Vocabulary for Chapter 17 – EM waves
advertisement

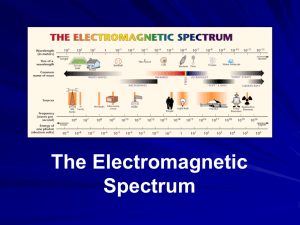
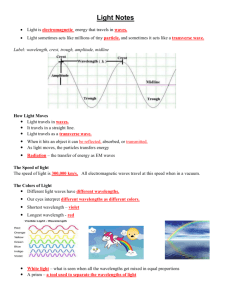
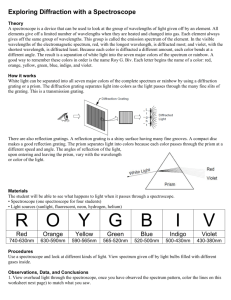
Vocabulary for Chapter 17 – EM waves 1. electromagnetic wave – A disturbance that transfers energy through a field. 2. radiation – energy that moves in the form of EM waves. 3. EM spectrum – the range of all EM frequencies known. 4. radio waves – EM waves that have the longest wavelengths, the lowest frequencies, and the lowest energies. 5. microwaves – EM waves with shorter wavelengths, higher frequencies, and higher energy than other radio waves. 6. infrared light – part of the EM spectrum consisting of EM frequencies between microwaves and visible light. 7. visible light – part of the EM spectrum that human eyes can see. 8. ultraviolet light – part of the EM spectrum consisting of frequencies above those of visible light and partially below those of x-rays. 9. x-rays – part of the EM spectrum with frequencies between ultraviolet and gamma rays. 10. gamma rays – part of the EM spectrum that has the highest frequencies and energies. 11. incandescence – the production of light by materials at high temperatures. 12. luminescence – the production of light without the high temperatures needed for incandescence. 13. bioluminescence – production of light by living organisms. 14. fluorescence – when a material absorbs EM radiation of one wavelength and gives off EM radiation of another. 15. transmission – the passage of an EM wave through a medium. 16. absorption – the disappearance of an EM wave into the medium. 17. scattering – the spreading out of light rays in all directions because particles reflect and absorb the light. 18. polarization – the quality of light in which all of its waves vibrate in the same direction. 19. prism – a tool that uses refraction to spread out the different wavelengths that make up white light. 20. primary colors – the three colors of light---red, green, and blue----that can be mixed to produce all possible colors. 21. primary pigments – three colors of substances ---cyan, yellow, and magenta---- that can be mixed to produce all possible colors.