Plate Tectonics: Convergent, Divergent, Transform Boundaries
advertisement
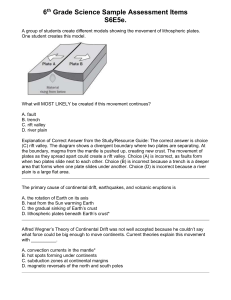
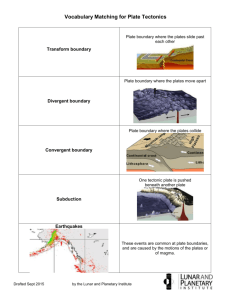
Complete a foldable :] You need three tabsone for each boundary type (convergent, divergent, transform) The front: Boundary type Picture of what the plates are doing Key word to help remember The inside: Definition of plate boundary (what are the plates doing?) The different types of crust What each type of crust forms at each boundary Real life examples How do the plates move? Convection currents, in the plastic like layer of the mantle of the earth, constantly churn in a circular motion, the hot magma rises, cools, then falls back down to the core. This movement causes tectonic plates to meet at plate boundaries . Plate Boundaries Convergent- tectonic plates collide or combine • Divergent- tectonic plates move apart from each other • Transform/Transverse- tectonic plates slide/grind past each other Convergent Boundaries 1. Continental-Continental crust Fold mountains, mountain ranges. EX: The Himalayas 3. Continental – Oceanic crust 2. Oceanic- Oceanic crust Creates deep trenches Sometimes volcanoes can be formed Ex: Marianas Trench •Dense oceanic plate subducts under less dense continental plate, which creates a subduction zone. •This can create ocean trenches (rarely), and very violent subduction volcanoes such as Mt. St. Helens. Ring of firePacific Plate Oceanic-continental convergence Divergent boundaries Continental- Continental crust Oceanic- Oceanic crust Forms Rift Valleys, water can fill in the rift (new ocean) Remember the seafloor spreading theory?? Ex: The Great African Rift Older crust is found further away from the ridge, while younger crust is found just near the ridge. Forms mid ocean ridges Ex: Mid-Atlantic Ridge Transform boundaries Forms Transform Faults and fault lines (zones) Ex: The San Andreas Fault line- North American Plate and the Pacific Plate Remember! :] Convergent- collide Divergent- divide Transform plates- slide