here.
advertisement
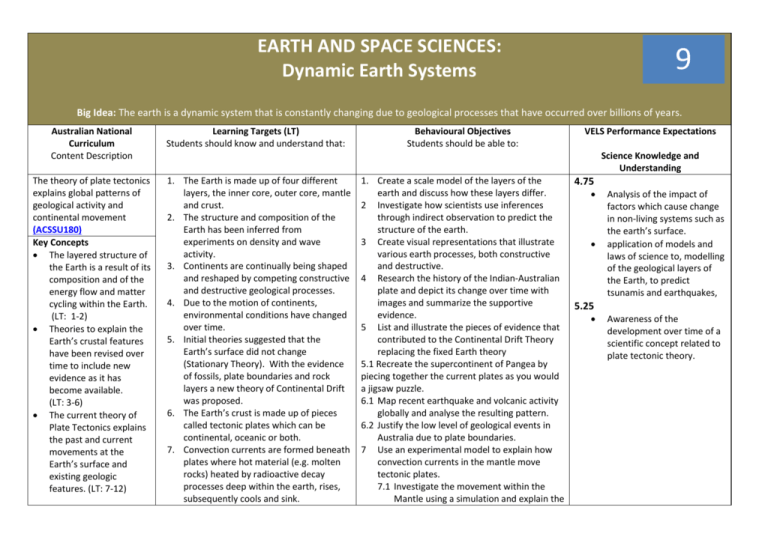
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCES: Dynamic Earth Systems 9 Big Idea: The earth is a dynamic system that is constantly changing due to geological processes that have occurred over billions of years. Australian National Curriculum Content Description The theory of plate tectonics explains global patterns of geological activity and continental movement (ACSSU180) Key Concepts The layered structure of the Earth is a result of its composition and of the energy flow and matter cycling within the Earth. (LT: 1-2) Theories to explain the Earth’s crustal features have been revised over time to include new evidence as it has become available. (LT: 3-6) The current theory of Plate Tectonics explains the past and current movements at the Earth’s surface and existing geologic features. (LT: 7-12) Learning Targets (LT) Students should know and understand that: Behavioural Objectives Students should be able to: VELS Performance Expectations Science Knowledge and Understanding 1. The Earth is made up of four different layers, the inner core, outer core, mantle and crust. 2. The structure and composition of the Earth has been inferred from experiments on density and wave activity. 3. Continents are continually being shaped and reshaped by competing constructive and destructive geological processes. 4. Due to the motion of continents, environmental conditions have changed over time. 5. Initial theories suggested that the Earth’s surface did not change (Stationary Theory). With the evidence of fossils, plate boundaries and rock layers a new theory of Continental Drift was proposed. 6. The Earth’s crust is made up of pieces called tectonic plates which can be continental, oceanic or both. 7. Convection currents are formed beneath plates where hot material (e.g. molten rocks) heated by radioactive decay processes deep within the earth, rises, subsequently cools and sink. 1. Create a scale model of the layers of the earth and discuss how these layers differ. 2 Investigate how scientists use inferences through indirect observation to predict the structure of the earth. 3 Create visual representations that illustrate various earth processes, both constructive and destructive. 4 Research the history of the Indian-Australian plate and depict its change over time with images and summarize the supportive evidence. 5 List and illustrate the pieces of evidence that contributed to the Continental Drift Theory replacing the fixed Earth theory 5.1 Recreate the supercontinent of Pangea by piecing together the current plates as you would a jigsaw puzzle. 6.1 Map recent earthquake and volcanic activity globally and analyse the resulting pattern. 6.2 Justify the low level of geological events in Australia due to plate boundaries. 7 Use an experimental model to explain how convection currents in the mantle move tectonic plates. 7.1 Investigate the movement within the Mantle using a simulation and explain the 4.75 Analysis of the impact of factors which cause change in non-living systems such as the earth’s surface. application of models and laws of science to, modelling of the geological layers of the Earth, to predict tsunamis and earthquakes, 5.25 Awareness of the development over time of a scientific concept related to plate tectonic theory. 8. Tectonic plate boundaries can be converging, diverging or transforming each with predictable geological consequences. 9. New crustal material is added to plates through the action of the sea floor spreading or through subducting of two plates. 10. ***Natural disasters occur as a result of dynamic Earth processes at plate boundaries.*** Vocabulary: core, crust, mantle, tectonics, convection, subduction process. 8 Compare and contrast the processes that occur at the following plate boundaries: diverging, converging and transforming. Provide examples of where each is occurring on the Earth’s surface. 8.1Cite and describe evidence that supports the theory that the plates have moved throughout geological history. 9 Model the spreading of the ocean floor to explain the creation of new tectonic plate material. 9.1 Illustrate the process of subduction of two plates and describe where this is actively occurring on Earth. 10. Describe two natural disasters that have occurred in the past 12 months as consequences of plate interactions. WT – Worthwhile Task