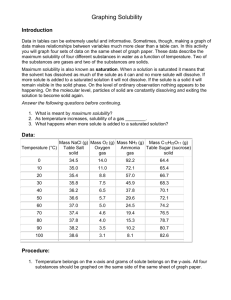
Notes: Solutions and Solubility The formation of solutions is a
advertisement

Notes: Solutions and Solubility o The formation of solutions is a physical change forming a homogeneous mixture. o A solution is made up of a solute and a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving. The solute is the substance that is dissolved. o Some things dissolve easier in one kind of substance as opposed to another. Sugar dissolves easily in water and oil does not. Water has a low solubility when it comes to oil. Since oil is not soluble in water, it will never truly dissolve. o A solute will dissolve in a solvent if the solute-solvent forces of attraction are great enough to overcome the solute-solute and solvent-solvent forces of attraction. o A solute will not dissolve if the solute-solvent forces of attraction are weaker than individual solute and solvent intermolecular attractions. o “Like dissolve like” o The expression means that dissolving occurs when similarities exist between the solvent and the solute. Water is polar, while C6H14 and CCl4 are nonpolar. As a result, neither substance will dissolve in water. o Solubility- the maximum quantity of the substance, expressed in grams that will dissolve in a certain solvent at a specific temperature. o Types of solution Saturated – a solution that contains the maximum quantity of solute that dissolves at that temperature. Unsaturated – a solution that contains less than the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve at a particular temperature. Supersaturated – a solution that contains more solute than a saturated solution. Supersaturated solutions can be attained by heating the solution up to dissolve more solute at that higher temperature and then letting the solution cool. Once cooled, agitation causes crystals to precipitate (separate from solution) out of the supersaturated solution. o Solubility and Temperature Increasing the temperature of solvent speeds up the particle movement. This causes more solvent particles to bump into the solute, resulting in solute particles breaking loose and dissolving faster. o Solubility Curve A graph of the solubility of a compound (grams/100 grams water on the Y-axis) at various temperatures (Celsius on X-axis). Each compound has a different curve. o Solubility Curve Graph Solubility is dependent on temperature What trends do you see on the graph? How is the solubility of gases and solids different? If you stir faster, will that make you dissolve more? No, it allows you to dissolve substances faster but not more. Increasing the temperature does allow you to dissolve more. o Solids dissolve in liquid: solids are more soluble at…higher temperatures. o Gases dissolved in liquids: Gases are more soluble at…lower temperatures and higher pressures.