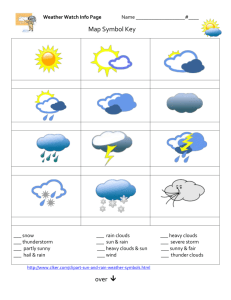
File
advertisement
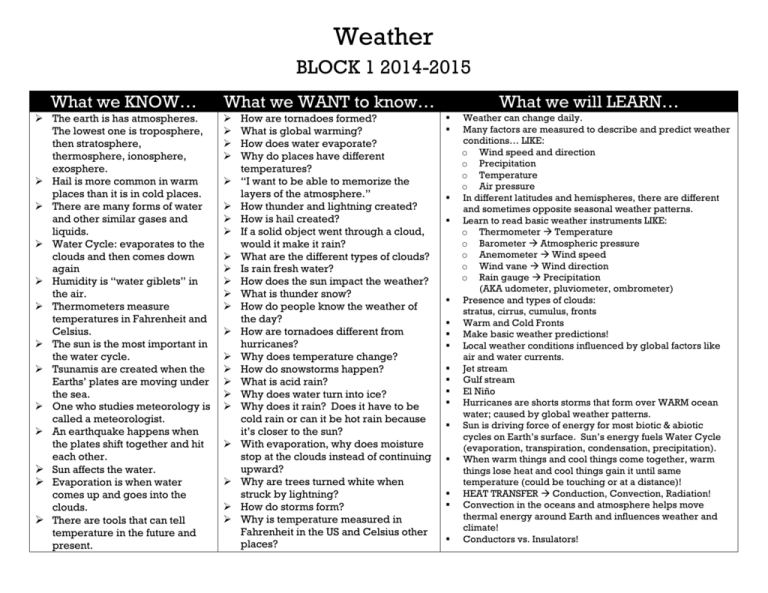
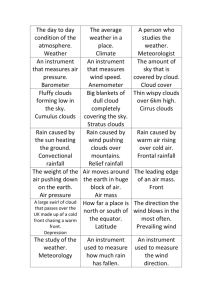
Weather BLOCK 1 2014-2015 What we KNOW… The earth is has atmospheres. The lowest one is troposphere, then stratosphere, thermosphere, ionosphere, exosphere. Hail is more common in warm places than it is in cold places. There are many forms of water and other similar gases and liquids. Water Cycle: evaporates to the clouds and then comes down again Humidity is “water giblets” in the air. Thermometers measure temperatures in Fahrenheit and Celsius. The sun is the most important in the water cycle. Tsunamis are created when the Earths’ plates are moving under the sea. One who studies meteorology is called a meteorologist. An earthquake happens when the plates shift together and hit each other. Sun affects the water. Evaporation is when water comes up and goes into the clouds. There are tools that can tell temperature in the future and present. What we WANT to know… How are tornadoes formed? What is global warming? How does water evaporate? Why do places have different temperatures? “I want to be able to memorize the layers of the atmosphere.” How thunder and lightning created? How is hail created? If a solid object went through a cloud, would it make it rain? What are the different types of clouds? Is rain fresh water? How does the sun impact the weather? What is thunder snow? How do people know the weather of the day? How are tornadoes different from hurricanes? Why does temperature change? How do snowstorms happen? What is acid rain? Why does water turn into ice? Why does it rain? Does it have to be cold rain or can it be hot rain because it’s closer to the sun? With evaporation, why does moisture stop at the clouds instead of continuing upward? Why are trees turned white when struck by lightning? How do storms form? Why is temperature measured in Fahrenheit in the US and Celsius other places? What we will LEARN… Weather can change daily. Many factors are measured to describe and predict weather conditions… LIKE: o Wind speed and direction o Precipitation o Temperature o Air pressure In different latitudes and hemispheres, there are different and sometimes opposite seasonal weather patterns. Learn to read basic weather instruments LIKE: o Thermometer Temperature o Barometer Atmospheric pressure o Anemometer Wind speed o Wind vane Wind direction o Rain gauge Precipitation (AKA udometer, pluviometer, ombrometer) Presence and types of clouds: stratus, cirrus, cumulus, fronts Warm and Cold Fronts Make basic weather predictions! Local weather conditions influenced by global factors like air and water currents. Jet stream Gulf stream El Niño Hurricanes are shorts storms that form over WARM ocean water; caused by global weather patterns. Sun is driving force of energy for most biotic & abiotic cycles on Earth’s surface. Sun’s energy fuels Water Cycle (evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation). When warm things and cool things come together, warm things lose heat and cool things gain it until same temperature (could be touching or at a distance)! HEAT TRANSFER Conduction, Convection, Radiation! Convection in the oceans and atmosphere helps move thermal energy around Earth and influences weather and climate! Conductors vs. Insulators! Weather BLOCK 2 2014-2015 What we KNOW… What we WANT to know… Everything is really black and white but the air and sun affect our eyes to see color. Weather is storms, droughts, tornadoes, etc. In the desert there are sand holes. “I think tornadoes make sand holes.” The Water Cycle is a pattern. Due to some weather changes, there can be an effect on Earth. For example, ice can cause rock to crack. Rain makes metal rust. Tornadoes happen by hot air and cold air mixing. Water vapor goes up to the clouds and if it’s cold, the water vapor will turn into ice. Condensation is when water freezes and turns into a different type of precipitation. Weather