Heart Rate Monitor Project - Red Hook Central School District
advertisement
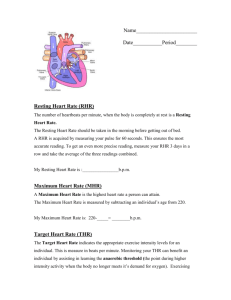
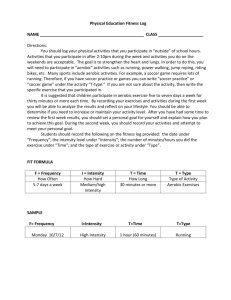
Heart Rate Monitor Project PE Grades 9&10 Last completed Spring 2014 New Project Spring 2016 Heart Rate Data Collection Record #1 Date 3/7/14 Activity X-C Skiing Time in Zone 12:00.6 min Average HR 156 bpm Time Above Zone 0:00:00min Time Below Zone 8:00 min Exercise Time 20:00.6min Final HR 153bpm 1 Min Post HR 123bpm 2 Min Post HR 103bpm Tips to getting good data • Make sure your watch is coded and recording • Learn how to use the watch correctly • Look for a final heart rate toward the end of your physical activity movement time • Stand for 1 minute to watch HR go down • Sit for one more minute and watch HR go down • Hit Blue/Blue/Blue then retrieve file data 4 Records of Data • The four records should be different activities if possible. There should be at least 2 records that have recovery heart rate information. • Think about the activity you are doing, is it aerobic or anaerobic ? Should it elevate heart rate, if so, why is my heart rate so low? Try to get as much active movement time as possible. The HRM Report • This report will be due in the 4th marking period and will be worth 20% of your final 4th marking period grade. The report must be typed and minimum 2 pages of double spaced, size 12 font with no greater than 1/2inch margins on top, and bottom and sides. • All answers to the questions should be in order in respective paragraphs. • Any late paper not received within a PE class will be 10 points off the final score. • You will see your final grade on the paper, but the papers will be kept in your PE file as evidence of learning. Factors about heart rate you should know… What physical activities will increase heart rate at least into the minimum threshold to gain cardiovascular benefits from the exercise? Aerobic – those which maintain a constant level of intensity – running, using CV machines in the Wellness Center, snowshoeing, cross-country skiing, swimming, long distance track races Anaerobic – many start and stop activities will elevate heart rate but usually not for a long period of time - basketball, soccer, dancing, tennis Reference: CR 4A pg 2 (Pyramid pg 2) and CR 4D , pg 5 Heart Rate Intensity The minimum intensity of exercise is to gain CV benefits 40% THR Zone or about 130 to 135 bpm for students 50% THR Zone is recommended for teens as a minimum intensity (about 145bpm) The THR Zone that is most effective to increase CV Fitness 60-85% intensity Reference: 6A & 6B, pg 2&3 Why it is good to increase CV Fitness? Keeps heart in good shape, maintains or increases the effectiveness of the heart’s pump (stroke volume); decreases bad cholesterol (LDL and VLDL) but increases good cholesterol (HDL) Reference: CR 7A, B, D, Pg 2, 3 & 5 / CR 3A&C Pg 2,4 FITT Principle The minimum training for CV Conditioning – Frequency – at least 3 days /week Intensity – 40-85% of Max Heart Rate Time – 20 minutes (10 min bouts/min x2) Type – Aerobic best Optimal training for CV Conditioning Frequency – 5 days/week Intensity – 60-85% of Max Heart Rate Time - 30 minutes (cumulative or continuous) Type – Physical Activities that elevate Heart Rate Resting Heart Rate • a normal RHR is 60-90 bpm • stimulants such as nicotine and caffeine can elevate HR also some herbs such as ginseng and Ginko Blikoba, some medicines increase RHR, stress elevates RHR, fight or flight stage of anxiety How to take Resting Heart Rate • Common sites to take pulse include carotid (neck) or radial (wrist) artery • Minimum 10 seconds x 6 • or 15 x 4 • or if rest, full 60 seconds – check for rhythm and regularity Heart Rate Recovery • a good recovery heart rate after exercise is completed – – A drop of 20-30 bpm within the first minute shows good cardiovascular fitness level. • If heart rate does not drop quickly, it is a sign of CV deconditioning and they should take action to increase their CV fitness level Cardiovascular Fitness Testing • We measure student’s CV Fitness level? – Mile Run times – in minutes, but also as a VO2 Max level or METs are other terms – 20M Shuttle Run (Pacer) For adults, it is usually measured by a stress test (graded exercise tolerance test on a treadmill) Lactic Acid & Anaerobic Threshold • Discomforts of training for CV Fitness & how to resolve it – • If a person wants to get faster or more fit, they should continue to push toward the higher intensity of training, this will increase the person’s Anaerobic Threshold - this high intensity usually results in lactic acid building up and then fatigue. Lactic Acid is a byproduct of anaerobic respiration that can cause discomfort by increasing the acidity in the body. • Reducing the level of intensity will help to reduce the acidity and therefore fatigue will diminish – usually a 2 minute cool down is necessary for the most fit people but less fit people will require a longer cool down period The Cool Down from CV exercise • The Cool-Down – decreasing intensity of activity, slower movements returning the body back toward resting levels – this should always be done, to allow blood flow to return back to the viscera from the periphery where it was supplying working muscles. If not done, one can experience lightheadedness and dizziness.