Passive transport: the movement of substances across a cell
advertisement

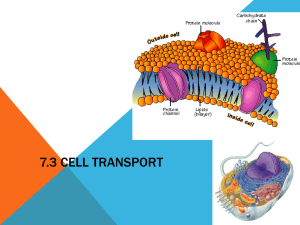
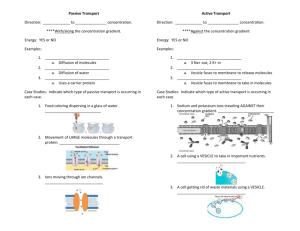
1. Passive transport: the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use energy by the cell 2. Diffusion: the movement of molecules from a higher area of concentration to a lower area of concentration 3. Concentration gradient: difference in concentration of molecules across a distance. 4. Equilibrium: the concentration of molecules will be the same throughout the space the molecules occupy. 5. Osmosis: the process by which water molecules diffuse across a cell membrane from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. 6. Hypotonic: the concentration of solute molecules outside the cell is LOWER than the concentration in the cytosol. Water diffuses INTO the cell until equilibrium. 7. Hypertonic: the concentration of solute molecules outside the cell is HIGHER than the concentration in the cytosol. Water diffuses INTO the cell until equilibrium. Water diffuses out of cell until equilibrium. 8. Isotonic: the concentration of solutes outside and inside the cell are equal. Water diffuses in and out of cell at equal rates—no net movement. 9. Contractile vacuole: organelles that remove water. Collect access water and the pump water out of cell. 10. Turgur pressure: pressure water exerts against cell wall. 11. Plasmolysis- cells shrink away from osmosis. Reason plants wilt if don’t receive enough water. 12. Cytolysis- bursting of cells. (Water diffuses into cells causing to swell and burst) 13. Facilitated diffusion- type of passive transport used for molecules that cannot readily diffuse thru cell membranes. 14. Carrier protein: assist movement of certain molecules for facilitated diffusion. 15. Ion channel: a complex of protein molecules in a cell membrane that forms a pore thru which ions can pass. 16. Active transport: the movement of chemical substances usually across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient; requires cell to use energy 17. Sodium potassium pump: a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell. 18. Endocytosis: process by which cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules and large particles including other cells. 19. Vesicle: a small cavity or sac that contains materials in a eukaryote cell: forms when part of the cell membrane surround the materials taken into the cell or transported within the cell. 20. Pinocytosis- involves transport of solutes or fluids 21. Pahgocytosis- movement of large particles or whole cells. 22. Phagocyte- certain animal cells that use phagocytosis to ingest bacteria and viruses that invade the body. Allow lysosomes to fuse vesicles that contain ingested bacteria and viruses. 23. Exocytosis: the process by which a substance is released from the cell thru a vesicle that transport the substance to the cells surface with the membrane to let the substance out of the cell.