EM Spectrum Notes: Electromagnetic Waves Explained
advertisement

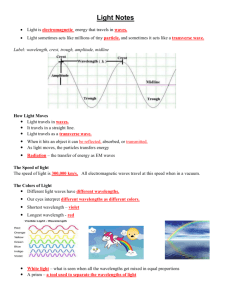
Electromagnetic (EM) Spectrum Notes Electromagnetic spectrum is…. All the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic wave is a wave that can travel through a vacuum, like space, and is made up of both electric and magnetic fields. Electromagnetic radiation is created in stars, like our sun, and travels through space. EM’s Identify Crisis Scientific studies of electromagnetic waves conclude that in some situations, electromagnetic waves act like a particle, and sometimes they act like a transverse wave. How Electromagnetic (EM) waves move EM radiation travels in waves. Radiation - the transfer of energy as EM waves EM radiation travels in a straight line through a vacuum, like space, but will slow down and travel at different speeds when it enters a medium, like air, water, or dirt. EM radiation travels as a transverse wave. Speed of EM Waves EM waves travel very quickly, at the speed of light – 300,000 km/s. EM waves reach from the sun to Earth in about 8 minutes. All waves in the EM spectrum travel at this speed when in a vacuum. The Colors of Visible Light Different light waves have different wavelengths. Our eyes interpret different wavelengths as different colors. The longest wavelength is red. The shortest wavelength is violet. White light - what is seen when all the wavelengths get mixed in equal proportions. A prism – a tool used to separate the wavelengths of visible light. Your Eyes… Only recognize or see 3 colors – red, green, and blue. These are called the primary colors of light. All other colors we see are just a mixture of these three – this is different than what you are used to when mixing paints. Visible Light Spectrum As wavelength decreases frequency increases. Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum we can see and it is the smallest part of the entire spectrum. ROY G. BIV - an acronym to help you remember the colors in the visible light spectrum. Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet - Remember, some people aren’t including indigo in the visible light spectrum any more. The Electromagnetic Spectrum Visible light is just one type of radiant energy. There is a lot of energy that travels in waves that we can’t see. The Electromagnetic Spectrum – the range of frequencies possessed by electromagnetic waves. Mnemonic to help you remember the order of the EM waves from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength. Rabid Monkeys In Velvet Underpants eXcrete Goo - or make up your own! EM Uses Radio – TV, radio stations, cordless phone signals, airplane communications Microwaves – cell phones, cook food, Doppler Radar (weather), police radar Infrared – TV remote control, heat treatments for illness, night vision goggles to see body heat Visible Light – fiber optics, mirrors & lenses, flashlights, light bulbs, LED bulbs, lasers for laser pointers for surgery and cutting things Ultraviolet – suntan, kill bacteria & viruses, detect forgery, black light to find blood and saliva X-ray – see broken bones, look for hidden objects at airports Gamma rays – kill cancer, sterilize, smoke detectors, check for leaks in the welds of pipes, determine the width of metal sheets, create energy in nuclear fission power plants Too Much EM? The sun is the primary source of EM radiation here on Earth. Our atmosphere acts as a shield to most of the dangerous EM waves Remember: o High frequency = more energy o More energy = more dangerous