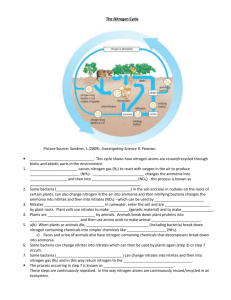
Nitrogen Cycle Activity

Nitrogen Cycle
Plants cannot utilize atmospheric nitrogen so it should be converted into utilizable form such as ammonia.
Without Nitrogen, plants are stunned, yellow and die.
The atmosphere is 78% Nitrogen.
Dead
Animal/
Waste
(org. N
2
N
2
)
NH
3
Ammonia
NO
2
Nitrites
N
2
Animal
NO
3
Nitrates
Plant
(protein)
Cut and glue the descriptions and name in the right place on the cycle.
THESE ARE SCRAMBLED. CUT THEM OUT
INDIVIDUALLY AND GLUE THEM ONTO THE
CYCLE CORRECTLY.
Word Description
Ammonification
Denitrification
Nitrification
Nitrogen
Assimilation
Nitrogen
Fixation
The process of absorbing
Nitrates and Ammonia into
Organic nitrogen, usually when it is consumed by animals.
The process of converting organic nitrogen into ammonia when animals die and are decomposed by bacteria or fungi. Ammonia is also produced in excretions by animals.
Ammonia is converted into
Nitrites by one bacteria that are converted into Nitrates by another nitrifying bacteria.
Nitrates are converted into molecular nitrogen through
Nitric oxide by denitrifying bacteria. It is released into the atmosphere and soil.
Maintains equilibrium of nitrogen in the atmosphere by releasing back.
Conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into Ammonia for living organisms by bacteria such as Rhizobium. It is carried out by leguminous plants.
THESE ARE SCRAMBLED. CUT THEM OUT
INDIVIDUALLY AND GLUE THEM ONTO THE
CYCLE CORRECTLY.
Word Description
Ammonification
Denitrification
Nitrification
Nitrogen
Assimilation
Nitrogen
Fixation
The process of absorbing
Nitrates and Ammonia into
Organic nitrogen, usually when it is consumed by animals.
The process of converting organic nitrogen into ammonia when animals die and are decomposed by bacteria or fungi. Ammonia is also produced in excretions by animals.
Ammonia is converted into
Nitrites by one bacteria that are converted into Nitrates by another nitrifying bacteria.
Nitrates are converted into molecular nitrogen through
Nitric oxide by denitrifying bacteria. It is released into the atmosphere and soil.
Maintains equilibrium of nitrogen in the atmosphere by releasing back.
Conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into Ammonia for living organisms by bacteria such as Rhizobium. It is carried out by leguminous plants.