Chapter 11: Human Heredity
advertisement

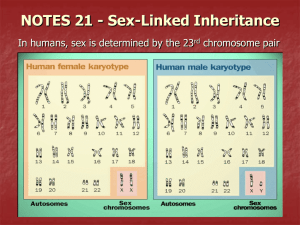
Chapter 11: Human Heredity Section 3: Sex-Linked Inheritance Sex-Linked Inheritance Genes that are located on the _______________________________________ of an organism are inherited in a sex-linked pattern As in many organisms, the sex in humans is determined by the __________________________________________________ In females, meiosis produces _________________________ that contain one _______________________________ and ______________________________ In males, meiosis produces ___________________________ of which ____________________ contain one X chromosome and 22 autosomes The sex of a person is determined by whether an egg cell is fertilized by an Xcarrying sperm or a Y-carrying sperm The Human XY System Although meiosis is a precise mechanism that separates the two sex chromosomes of a diploid cell into single chromosomes of haploid gamete cells, errors sometimes do take place The most common of these errors is ____________________________________ Nondisjunction is the failure of chromosomes to separate properly during one of the stages of meiosis Nondisjunction Disorders Roughly __________________________________ is affected by an abnormality involving nondisjunction of the sex chromosomes o ____________________________________________ Female in appearance but their female sex organs do not develop at puberty and they are sterile ___________ or __________________ o ____________________________________________ Male in appearance, and they, too, are sterile ____________________ What can we learn from these abnormalities of the sex chromosome? o An X chromosome is absolutely essential for survival o Sex seems to be determined by the _______________________________ __________________________ of a Y chromosome and not by the number of X chromosomes o The Y chromosome contains a gene that _______________________________ the male pattern of growth during embryological development If this gene is absent, the embryo follows a female pattern of growth Sex-Linked Genetic Disorders Genes that are carried on either the X or the Y chromosome are said to be _____________________________________ In humans, the small Y chromosome carries very few genes The much larger X chromosome contains a number of genes that are vital to proper ___________________________________________________ Recall that males have one X chromosome Thus all X-linked alleles are expressed in males, even if they are recessive In order for a recessive allele to be expressed in females, there must be two copies of it Colorblindness Colorblindness is a recessive disorder in which a person cannot distinguish between certain colors Most types of colorblindness are caused by sex-linked genes located on the X chromosome The alleles for colorblindness render people unable to make some of the pigments in the eye necessary for color vision Most common is ___________________________________________________ In humans, color vision depends on the varying sensitivity of three groups of specialized ________________________________ in the retina of the eye One group is sensitive to _________________ light, one to _____________ light, and one to _____________________ light Colors of any given shade excite a specific level of activity from each of the three groups of nerve cells Because the gene for color vision is carried on the X chromosome, the dominant allele for normal color vision is represented as ____________ and the recessive allele for red-green color blindness is represented as ____________ Homozygous (ZCZC) and heterozygous (XCXc) females have _________________ color vision A female who is heterozygous for colorblindness is said to be a _______________________ because she carries the recessive allele but does not express it Although she is not colorblind, she is capable of passing on the allele for colorblindness to her offspring Only homozygous recessive females _____________________ are colorblind Because males have only one X chromosome, they are either colorblind (XcY) or have normal color vision (XCY) Hemophilia Another recessive allele on the X chromosome produces a disorder called hemophilia, or ________________________________________ In hemophilia, the protein ______________________________________ (AHF) necessary for normal blood clotting is __________________________ People with hemophilia can bleed to death from minor cuts and may suffer internal bleeding from bumps or bruises Hemophilia can be treated by injecting AHF isolated from donated blood Muscular Dystrophy Muscular dystrophy is an inherited disease that results with the progressive wasting away of ______________________________________ Children with muscular dystrophy rarely live past early adulthood The most common form of MD is caused by a defective version of the gene that codes for a muscle protein known as ____________________________ This gene is located on the X chromosome Researchers are now using molecular techniques to _______________________ ________________________________________ of the dystrophin gene into muscle cells Sex-Influenced Traits Many traits that may seem to be sex-linked, such as male pattern baldness, are actually caused by genes located on ____________________________, not on sex chromosomes Why then is baldness so much more common in men than it is in women? Male pattern baldness is a ____________________________________________ A sex-influenced trait is a trait that is caused by a gene whose __________________________________ differs in males and females