has to do with climate. Cloud cover is when clouds cover part of the sky. Rain falls from the clouds because the clouds get so heavy. Weather has to do with water. How do meteorologists tell the weather? How do tornadoes form? What changes weather? How do you make clouds? Why is lightning attracted to metal? How do anemometers and barometers work? What makes tsunamis? How do people make black clouds? How does water fall from the sky? How are hurricanes and hail storms made? Are there any more different clouds than what are listed in the weather glossary? When water evaporates, how does it stop? Can there be weather when there is no gravity? What is magma? How do clouds turn grey? How does lightning form? Does weather change in space? Do heat waves create fires? Why do clouds stay in the sky? What is barometric pressure? How does a storm crack a rock or stones? If clouds are in the air for a long period of time, how do they disappear? What we will LEARN… Weather can change daily. Many factors are measured to describe and predict weather conditions… LIKE: o Wind speed and direction o Precipitation o Temperature o Air pressure In different latitudes and hemispheres, there are different and sometimes opposite seasonal weather patterns. Learn to read basic weather instruments LIKE: o Thermometer Temperature o Barometer Atmospheric pressure o Anemometer Wind speed o Wind vane Wind direction o Rain gauge Precipitation (AKA udometer, pluviometer, ombrometer) Presence and types of clouds: stratus, cirrus, cumulus, fronts Warm and Cold Fronts Make basic weather predictions! Local weather conditions influenced by global factors like air and water currents. Jet stream Gulf stream El Niño Hurricanes are shorts storms that form over WARM ocean water; caused by global weather patterns. Sun is driving force of energy for most biotic & abiotic cycles on Earth’s surface. Sun’s energy fuels Water Cycle (evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation). When warm things and cool things come together, warm things lose heat and cool things gain it until same temperature (could be touching or at a distance)! HEAT TRANSFER Conduction, Convection, Radiation! Convection in the oceans and atmosphere helps move thermal energy around Earth and influences weather and climate! Conductors vs. Insulators! Weather BLOCK 3 2014-2015 What we KNOW… What we WANT to know… I know there is evaporation when hot air comes – this is a part of the Water Cycle. Lightning is produced when positive and negative energies combine. Thunder is produced when hot molecules created by lightning mix with cold molecules. Snow is formed when water evaporates into clouds, the molecules freeze and mix together. A meteorologist is a person who studies weather. Weather can affect solids. When water molecules aren’t in motion very much, they get packed together and become solid water to create snow/hail. Precipitation is rain, snow, hail, ice, etc. Tornadoes are formed when warm air and cool air are combined and wind starts to move around. Then the cyclone touches down. When it’s below zero degrees, it’s below freezing. A cloud is made up of gases and water. When it holds too much water, it rains. Weather controls how the day would look outside. If there was no weather, what would happen? How does the weather man predict tomorrow’s weather? How does everything work with weather? How does water form to ice and snow? What are clouds made of? Why is the sky blue during the day? What is the purpose of weather? More about the types of clouds… How is humidity formed? How are tornadoes formed? Why does it rain? How does weather start? How does lightning happen? What is the ocean’s affect on weather? What is weather’s affect on the ocean? How are different tools used in weather? What makes clouds white? Why isn’t the earth pulling clouds to it with gravity? Why does gravity pull clouds down as fog in certain times? How does a hurricane start? How does the water cycle start? How