Study Guide for Chapter 12 and 13 Name: : Class:______ The
advertisement

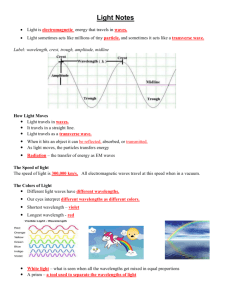
Study Guide for Chapter 12 and 13 Name:_______________Date:_________________ Class:_______ The Electromagnetic Spectrum________________________________________________________________ 1. The entire range of electromagnetic wave frequencies is known as the ___electromagnetic spectrum______________________. 2. What is the speed of the different waves of the electromagnetic spectrum? they all travel at the speed of light 3. How are electromagnetic waves produced and what type of fields surround these waves? They are produced by a vibrating electric charge. An EM wave consists of electric fields and magnetic fields that are present in a wave at right angles to each other. 4. What word is used to describe the number of waves passing per second? frequency 5. Arrange the electromagnetic spectrum in order from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength. Radio wave, microwave, infrared wave, visible light, ultraviolet light, x ray, gamma ray 6. What type of wave has the highest frequency of all and what type of wave is closest to it? Gamma rays have the highest frequency. They are next to x rays. 7. What type of wave has the longest wavelength? Radio waves. 8. Next to each type of wave, name two key features that can help you identify it. Radio – very long wavelength, low frequencies, used for communications Microwave – used for communications, also used for cooking. Infrared – transmit heat, used for remote controls and night vision goggles Visible light – ROYGBIV colors, represent the visible spectrum that people can see Ultraviolet light – harmful to skin, used to kill bacteria x-rays – used for medical/dental imaging and airport security Gamma Rays – harmful to tissue, but used for cancer treatment, short wavelength, high frequency 9. Arrange the waves in order from low frequency to high frequency. Draw a transverse wave below the names to show the change in frequency. Radio micro infrared visible light ultraviolet x-ray gamma ray 10. What type of waves produce thermal energy? infrared 11. Arrange the colors of the visible spectrum in order from lowest frequency to highest frequency: Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet Light_________________________________________________________________________________ 12. Describe the difference between reflection and refraction. Reflection – light hits a surface and bounces off of it Refraction – light travels from one medium to another medium where the speed of light is different. Because of the difference in the speed of light in the two media, the light bends (refracts). 13. Describe the following terms or draw a diagram showing how each relates to light: transparent- most light passes through, little light is reflected or absorbed translucent- some light passes through, some light is reflected and absorbed opaque- no light passes through, all light is reflected or absorbed absorbed- light enters an object but does not pass all the way through reflected- light bounces off of an object regular (specular) reflection- mirrors, shiny reflection diffuse reflection- rough surfaces reflect light, but because they are rough, the reflected light scatters randomly light ray- a narrow beam of light that travels in a straight line photon- a particle that carries radiant light energy mirage-an image of a distant object created by bending light rays 14. Label the primary colors of the spectrum in the diagram to the right. After labeling, what colors would be at each letter in the middle F- yellow H white Gmagenta K- cyan 15. What are the primary pigment colors? Cyan, magenta, yellow red green blue 16. What color is produced when you combine all the different pigments? black 17. What color would be reflected by the following objects? Color Reflected Colors Absorbed Green shirt green all others Red apple red all others Blue sky blue all others 18. What is the order of colors, from least refracted to most refracted, after passing through a prism: Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet 19. What is the primary function of the retina and what is the difference between rods and cones? Retina- collects light and transmits it to the brain Rods- detect motion and are used in dim light Cones- detect color 20. Define six different ways of producing light: next to each, name a way it is used and how light is produced Incandescent lights- electricity is passed through a tungsten filament which glows from the heat. Used in common light bulbs for household lighting Fluorescent lights- tube is filled with gas, and when electric current is passed through the tube, the gas glows and gives off light Neon Lights- similar to fluorescent lights, but different gases are used to produce different colors Sodium Vapor lights- a tube contains neon, argon, and sodium metal. When electricity passes through, the sodium vaporizes and gives off light. Used for streetlights. Tungsten-halogen lights- tungsten filament in gas gets very hot when electricity is passed through it and produces a bright light. Used for car headlights. Lasers- a beam of coherent light, used in medicine, CD players, … 21. Describe the difference between coherent and incoherent light. Draw a picture of each next to the words below. Coherent light- waves are all in phase with each other Incoherent light- wave phases are all out of sync 22. Describe fiber optics and what makes fiber optic technology so efficient for carrying light and communication signals. Fiber optic cables are hollow cables that are lined with mirrors. Light passes through cables by “Total Internal Reflection”. Fiber optic cables are efficient because they are small, lightweight, and light signals travel through them with very little interference. Light is just reflected along the inside of the cable.