Genetics II notes and practice
advertisement

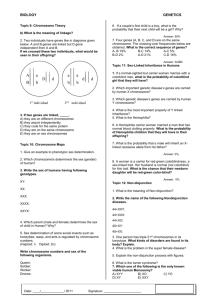
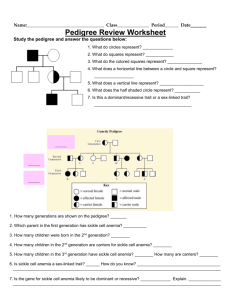
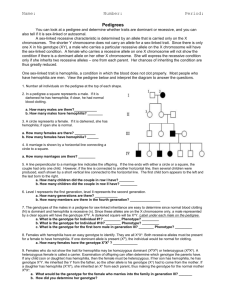
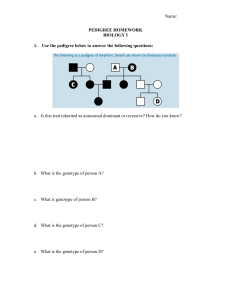
Genetics II – Applications of Genetics Karyotype – Cells are photographed during _________ when chromosomes are fully visible and they are grouped together in ____________. Human gametes have _____ chromosomes while human somatic cells have ____ chromosomes. Autosomal Chromosomes – NOT a ____ chromosome (pairs # _____) Sex Chromosomes – determine the organism’s _______ (pairs # ____) Male vs Female What are the odds of having a girl baby? _____ A boy baby? ______ Which person: mom or dad determines the sex of a baby? Practice: Use the karyotype to the right to answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. Is the baby a male or female? _________ What syndrome is shown? ___________________ Which chromosome pair is affected? _______ Is the affected chromosome pair an autosomal or sex chromosome pair? ____________________ 5. What type of mutation happened to cause this syndrome? ________________________ 6. Name two ways that chromosomes get arranged for a karyotype. Pedigree Chart – Used to help predict hereditary diseases. = ________ = _________ or = affected individual or = carriers Practice: Albinism which causes a lack of pigment in the skin, is a recessive trait disorder. Use the pedigree chart to the right to answer the following questions. 1. Fill in the pedigree to the right using (AA, Aa, aa). 2. Go in and half shade in any male or female who is Aa (not outwardly affected but a carrier of albinism). 3. How many grandchildren does the original first generation couple have? _______ 4. Of those grandchildren how many are boys? ______ 5. Does the original first generation couple have any great grandchildren affected with albinism? _______ 6. How many males on here are carriers of albinism? _____ Females? ______ Sex-Linked Genes – located on the ___________ chromosomes. All the disorders we will study are found on the ____ chromosome because it is larger and carries more genes unlike the Y chromosome. Males: Since males only have one X chromosome they will… Females: In order for a female to express a sex-linked gene they must… Example: ________________, ______________________, & ____________________ Practice 1: Hemophilia is a sex-linked trait on the X chromosome. Hemophilia is caused by a recessive allele so N = Normal and n = hemophilia. Since hemophilia is sex-linked remember a woman will have an allele on both of her X chromosomes while a man will only have one allele on his X chromosome. 1. A woman who is heterozygous (a carrier) for hemophilia marries a normal man. What are the genotypes of the parents? __________x ___________ 2. Make a Punnett square for the above cross. 3. What is the probability that a child (boy or girl) will have hemophilia? ________ Practice 2: In humans, the gene for normal color vision (C) is dominant to the gene for red-green color blindness (c). The trait is sex linked on the X chromosome. Cross a colorblind male to a heterozygous normal color vision female. 1. The genotype of the parents is: ____________x___________ 2. What is the probability that you have a normal vision baby girl? ______ A normal vision baby boy? ________ 3. What is the probability that you have a colorblind baby girl? _________ A colorblind baby boy? ________ Practice 3: Sex-linked pedigree practice. Color-blindness in humans is caused by recessive sexlinked allele. Use the pedigree to answer the following questions. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is the genotype of individual 3? _________ What is the genotype of individual 8? _________ What is the genotype of individual 16? ________ What is the genotype of individual 1? _________ What is the relationship of individual 10 to individual 3? ________ 6. What is the relationship of individual 15 to individual 2? ________ Practice 4: Create your own pedigree on a separate sheet of paper to turn in remembering that Colorblindness is a sexlinked recessive trait. Ray and Elaine were married in 1970. They both had normal vision. They had 2 daughters and then a son. Both daughters, Alicia and Candace, had normal vision and never had any children of their own. The son, Mike, was colorblind. The son married Beth who also had normal vision and they had 2 children of their own, first Greg then Victoria. Victoria was colorblind, but Greg was not. Make sure to use the appropriate shapes Put the names AND genotypes under each shape. Color the individuals the following colors: o Red = Colorblindness White = Normal vision o Blue = individuals with regular vision but are carriers Green = unknown genotype.