do we get droughts when it’s moist? When it rains, where does water go after it goes into sewers? How does the soil absorb water? How does it rain sometimes in one spot but not in another? What we will LEARN… Weather can change daily. Many factors are measured to describe and predict weather conditions… LIKE: o Wind speed and direction o Precipitation o Temperature o Air pressure In different latitudes and hemispheres, there are different and sometimes opposite seasonal weather patterns. Learn to read basic weather instruments LIKE: o Thermometer Temperature o Barometer Atmospheric pressure o Anemometer Wind speed o Wind vane Wind direction o Rain gauge Precipitation (AKA udometer, pluviometer, ombrometer) Presence and types of clouds: stratus, cirrus, cumulus, fronts Warm and Cold Fronts Make basic weather predictions! Local weather conditions influenced by global factors like air and water currents. Jet stream Gulf stream El Niño Hurricanes are shorts storms that form over WARM ocean water; caused by global weather patterns. Sun is driving force of energy for most biotic & abiotic cycles on Earth’s surface. Sun’s energy fuels Water Cycle (evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation). When warm things and cool things come together, warm things lose heat and cool things gain it until same temperature (could be touching or at a distance)! HEAT TRANSFER Conduction, Convection, Radiation! Convection in the oceans and atmosphere helps move thermal energy around Earth and influences weather and climate! Conductors vs. Insulators! 5.E.1.1 Weather can change daily. Many factors are measured to describe and predict weather conditions… LIKE: o Wind speed and direction o Precipitation o Temperature o Air pressure In different latitudes and hemispheres, there are different and sometimes opposite seasonal weather patterns. 5.E.1.2 Collect and compare weather data to predict the chances of a particular weather condition. Learn to read basic weather instruments LIKE: o Thermometer Temperature o Barometer Atmospheric pressure o Anemometer Wind speed o Wind vane Wind direction o Rain gauge Precipitation (AKA udometer, pluviometer, ombrometer) Atmospheric conditions associated with weather patterns… LIKE: o Presence and types of clouds: stratus, cirrus, cumulus, fronts o Fronts (Warm and Cold) Make basic weather predictions! 5.E.1.3 Local weather conditions are influenced by global factors like air and water currents. Jet stream = air current in upper atmosphere (over North America) that has powerful influence on weather conditions there. Flows from WEST to EAST and changes location depending on global conditions. GULF stream = warm water surface current in Atlantic Ocean that moves from SOUTH Florida UP the EASTERN seaboard and ACROSS the ATLANTIC. o Moderates weather along EASTERN seaboard, warms the air and land there during cooler months. El Niño = Water in the PACIFIC Ocean (near equator) gets hotter than usual. Warm water in WEST Pacific in a normal year (forms thunderstorms); In an El Niño year, warmest water moves EAST across Pacific; thunderstorms disrupt the jet stream and change weather pattern. Affects North & South America for a long time. Hurricanes are shorts storms that form over WARM ocean water; caused by global weather patterns. o 5.P.2.1 Sun is driving force of energy for most biotic & abiotic cycles on Earth’s surface. Sun’s energy fuels water cycle (evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation). When warm things and cool things come together, warm things lose heat and cool things gain it until same temperature (could be touching or at a distance)! HEAT TRANSFER Conduction, Convection, Radiation! Convection in the oceans and atmosphere helps move thermal energy around Earth and influences weather and climate! 5.P.3.2 Heating and cooling can cause changes in materials, but not all materials are the same. Many kinds of changes occur at faster and higher temps.! Conductors vs. Insulators!