Light Notes
advertisement

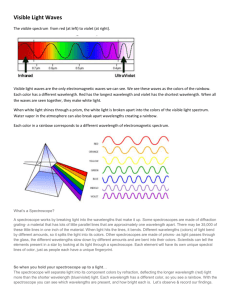
Light Notes Light is electromagnetic energy that travels in waves. Light sometimes acts like millions of tiny particle, and sometimes it acts like a transverse wave. Label: wavelength, crest, trough, amplitude, midline How Light Moves Light travels in waves. It travels in a straight line. Light travels as a transverse wave. When it hits an object it can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted. As light moves, the particles transfers energy Radiation – the transfer of energy as EM waves The Speed of light The speed of light is 300,000 km/s. All electromagnetic waves travel at this speed when in a vacuum. The Colors of Light Different light waves have different wavelengths. Our eyes interpret different wavelengths as different colors. Shortest wavelength – violet Longest wavelength - red White light – what is seen when all the wavelengths get mixed in equal proportions A prism – a tool used to separate the wavelengths of light Your Eyes Only register 3 colors – red, green, and blue They are called the primary colors. All other colors we see are just a mixture of these three The Visible Spectrum As wavelength decreases frequency increases. Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that we can see. ROY G. BIV - an acronym to help you remember the colors in the visible spectrum. Colors of visible light red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet The Electromagnetic Spectrum - the range of frequencies possessed by electromagnetic waves Mnemonic to remember the order of the EM spectrum waves: (Pick one from the PowerPoint or make your own) Raul’s Mother Is Visiting Uncle Xavier’s Garden Rabid Monkeys In Velvet nderpants eXcrete Goo Gate X Usually Lets In Most Radiation - this one is backwards – gamma to radio Wavelength Comparison Write in a comparison of sizes in the box below for the wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. Each wave is larger than or smaller than the object listed below: Radio waves: microwaves: infrared: visible light: ultraviolet: > _________ < _________ < _________ < __________ < _________ soccer field baseball cell bacteria virus X-ray: < __________ waer molecule gamma ray: < ________ atom What are examples of things we use today for each of the wavelengths of the EM spectrum? Radio: TV, radio, cell phones & cordless phone signals Microwaves: cook food, Doppler Radar, police radar Infrared: heat treatment for illness, pictures in the dark of body heat, TV remote control Visible (light): rainbow colors, laser, LED lights, fiber optics Ultraviolet: suntan, kill bacteria & viruses, detect forgeries for paintings X-ray: see broken bones, look for hidden bombs Gamma ray: kill cancer cells & sterilize Too Much EM? The sun is the primary source of EM radiation Our atmosphere acts as a shield to most of the dangerous EM waves Remember: High frequency = more energy More energy = more dangerous Interactions of light and matter 1. Transmitting light Transmitting light or allowing light to pass through Transparent – objects that can be seen clearly through Examples: water, glass, air - Translucent – transmit some light, but do not allow light to travel straight through; The image appears foggy or fuzzy - Examples: frost, chiseled or frosted glass, tissue paper 2. Absorbing light Absorption is the transfer of light energy into matter - Opaque – materials that do not let any light pass through them - Ex. Bricks, rocks, paper 3. Reflecting light Happens when light strikes an object and bounces off Examples: mirror or other shiny surface An object must be opaque in order to reflect light 4. Refraction – bending of waves that occur when light changes its medium Examples: Observing fish in water, prism, pencil in cup of water 5. Diffraction – bending of waves around a barrier Examples: Radio waves moving around buildings, fuzzy edges around a shadow. 6. Scattering – occurs when light is sent in many directions as it passes through a medium Light Interactions: Draw and label the wave patterns for the following terms: absorbed, reflected, refracted, scattered, transmitted transmitted absorbed scattered refracted reflected Interference When two or more waves combine to make a new wave Can make the wave stronger (constructive interference) or weaker (destructive interference). Examples: interference patterns in space tell scientists about the location of other stars and galaxies. Wave pool – in some places the waves come together to make a bigger wave, and some places they flatten each other out.