Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle
advertisement

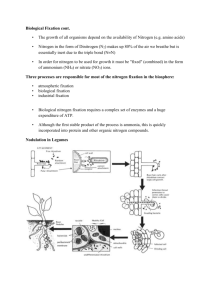
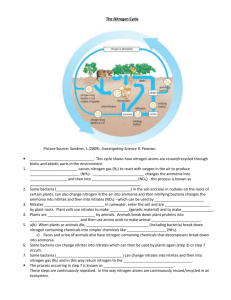
Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle Learner Outcomes • You should be able to describe the sinks sources and exchange for carbon • You should be able to describe the impact of different types of fossil fuel and their relation to atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations • Your should be able to describe the basic nitrogen cycle and which component of it humans have had the most impact Carbon Dioxide • Sources • Sinks • exchange Trends in Atmospheric Concentrations and Anthropogenic Emissions of Carbon Dioxide Carbon Cycle • Major storage or sink is ocean • Other sources are biomass, soil, rock/sediment • Transferred/released to atmosphere Units Gigatons Fluxes are Gigatons/year Practices that release/uptake Carbon Dioxide Release • Burning of fossil fuels • Deforestation • Cement manufacturing • Volcanic gases Uptake • Reforestation • Absorption into ocean • Uptake by biological processes (corals, shells) How is organic carbon stored in sediments and rocks? • Fossil fuels are concentrations of peat, coal, oil, and natural gas. • 1 unit of coal produces approximately • 1.5- 2X amount of CO2 as petroleum, • and 2X CO2 as natural gas A peat bog in western Ireland World Carbon Dioxide Emissions by Region, 2001-2025 (Million Metric Tons of Carbon Equivalent) Nitrogen Cycling • • • • Fixation Decay Nitrification denitrification Nitrogen Cycle: Source and Fixation • Air is major reservoir (source) • Most organisms cannot use N2 so they have to “fix” it – Nitrate ions (NO3-) – Ammonia (NH4 ) – Urea (NH2 ) 2CO Nitrogen Cycle: Fixation • Atmospheric fixation (lightening strikes) 5-8% of total nitrogen fixed • Biological fixation-certain microbes or symbiotic relationship with some plants and animals • Industrial-make ammonia, urea and ammonium nitrate. Nearly 50% of total nitrogen fixed Nitrogen Cycle: Decay • Following biological fixation: nitrogen passes through the food chain • Waste product decays and is broken down into ammonia Nitrogen Cycle: Nitrification • Remember ammonia? • Taken up by plants directly or converted into nitrates/nitrites by nitrifying bacteria • Nitrites (NO2-) • Nitrates (NO3-) Nitrogen Cycle: Denitrification • Bacteria reduces nitrates to nitrogen gas • Replenishes the atmosphere • Question: Can denitrifiers keep up with agricultural impact on nitrogen fixation? Nitrogen Cycle