HNC Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering (Sept 2014)
advertisement

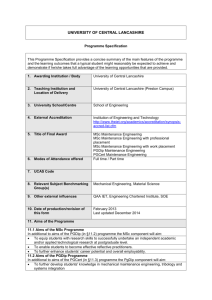
8. Appendices 8.1 Programme Specification UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL LANCASHIRE Programme Specification This Programme Specification provides a concise summary of the main features of the programme and the learning outcomes that a typical student might reasonably be expected to achieve and demonstrate if he/she takes full advantage of the learning opportunities that are provided. 1. Awarding Institution / Body University of Central Lancashire 2. Teaching Institution and Location of Delivery Burnley College 3. University Department/School School of Engineering 4. External Accreditation None 5. Title of Final Award Higher National Certificate in Mechanical & Manufacturing Engineering 6. Modes of Attendance offered Part Time 7. UCAS Code N/A 8. Relevant Subject Benchmarking Group(s) QAA Engineering 9. Other external influences Not applicable 10. Date of production/revision of this form February 2014 11. Aims of the Programme To provide a sound, intellectually demanding, vocational learning experience for students so that they can develop the competencies necessary for a range of technical and management careers in engineering. To provide flexibility, knowledge, skills and motivation as a basis for progression to graduate, post-graduate and professional body status. To develop students’ abilities to consider aspects of problems associated with engineering principles, applications and techniques through the systematic use of appropriate methods for analysing, synthesising and evaluating, and to integrate, where possible these discrete aspects of engineering activity included above. To develop a range of skills, including communicating, planning, implementing, appraising and self-development. To provide programmes of study in specific activities in engineering which are appropriate to the requirements of national and local industry. To provide programmes of study which contribute to the student's developing personal, intellectual and practical skills in addition to fulfilling their vocational needs thereby improving the students employability. To provide a programme with sufficient academic content that subsequent awards represent a level of attainment satisfactory to the engineering profession, industry and student. To ensure that the student is aware of the Higher Technician Engineer's responsibilities to the engineering profession, industry and society. To develop in students a high level of expertise in a particular field and a broad base of skill and knowledge from which they can adapt themselves to change. To create the interest, motivation and intellectual grounding which can provide the basis for further study. To utilise the previous training, education and continuing industrial experience wherever possible, and to relate and interpret such experience in the light of student's studies To enable the students to appreciate the effects of globalisation in the manufacturing sector. A disciplined treatment of the concepts of information technology, pertinent to the fields of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering. Application of these concepts to the analysis, design and development of engineering systems. Specialist studies in area of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering relevant to the student's requirements. 12. Learning Outcomes, Teaching, Learning and Assessment Methods A. Knowledge and Understanding e.g. A1. Understand the principles of mechanical and manufacturing engineering A2. Describe and illustrate the scope, context and significance of the role of operations management A3. Identify a range of applications of mechanical and manufacturing engineering A4. Define the role of an engineer/designer in a multidisciplinary engineering team Teaching and Learning Methods Year 1 includes lectures, seminars, individual assignments with a small number of group assignments. Each week, students spend time in the student workshops in order to develop direct experience of manufacturing processes. Year 2 includes individual and team assignments and projects of increasing complexity some involving the use of software such as Inventor & MasterCam. The Project and Design modules will develop the students’ understanding of the role of the Engineer in an industrial and commercial context. Assessment methods Year 1 includes workbooks, reports, small assignments and formal examinations. Year 2 includes reports, oral presentations, group work, individual working, designing, manufacturing, portfolios and associated commentaries, and the use of technology associated with design and manufacture such as CAD and operations software. The assessment scheme includes the flexibility for students to influence the design of their assignments by suggesting the product/application that they will study B. Subject-specific