Fitness Study Guide
advertisement

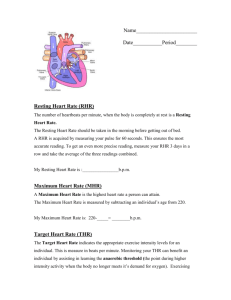
Cardiovascular Fitness Definitions: Aerobic- meaning “with or in the presence of oxygen.” Aerobic exercise (cardiovascular exercise) is performed at a low enough intensity to keep the individual from running out of oxygen. Heart rate- a term used to describe the frequency of the cardiac cycle; it is considered one of the four vital signs; it is usually calculated as the number of contractions (heart beats) of the heart in one minute and expressed as “beats per minute” (bpm); usually 60100 bpm in adults Maximum heart rate- the highest number of time the heart can beat in one minute Resting heart rate- the number of heartbeats in 60 seconds when you first awake; this is taken before lifting your head or sitting up Target heart rate (THR): a desired range of heart rate reached during aerobic exercise which enables one’s heart and lungs to receive the most benefit from a workout Heart Rate Calculations: Maximum heart rate: MHR= 208- (0.70 x your age) Target heart rate (Simple Method): THR = MHR x % Intensity Example for someone with a MHR of 180: 50% intensity: 180 x 0.50 = 90 bpm 85% intensity : 180 x 0.85 = 153 bpm Target heart rate (Karvonen Method): The Karvonen Method is more accurate, factoring in Resting Heart Rate (RHR): THR = ((MHR – RHR) x % Intensity) + RHR Example for someone with a MHR of 180 and a RHR of 70: 50% intensity: ((180-70) x 0.50) + 70 = 125 bpm 85% intensity: ((180-70) x 0.85) + 70 = 163 bpm Components of Fitness Health-Related Body Composition: the amount of body fat compared to lean tissue (Ex. A person whose muscles are defined and tone) Cardiovascular endurance: how well the heart and lungs get oxygen to the body during exercise and how quickly they return to normal (Ex. Running the mile) Flexibility: ability to move body joints in certain ways (Ex. Bending over and touching your toes) Muscular endurance: ability of the muscle to work for extended periods of time without tiring (Ex. Rowing or cycling) Muscular strength: the most work muscles can do at any given time (Ex. Pull-up) Skill-related Agility: the ability to rapidly change the position of the body when moving from point to point (Ex. Zig-zag running or cutting plays) Balance: the ability to keep one’s body in a desired position without falling (Ex. Handstand) Coordination: the ability to make different parts of your body move together in a controlled way (Ex. Juggling) Power: the ability to perform one maximum explosive effort in as short a time as possible (Ex. Jumping) Reaction time: how long the body takes to respond to a stimulus (Ex. Any game played with a ball or object) Speed: the ability to cover a distance in the shortest time possible (Ex. 100-yard dash)