine components of competent performance • Identify activities that may be simplified or otherwise improved • Determine precisely what a worker must know, do, or feel to learn an activity • Clarify conditions needed for competent performances • Establish minimum expectations Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 8 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 TASK ANALYSIS (EXAMPLE) Task analysis for the goal “Make a video recording” Goal: Make a Video Recording Setup Lights 1.0 Mount camera on tripod 2.0 Operate videocam 3.0 Use diff shot sizes 4.0 Use diff camera movements 5.0 Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B CONTENT ANALYSIS Content analysis differs from task analysis because it stems from an examination of information or knowledge requirements whereas task analysis stems from sequences & procedures in performing work activities to achieve work results. In teaching business topics, you engage in content analysis rather than task analysis most of the time Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 9 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 CONTEXT/ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS • What environments (classroom, computer lab, home) are learners based at? What hardware & software will learners have? • What other tools, plug‐ins are required for the learning package • What internet bandwidth will learners have? • What cost will learners be willing to pay? • What constraints exist? Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B AFTER THE ANALYSES • Do not jump into design • Determine whether there is any existing resources that can be used whole, in part, or with modifications • Design and develop only the unavailable components Question: You found a video clip suitable for your topic but the narration is in Chinese. Can you use it? Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 10 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 DESIGN Create a road map for accomplishing the goals and objectives • Develop the instructional objectives for each task • Sequence and structure the instructional objectives e.g. easy task first • List the entry behaviours that the learner must demonstrate prior to training • Identify the strategies (media, method, tools) • Develop the performance tests to show mastery of the tasks to be trained e.g. written, hands‐on, etc Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B SPECIFIC INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES (SIO) • ABCD model –Audience –Behavior: observable verbs –Conditions –Degree Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 11 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 SIO: OBSERVABLE VERBS Could I observe learner doing this? Avoid ‘understand’ etc (refer ‘actionable verbs for objectives_Teo.doc’) Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Arrange, name, define, order, duplicate, recognize, label, recall, match, repeat, memorize, reproduce Classify, recognize, describe, report, discuss, restate, explain, review, identify, sort, indicate, tell, locate, translate Apply, operate, choose, practice, demonstrate, prepare, dramatize, schedule, illustrate, solve, interpret, use Analyze, differentiate, appraise, discriminate, calculate, distinguish, categorize, examine, compare, experiment, contrast, inventory, criticize, question, diagram, test Arrange, manage, assemble, organize, collect, plan, compose, prepare, construct, propose, create, set up, design, synthesize, formulate, write Appraise, judge, argue, predict, assess, rate, attack, score, choose, select, compare, support, estimate, value, evaluate Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B SIO: A GOOD EXAMPLE Given a bar, line, or circle graph, the seventh‐grade mathematics students will be able to verbally present all the statistical or numerical information shown on the graph with 100% accuracy. Which part is Audience, Behavior, Conditions, Degree? Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 12 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 SIO: A GOOD EXAMPLE Given a bar, line, or circle graph, the seventh‐grade mathematics students will be able to verbally present all the statistical or numerical information shown on the graph with 100% accuracy. Which part is Audience, Behavior, Conditions, Degree? Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B PAIR ACTIVITY REWRITE THE FOLLOWING SIO Students should be able to Do individual mind mapping Brainstorm for ideas with a partner within the group Gather information on the web on a soldier’s life at the battle of Gallipoli Duration: 10 mins Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 13 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 PAIR ACTIVITY (POSSIBLE ANSWERS) • Do individual mind mapping – Given the freemind software, Year 1 Deakin Management students will be able to draw a mind map representing key concepts of chapter 5 of the management textbook with inclusion of graphics and appropriate formatting. • Brainstorm for ideas with a partner within the group – With a partner within the group, Year 1 Deakin Management students will be able to brainstorm ideas for reducing property taxes by drawing a mind map on paper with consideration of the key principles of property management in chapter 6. • Gather information on the web on a soldier’s life at the battle of Gallipoli – Using a search engine and computer, Year 10 students will be able to write a 1000 word essay of a typical soldier’s life at the battle of Gallipoli with the inclusion of snippets of soldier’s activities before and during the war. Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B DESIGN Create a road map for accomplishing the goals and objectives • Develop the instructional objectives for each task • Sequence and structure the instructional objectives e.g. easy task first • List the entry behaviours that the learner must demonstrate prior to training • Identify the strategies (media, method, tools) • Develop the performance tests to show mastery of the tasks to be trained e.g. written, hands‐on, etc Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 14 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 DESIGN SEQUENCING OF TOPICS • Chronological – e.g. history • Order of Performance – e.g. flower arrangement • Known to Unknown – build on pre‐knowledge • Taxonomical – e.g. periodic table in chemistry; taxonomies of human behaviour • Simple to Complex • Easy to Difficult to learn – e.g. easier topics first • Availability of Resources – real world constraints e.g. media, facilities, people Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B DESIGN – IDENTIFY STRATEGIES SELECTING INSTRUCTIONAL METHODS & TOOLS Little Some Much Teacher Support Role Self-directed • • • • • • • • Tutorial software Drill & practice, quiz Web material Simulation, Virtual lab Blogs- reflection Textbooks/Readings/PPT Job aids Learner stories • • • • • • • • • • Case study Workbooks Training manuals Practice exercises, Guided analysis/research • • • • • F2F Discussion/critique Case study Role play Debate Open forum • • • • Lecture F2F Questioning Dialogues Demonstration • Reports • Term papers Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] Collaborative Brainstorming Team work activities Blogs, Wikis Online Discussions Online Critique Multi-User Games, simulations • Peer tutoring 15 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 DESIGN Q. Why is it important to design performance tests before developing the materials? Develop the performance tests to show mastery of the tasks to be trained e.g. written, hands‐on, etc e.g. • Objective 1 – test item 1, test item 2, etc • Objective 2 – no test item? • Test item 5 – does not correspond to any objective? Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B DEVELOPMENT Create the elements laid out in the design stage • List activities that will help learners learn the task • Select delivery method such as videos, handouts, etc • Review existing material so that you do not reinvent wheel • Develop the instructional course • Synthesize courseware into a viable training program • Validate instruction to ensure it accomplishes all objectives Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 16 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 DESIGN Importance of learning guide (c) Justin Ferrer • Paste a deakin unit guide eg Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B DEVELOPMENT Refer to Template learning guide.doc Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 17 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 IMPLEMENTATION Deploy the training • Create a lesson plan for conducting the training • Conduct the training Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B IMPLEMENTATION Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] Refer to ‘Guide to lesson plan.doc’ 18 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 IMPLEMENTATION Gagne’s 9 events of instruction 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Gain attention Inform learners of objectives Stimulate recall of prior learning Present the content Provide learning guides Elicit performance (practice) Provide feedback Assess performance Enhance retention and transfer to the job Refer ‘Gagne nine events of instruction.doc Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B EVALUATION Measure whether the training works and goals have been achieved • Review and evaluate each phase (analyse, design, develop, implement) to make sure goals are accomplished • Perform external evaluations e.g. observe that the tasks that were trained are being performed by the learner on the job • Revise or modify training when necessary and to make it better Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 19 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 EVALUATION MAJOR TYPES • Formative vs Summative • Process vs Product Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B Refer Formative evaluation checklist_expert reviewers.doc FORMATIVE EVALUATION Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 20 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 SUMMARY EVALUATION • Criterion‐referenced tests, Performance tests, Case studies, Simulation, Attitude questionnaires, Interview questionnaires, Observation checklists Example: criterion-referenced test Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B AN INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN MODEL Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 21 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 In summary, Instructional Design Process Needs Assessment A Analysis • Can performance gaps be addressed by training? • • List Performance Goal/s Conduct learner analysis, content analysis, task analysis, environment anaylsis Design instructional objectives Sequence, structure objectives List entry behaviours Identify strategies, methods, tools Develop performance tests D Design • • • • • D Development • • • • List activities Select delivery method Review existing material Develop course I Implementation • • Create lesson plan Conduct training - Gagne’s 9 events of instruction E Evaluation • • Formative vs Summative Product vs process Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B REFERENCES • Rothwell & Kazanas (2004) Mastering the instructional design process • Dick, L. Carey, and J. Carey (2006) The systematic design of instruction Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 22 [Add presentation title, presenter name here] 4/12/2013 Thank You! Please fill in Evaluation Form Instructional Design Consultation yiong.teo@deakin.edu.au Deakin University CRICOS Provider Code: 00113B [Add Presenter contact details here] 23