Section 7.1 Reading worksheet
advertisement

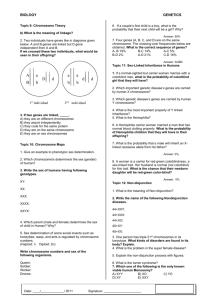
Name _______________________________________ Section 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype Date __________________ Main Ideas: Two copies of each autosomal gene affects phenotype Males and females can differ in sex-linked traits Vocabulary: Carrier Sex-linked gene 1. Remembering back to mitosis and meiosis, how many chromosomes does a normal human have? _____ Below is a karyotype of a human male and then a human female. A karyotype is a picture of the chromosomes in a cell. Chromosome pairs # 1 – 22 are called autosomes or body chromosomes while the last two are known as sex chromosomes. Male Female 2. How many autosomes does a normal male have? ______ Female? _______ 3. What is the term for the XY and XX chromosomes shown on the above karyotypes? ________________ 4. How is cystic fibrous inherited? 5. What is the term for someone who has a gene for the trait but also has a normal gene? ______________ 6. Some traits on carried on the X sex chromosome and not the Y sex chromosome. These traits are called: 7. What type of sex chromosomes do males have? _______ Females? _______ 8. If you are a male, who gave you your X chromosome? _______ Your Y? _________ 9. If you are a female, who gave you your X chromosomes? _____________ & _____________ 10. Look at the image of the X and Y chromosomes. What do you notice about the size of the X to the size of the Y sex chromosome? 11. What happens when there is a gene on the top of the X chromosome say for colorblindness and there isn’t one on the Y chromosome (because it is too short)? What if mom gave you a gene for colorblindness and you are a male? Could dad give you the dominant normal gene to save you from colorblindness? Unmatched area – no homologous genes present on the Y chromosome 12. If you are a male who is colorblind, who gave you the colorblind trait? 13. Let’s try a problem: In humans, colorblindness is inherited on the X chromosome and is recessive. The gene for normal color vision is dominant. Sex counts with these problems so put the genes on the top of the X chromosome. Do not put anything on the Y because it is too small N = Normal color vision gene n = Colorblind gene Cross a female who is a carrier of the gene (XNXn) with a normal male (XNY) XN Xn a. What is the probability of them having a son who has the colorblind gene (n) on his X chromosome XN and is therefore colorblind? ______% b. What is the probability of them having a colorblind daughter? She will need two colorblind genes to be Y colorblind? _______%