skills e.g. B1. apply appropriate design, analysis and synthesis skills in engineering B2. to specify, plan and manage a project B3. independently develop their own technical proficiencies and skills to solve engineering problems in the future B4. apply mechanical and scientific principles to given engineering problems B5. develop managerial strategies encountered in the workplace Teaching and Learning Methods Year 1 involves the introduction of engineering principles, design activity and technology to be related to range of applications through formal lectures, seminars, tutorials, workshop and technical activities. In Year 2 there is an increasing emphasis on integrating the aspects within design from physical laws to manufacturing organisation and methods through the direct introduction of work associated with the processes within the Product Design Cycle. Formal lectures, seminars, individual and team assignments and projects are used together along with work based assignments. Assessment methods Year 1 includes workbooks, reports, oral presentations and small assignments and formal examinations. Year 2 includes reports, oral presentations group and individual working. There are a small number of examinations. Both individual and group presentations are used. C. Thinking Skills e.g. C1. apply appropriate knowledge skills and competences in an engineering context C2. formulate and produce creative and innovative technical solutions to problems by applying engineering principles to real and simulated situations C3 evaluate alternative solutions to engineering problems C4 recognise the broader aspects of engineering in the business and industrial environment Teaching and Learning Methods Year 1 introduces engineering concepts and the use of learning outcomes in the curriculum. The approach is relatively direct and requires students to decompose engineering (design, organise and manufacture) and technical problems. Formal lectures supported with seminars and practical tests are used in the ‘scientific’ modules. The ‘technology’ modules use a more ‘hands-on’ approach using workshops, drawing rooms, CAD facilities, external visitor and student presentations. Year 2 provides increasing integration across the modules – this is particularly so of the Project and Design modules, which aims to develop thinking skills from all the modules in a manufacturing engineering context. Assessment methods Year 1 includes reports on practical experiments, assignments, formal examinations and workbooks and drawings. Year 2 uses broader assessment methods to require students to demonstrate integration across modules and disciplines and problems. These include formal reports with reflections on practical tests, designs, and CAD models. D. Other skills relevant to employability and personal development e.g. D1. communicate technical ideas accurately, persuasively and succinctly in a variety of appropriate formats. D2. work independently on significant sized projects relevant to the field D3. locate, use, and critically evaluate information from a number of sources, including the use of ILT based information sources D4. manage resources and time effectively Teaching and Learning Methods Teaching and learning methods include lectures, tutorials, laboratory work, directed selfstudy, and assignment research work. As the course progresses, there is greater emphasis on independent learning, and resource and time management. Assessment methods The assessment methods develop as students progress through the course with a change in the balance from the testing of specific learning outcomes in a direct manner to requiring students to develop the material used for reflection and commentary in the form of written reports. This emphasis enables and requires students to develop skills through the development of the relationship between competences and the work-based environment. 13. Programme Structures* 14. Awards and Credits* Level Module Code Module Title Credit rating Level 4 BE 1501 Analytical Methods (e) 20 Level 4 BE 1502 Engineering Science (e) 20 Level 4 BE 1401 Mechanical Principles (e) 20 Level 4 BE 1402 CADCAM (op) 20 Level 4 BE 1403 Statistical Process Control (op) 20 Level 5 BE 2721 Operations Management A (e) 20 Level 5 BE 2502 Project (e) 20 Level 5 BE 2504 Manufacturing Processes (e) 20 Level 4 BE 1507 Engineering Design (op) 20 Level 4 BE 1404 Project Management (op) 20 Level 4 BE1405 Advanced Material Technology 20 Higher National Certificate Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering Requires 160 credits at level 4 or above. Including 40 at level 5 e = essential op = optional * Delete rows not applicable to this Programme Specification 15. Personal Development Planning Personal Development Planning (PDP) is: Reflection on learning, performance, and achievement Planning for personal, educational, and career development. PDP involves review and reflection involving academic