Introduction to Genetics Notesheet
advertisement

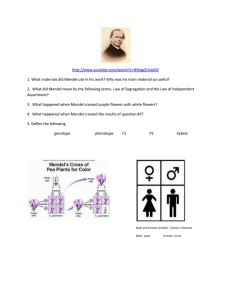
Introduction to Genetics Notes Name: Biology 5.0 Date: Period: Activating Prior Knowledge: 1. Name the two stages of cell division. 2. This process divides the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. 3. This process divides the cytoplasm of the cell. 4. Identify three differences between mitosis and meiosis. 5. Identify an advantage and a disadvantage for sexual and asexual reproduction. 6. Distinguish between the following terms: chromatid, centromere, chromatin, and chromosome. 7. This is the name given to a cell with one set of chromosomes. 8. This is the name given to a cell with two sets of chromosomes. 9. Name the two gametes produced during meiosis. 1 Section 11.1: The Work of Gregor Mendel Who is known as the father of heredity? What did he use for his experiments? Why? Chapter 11 Vocabulary 1) Heredity 2) Genetics 3) Fertilization 4) Self-Pollination 5) Traits 6) Cross-Pollination 7) Alleles 8) Genotype 9) Phenotype 10) Dominant 11) Recessive 12) Homozygous (Purbred) 13) Heterozygous (Hybrid) 2 Terms to know for Genetic Crosses: Generation Description P F1 F2 Mendel drew two conclusions from his experiments with pea plants. Mendel’s Conclusions: 1. 2. Segregation and Independent Assortment Segregation Independent Assortment Segregation and Independent Assortment happen during the formation of . Applying Mendel’s Principles Probability: Probability = _______________________________________________ 3 Examples: 1. What is the probability of a coin coming up heads as the result of a single toss? ______ 2. What is the probability of obtaining a six from a single roll of the dice? ______ 3. What is the probability of drawing the Queen of spades from a deck of playing cards? ______ 4. If two coins were tossed, what is the probability of both of them coming up heads? ______ 5. What is the probability of drawing a two from a deck of cards? ______ 6. If four coins were tossed, what is the probability of all of them coming up heads? ______ 7. If six quarters, two dimes, and eight nickels were in a jar, what is the probability of you reaching in and pulling out a quarter? ______ 8. If the names of all the students in this class were placed in a hat, what is the probability of the first name that is pulled out is a boy? ______ 9. If a dime, quarter, and a nickel were tossed at the same time, what is the probability of all coins coming up heads? ______ 10. What is the probability of drawing a face card from a deck of cards (excluding jokers)? ______ 11. If a family has three sons, what is the probability that their fourth child will be a girl? ______ 4 How To Make a Punnett Square for a One-Factor (Monohybrid) Cross: Step in the Process Example 5 How To Make a Punnett Square for a Two-Factor (Dihybrid) Cross: Determine what alleles are found in the possible gametes each parent could produce. Example Parents: Determine the phenotypic ratio of the possible offspring. (You will not need to determine the genotypic ratio of a dihybrid cross.). 6 Other Patterns of Inheritance – Section 11.3 What are some exceptions to Mendel’s principles? Some alleles are Many genes exist in several different forms, and are therefore said to have Many traits are produced by the Type of Inheritance Description Example(s) Incomplete Dominance Codominance Multiple Alleles Polygenic Traits 7 Genes and the Environment The characteristics of any organism are not determined solely by the genes that organism inherits. Genes provide a plan for development, but how that plan unfolds also . The of an organism is only partly determined by its Example: 8