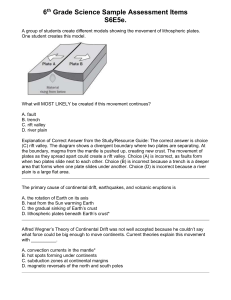
Unit 1B Practice Worksheets
advertisement
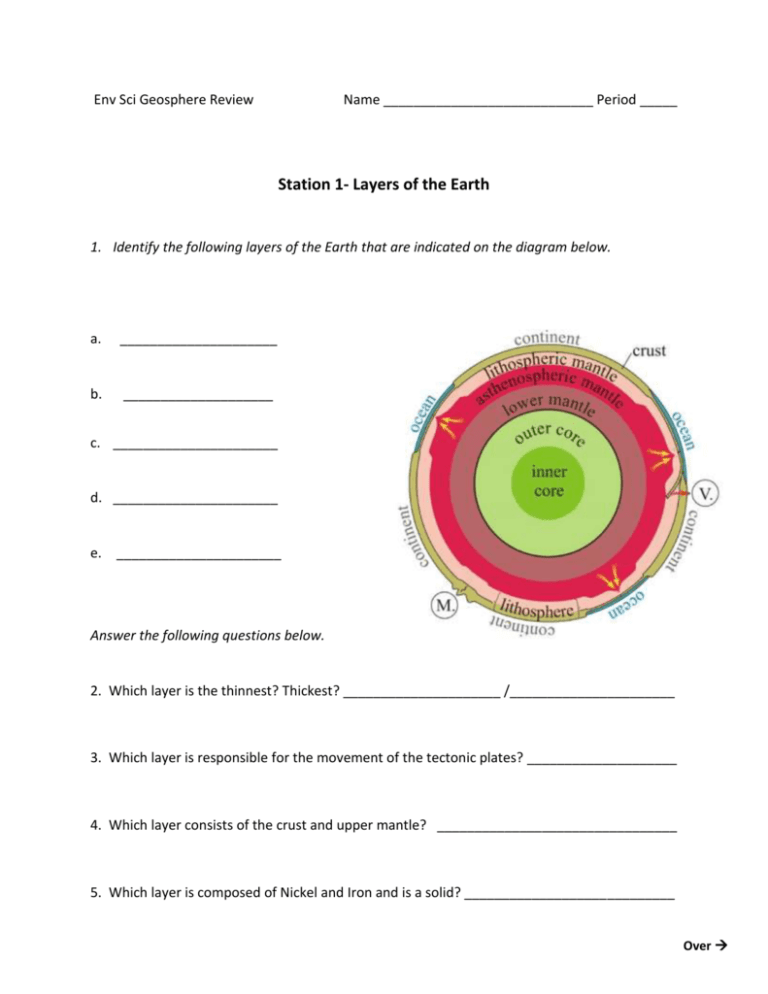
Env Sci Geosphere Review Name ____________________________ Period _____ Station 1- Layers of the Earth 1. Identify the following layers of the Earth that are indicated on the diagram below. a. _____________________ b. ____________________ c. ______________________ d. ______________________ e. ______________________ Answer the following questions below. 2. Which layer is the thinnest? Thickest? _____________________ /______________________ 3. Which layer is responsible for the movement of the tectonic plates? ____________________ 4. Which layer consists of the crust and upper mantle? ________________________________ 5. Which layer is composed of Nickel and Iron and is a solid? ____________________________ Over For #6-13 Label the following layers of the Earth on the diagram below. #6-8 Label the 3 compositional layers #9-13 Label the 5 physical layers CP Env Sci Geosphere Review Name ____________________________ Period _____ Sipe/Poposki Date ____________________ Station 2- Plate Tectonics, Boundaries, and Movement 1. What is the diagram to the right showing? Explain. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ 2. What was the name of this configuration of the early Earth? _____________________________________ 3. Label the diagrams below as diverging, converging, or transform boundaries. a. __________________ b. _________________ c. ________________ Over 4. The area where 2 plates meet is called a _______________________________. 5. Match the following terms in column II with the descriptions and examples in column I. Terms in column II may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Column I Column II _____ Plates spread apart _____Plates slide past each other a. converging _____Plates collide b. diverging _____ San Andreas Fault c. transform _____Himalayan Mountains _____ Mid Ocean Ridges 6. A ____________________ is a break in the Earth’s crust along which blocks of the crust slide relative to one another. When rocks that are under stress suddenly break along a fault, a series of ground vibrations is set off called an ___________________________ . 7. A _______________________ is a mountain built from magma (melted rock) that rises from the Earth’s interior to its surface. Their often located along __________________________ and can occur on land or under sea, where they can eventually form islands. CP Env Sci Geosphere Review Name ____________________________ Period _____ Sipe/Poposki Date ____________________ Station 3- Structure and Composition of the Earth Part I. Match the following terms in column II with the descriptions and examples in column I. Terms in column II may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Column I _____ 1. Solid because under enormous pressure _____ 2. Layer of the mantle just beneath the lithosphere Column II a. Lithosphere b. Inner Core and above mesosphere c. Mesosphere _____ 3. Made of liquid nickel and iron _____ 4. Consists of crust and uppermost mantle _____ 5. Lower part of the mantle, between asthenosphere d. Asthenosphere e. Outer Core and outer core _____ 6. Earth’s outer layer _____7. Aka “middle sphere” _____ 8. Plastic, solid layer of mantle made of rock that flows very slowly, allowing tectonic plates to move on top of it _____ 9. Layer that is the MOST dense _____ 10. Layer that is under the LEAST pressure _____ 11. Layer that is the HOTTEST Over 12. Scientists divide Earth into three layers, based on their composition or chemical make-up. These layers are composed of progressively denser materials toward the center of the Earth. These are known as _________________________________________. 