study, extra-curricular activities and career planning. It results in an understanding and ownership of learning. The student will be introduced to PDP during tutorial sessions which should be seen as an opportunity to develop a plan for the whole of the student’s time at University. Since learning is a lifelong process the work in PDP is not assessed. There are many similarities to work-based learning, and Continued Professional Development (CPD) - which is required for membership of professional societies. The skills in PDP are key components of employability – self-reflection, recording, target setting, action planning and monitoring. Web based materials relevant to PDP are found at: Personal Development Planning www.uclan.ac.uk/ldu/resources/pdp/intro1.htm Skills Learning Resources www.uclan.ac.uk/lskills/TLTP3/entersite.html There is also information available which can be located using a web search engine. Getting Started With PDP Early in Semester 1 the student will access the Personal Development Planning web page (above). At this stage the student will be working with the first FOUR sections. The student is recommended to read the information, and where there is an activity or exercise to: Download the files, and open them in Word (or another word processor) Fill them out on-line, and print out the finished version, OR Print out the blank page and fill in by hand. The four sections to complete are titled: Introduction Self Awareness Study Skills Reviewing Progress The results of the activity or exercise are best kept together in an A4 folder. A paper based system is suggested, due to concerns about the security, privacy, and long-term accessibility of records. To provide evidence of the student’s work with these materials, the student is invited to complete a Review Record. This is used by the student in the discussions within the Tutor group and also with the student’s meeting with their Personal Tutor. During the tutorial sessions there will be discussion around PDP elements and in particular anything the student may have found difficult, or in which he/she needs assistance. Alternative approaches may be considered and discussed, if the student has particular issues. By the end of their studies, the student is advised to have completed and reviewed all the activities and exercises. 16. Admissions criteria Programme Specifications include minimum entry requirements, including academic qualifications, together with appropriate experience and skills required for entry to study. These criteria may be expressed as a range rather than a specific grade. Amendments to entry requirements may have been made after these documents were published and you should consult the University’s website for the most up to date information. Students will be informed of their personal minimum entry criteria in their offer letter. ‘A’ Level Normally a student will have a least one A Level pass in either Mathematics or Physics, with supporting passes at GCSE Grades A* to C in an appropriate Science or Technology subjects. Mathematics must have been passed at GCSE. An additional Science or Technology subject must have been studied at 'A' Level. BTEC BTEC Diploma / Extended Diploma in an Engineering discipline with at least a full Merit profile - including merit in Maths Mature Student Mature students who do not fall into one of the above categories will be invited to attend an informal interview at which their previous learning, industrial experience, needs and aspirations can be thoroughly explored. If it is felt that they are in a position to benefit from the course, they will be offered a place. If it is felt that they are not yet ready to enter Stage One, they will be counselled as to the most suitable means of preparing for future entry. 17. Key sources of information about the programme Fact Sheet Student Handbook Course Rational Burnley College Website: http://www.burnley.ac.uk/ http://www.qaa.ac.uk/academicinfrastructure/benchmark/honours/engineering.pdf http://technology.uclan.ac.uk/cms/html/fusion_pages/index.php?page_id=30 18. Curriculum Skills Map Please tick in the relevant boxes where individual Programme Learning Outcomes are being assessed Programme Learning Outcomes Module Level Code Module Title Core (C), Compulsory (COMP) or Option (O) Knowledge and understanding LEVEL 5 LEVEL 4 A1 BE 1501 Analytical Methods C BE 1502 Engineering Science C BE 1401 Mechanical Principles C BE 1402 CADCAM O BE 1403 O BE 1507 Statistical Process Control Engineering Design BE 1404 Project Management O BE1405 Advanced Materials Technology Operations Management A Project O BE 2721 BE 2502 O A3 B1 B2 B4 B5 C1 C2 C3 C4 D1 D2 D3 D4 Thinking Skills B3 A4 C C A2 Subject-specific Skills Other skills relevant to employability and personal development BE 2504 Manufacturing Processes C Note: Mapping to other external frameworks, e.g. professional/statutory bodies, will be included within Student Course Handbooks