Lesson 3 Light Notes
advertisement

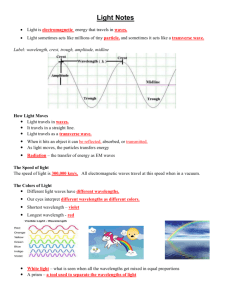
Chapter 12 Lesson 3-Light Vocabulary 1. Wavelength- 2. Photon- 3. Translucent- 4. Image- 5. Refraction- 6. Prism- 7. Spectrum- 8. Electromagnetism- Notes What is light? Light is made of vibrating electric and magnetic energy. o This energy travels as a wave. o It has both frequency and amplitude. Light waves vibrate in the direction perpendicular to the direction of their motion. o Transverse Waves Light does not depend on compressions or rarefactions. o Can travel with or without a medium. In a vacuum, light travels very fast (300,000 km/s or 186,000 miles/s). Travels slowly through mediums like air, water, or glass. Scientists think that nothing travels faster than light. o Speed of light may be the speed limit of our universe. When you multiply the wavelength of a wave by its frequency, you get the speed of that wave. Light is also a particle. o Light travels in straight lines called light rays. o Does not have mass, but does have momentum. o Particles of light are called photons. o Energy of a single photon is very small. Photon of red light is 0.0000000000000000003 Joules of energy. o Each photon acts like a wave with frequency. o Higher frequency has more energy. How does light make shadows? Scattering-when light strikes an object’s surface causing photons to bounce off at random angles. Absorbed objects gain energy. o Transformed into heat. o Darker objects absorb more light than lighter objects. Light may pass through objects. o These objects are transparent. Objects that blur light as it passes through are translucent. Objects that allow little to no light through are opaque. Whether an object is opaque, translucent, or transparent depends on its material, thickness, and color of light. Opaque and translucent objects block light. o Area behind these objects is darker (they have a shadow). Shadows are just the absence of light. When an object is between a light source and another object, it will cast a shadow on the other object. Light from the sun travels toward you at a small angle. o Takes a long distance for the light to hit the ground behind you. o As the sun rises, the angle of the sunlight increases and your shadow become shorter. Shadows depend on the angle and distance between a light source and an object, and between the object and the place where the shadow is cast. The closer a light source is to an object, the larger the shadow an object will cast. How does light bounce and bend? Light reflects off a mirror like sound echoes off a cliff. Reflection is just the organized scattering of a wave. Law of reflection o The angle of an incoming light ray equals the angle of the reflected light ray. An image in a flat mirror appears to be behind the mirror. Mirrors that curve in are concave. o Form many kinds of images. Mirrors that curve out are convex. o Ex: upright, upside down, enlarged, reduced. Always produce images that are upright and reduced. When you place an object in a glass of water, it appears to bend. o It is the light from the object that is bending. When light changes mediums it also changes speed. When light changes speed, they refract. Refraction is not very noticeable with sound waves. o With light waves you see it easily. Rays entering a denser medium bend to make a steeper angle with the surface. Rays leaving a denser medium bend in the opposite direction. Lenses use refraction to shape images. o Used in eyeglasses to make objects appear in focus. o Used in cameras and telescopes. The size and location of the image depend on where the object and lenses are in relation to each other. Why do we see colors? Our eyes see light waves with different wavelengths as different colors. Visible light waves with longer wavelengths look red. Visible light waves with shorter wavelengths look violet. All the colors in between have wavelengths in the middle of those two. White light is actually just a collection of many different wavelengths mixed together. Different wavelengths of light will reflect and refract at different angles. o This is why when white light is refracted by raindrops it is spread out into a rainbow. You can separate light using a prism. Whether an object scatters, absorbs, or transmits light may depend on the wavelength of the light. When light hits an opaque object it is scattered and/or absorbed. o Objects appear the color of light that they scatter. o Absorb all other colors of light. Translucent object o Some colors are absorbed and others pass through. Translucent objects o Appear the color of the light that passes through them. o Absorb all other colors of light. The picture on a color television is made up of red, green, and blue dots of light. o We can create any color of light by mixing red, green, and blue light in the right amounts. o Red, Green, and Blue are called primary colors of light. o If mixed equally, they will produce white light. Magenta, cyan, and yellow are often used to create color by scattering. Magenta scatters only red and blue. Cyan scatters only blue and green. When the two are mixed, magenta absorbs cyan’s green, and cyan absorbs magenta’s red. o Together they only scatter blue. (The color they share) Is all light visible? Light is made of electric and magnetic waves that can move through space. Light is just a form of electromagnetic radiation. Different forms of electromagnetic radiation all travel at the speed of light and can move through a vacuum. They differ in wavelength and energy. Together they make up the electromagnetic spectrum. The sun can produce all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Most of the radiation from the sun is infrared, visible and ultraviolet light. Solar flares give off all forms of electromagnetic radiation when they erupt.