13. What are the three layers referred to in #12? a. ___________________________________ b. ___________________________________ c. ___________________________________ 14. If we consider the physical properties of each layer, instead of their chemistry, the Earth is divided into 5 layers, called the _____________________________________. 15. Compare and contrast the inner and outer core. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ CP Env Sci Geosphere Review Name ____________________________ Period _____ Sipe/Poposki Date ____________________ Station 4- Plates & Boundaries 1. The picture to the right represents which type of convergent boundary? _________________________________________ 2. In the diagram to the upper right, which plate is the densest? ______________________________ 3. What happens to the dense plate when the 2 plates come together? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. What happens to the LESS dense plate when the two plates come together? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 5. How do tectonic plates move? _______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Over 6. What does the image to the left represent in which there is a stationary pool of magma? _____________________________________ 7. Which island is the OLDEST? ______________________________________ 8. Complete the table below. Boundary type Description Characteristic features c-c C=continental crust O=oceanic crust Convergent Divergent Transform o-c o-o Examples of where this is occurring on Earth today CP Env Sci Geosphere Review Name ____________________________ Period _____ Sipe/Poposki Date ____________________ Station 5- Mixed Vocabulary Terms Part I. Match the following terms in column II with the descriptions and examples in column I. Terms in column II may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Column I _____1. Process that causes the tectonic plates to move _____2. Layer of the Earth consisting nickel and iron and exists in of two states of matter- solid and liquid _____3. Caused the formation of the Hawaiian Island _____4. Convergent, divergent, transform _____5. Layer responsible for tectonic plate movement _____6. Caused primarily from transform boundaries _____7. Term given to the process when one plate is pushed under another _____8. Stationary pools of magma (not at plate boundaries) _____9. Series of waves caused by convergent or divergent boundaries _____10. Caused by plate boundaries that are subducting or Column II a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. Fault Atmosphere Hot spot Core geosphere Volcanoes Earthquakes Tsunamis Subduction hydrosphere Mantle Tectonic plates m. n. o. p. Crust Biosphere Plate boundaries Convection currents diverging 11. Look at the image below. Where is the hot spot located, nearer to X or Y? _________ CP Env Sci Geosphere Review Name ____________________________ Period _____ Sipe/Poposki Date ____________________ Station 6- Interacting Spheres 1. What are the four spheres of the Earth? a. __________________________ b. __________________________ c. __________________________ d. __________________________ 2. Give one example of 2 interacting spheres. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. Name two ways humans affect the geosphere. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____ 4. The part of Earth that contains the air we breathe is called the a. hydrosphere c. geosphere b. atmosphere d. biosphere _____ 5. The part of Earth that contains all water resources is called the a. hydrosphere c. geosphere b. atmosphere d. biosphere